| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 3 Wyoming votes to the Electoral College | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
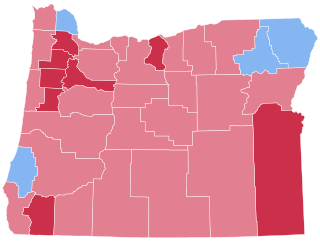
 County Results
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Wyoming |
|---|
 |
The 1956 United States presidential election in Wyoming took place on November 6, 1956, as part of the 1956 United States presidential election. State voters chose three [4] representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Contents
Wyoming was won by incumbent President Dwight D. Eisenhower (R–Pennsylvania), running with Vice President Richard Nixon, with 60.08 percent of the popular vote, against Adlai Stevenson (D–Illinois), running with Senator Estes Kefauver, with 39.92 percent of the popular vote, a Republican victory margin of 20.2%. [5] [6] This margin represented a slight decrease from Eisenhower's victory in the state 4 years earlier in 1952, despite the fact that he won nationwide by a larger margin. Nevertheless, Wyoming still weighed in as 2.8% more Republican than the rest of the nation. Ironically enough, despite his margins in most of the counties he won being slightly less than 1952, Eisenhower was able to improve upon his margins in the heavily unionized Sweetwater County, with the area swinging to the right by 6.7%, making him the first Republican to break 40% of the county's vote since Herbert Hoover in 1928.
Eisenhower's underperformance relative to 1952 was not unique to just Wyoming, as most of the Mountain West swung a few points against him. Given the fact that the state's economy relied heavily upon agriculture, this is possibly due to a 5 year long drought in the High Plains, which encompasses parts of Wyoming, Montana, Colorado, and New Mexico. [7] This election was the first time that television ads were the dominant medium for both sides, with many of these ads focusing on women voters, who had been crucial to Eisenhower's 1952 victory. Stevenson promoted increases in government spending on social programs and treaties with the Soviet Union to end nuclear testing on both sides and decrease military spending. Heightened racial tensions and segregation were also a major issue in the campaign, with the Supreme Court's ruling in Brown v. Board of Education ending legal segregation in schools, a position that the Eisenhower administration supported, and one which Stevenson opposed, as he believed the federal government should not be involved in the issue, which was a complete reversal of the Democratic Party's 1948 endorsement of civil rights. [8] [9]
Ultimately however, with the end of the Korean War in July 1953, and an otherwise strong economy, voters had little to no reason to reconsider voting for Stevenson. Additionally, Eisenhower's popularity was also aided by his experience from having served as The Supreme Commader of the Allied Expeditionary Force in Europe in World War II, and his popular responses to the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 and Suez Canal Crisis, both of which happened weeks before the elections, made him unbeatable in what was already an uphill battle for the Democrats, and the popular incumbent even managed to carry 40% of black voters, a feat no Republican since has matched. This would be the last time that Wyoming would give 60% or more of its vote to any candidate until Richard Nixon's 1972 landslide victory, and the last time that Carbon and Laramie counties would select the Republican nominee until 1968 and 1972, respectively.