
John Obadiah Westwood was an English entomologist and archaeologist also noted for his artistic talents. He published several illustrated works on insects and antiquities. He was among the first entomologists with an academic position at Oxford University. He was a natural theologian, staunchly anti-Darwinian, and sometimes adopted a quinarian viewpoint. Although he never travelled widely, he described species from around the world on the basis of specimens, especially of the larger, curious, and colourful species, obtained by naturalists and collectors in England.
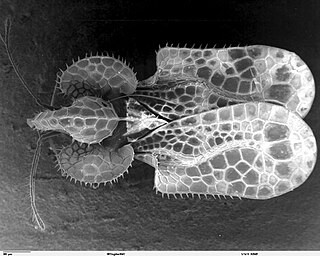
The Cimicomorpha are an infraorder of insects in the order Hemiptera, the true bugs. The rostrum and other morphology of some members apparently is adapted to feeding on animals as their prey or hosts. Members include bed bugs, bat bugs, assassin bugs, and pirate bugs.

The Megaspilidae are a small hymenopteran family with 13 genera in two subfamilies, and some 450 known species, with a great many species still undescribed. It is a poorly known group as a whole, though most are believed to be parasitoids, and a few hyperparasitoids. Many are found in the soil, and of these, a number are wingless.

Endomychidae, or handsome fungus beetles, is a family of beetles with representatives found in all biogeographic realms. There are around 120 genera and 1300 species. The family was established based on the type genus Endomychus, a genus erected in 1795 by Panzer which was applied to a species that Linnaeus called Chrysomela coccinea. As the common name suggests, Endomychidae feed on fungi. Crowson, in his influential treatment of the beetles, placed the family within the Cucujoidea. They have a tarsal formal of 4-4-4 or 3-3-3 and the wings lack a closed radial cell. The second antennal segment has a sensory appendage that is as long as the third antennal segment. The family has also been grouped with the Coccinellidae in a group called the Trimera for having pseudotrimerous tarsi. A 2015 molecular phylogeny study found that the Cucujoidea were found to be non-monophyletic and the Endomychidae was refined with the removal of the Anamorphinae from within the family and elevated to the status of a full family, Anamorphidae. Mycetaeinae and Eupsilobiinae were also found not to belong within the clades of the core Endomychidae, and likewise reclassified into the families Mycetaeidae and Eupsilobiidae.

The Harpactorinae are a large subfamily of the Reduviidae. About 300 genera and 2,000 species worldwide have been described. Some of the species of the genera Zelus, Pselliopus, Sinea, and Apiomerus are of interest as biological pest control agents.

The Euphorinae are a large subfamily of Braconidae parasitoid wasps. Some species have been used for biological pest control. They are sister group to the Meteorinae.

Platyrhopalus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following species:
Pentaplatarthrus is a genus of in the beetle family Carabidae. There are about eight described species in Pentaplatarthrus, found in Africa. These are ant nest beetles and are obligate myrmecophiles, predatory on ant larvae and workers.

The Bethylidae are a family of aculeate wasps in the superfamily Chrysidoidea. As a family, their biology ranges between parasitoid wasps and hunting wasps.

Paussini is a tribe of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are more than 25 genera and 610 described species in Paussini. They are found mainly in Africa, southern Asia, and the Pacific, although the genus Homopterus is found in the Americas.
Liopteridae is a family of wood-boring parasitoid wasps. They occur worldwide with concentrations in the African Tropics. These insects have a petiolate abdomen. There are 10 genera and more than 140 species known.

Sclerodermus is a genus of cuckoo wasps in the family Bethylidae. There are at least 20 described species in Sclerodermus.

Saccharosydne is a genus of delphacid planthoppers in the family Delphacidae. There are about nine described species in Saccharosydne.

Anisoscelis is a genus of leaf-footed bugs in the family Coreidae. There are about 11 described species in the genus Anisoscelis.
Cephalonomia is a genus of parasitoid wasps in the family Bethylidae. There are more than 20 described species in Cephalonomia.

Mesopolobus is a genus of insects belonging to the family Pteromalidae. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution. This genus has a variety of life histories, with the majority of species being parasites of pupae.

Embolemus is a genus of wasps belonging to the family Embolemidae. There is debate regarding the status of the genus named Ampulicomorpha by Ashmead in 1893, generally considered now to be a junior synonym of Embolemus (e.g.,), as a few authorities dispute this (e.g.,).

Nemia is a genus of insects belonging to the family Nemopteridae.
Pachymorpha is a genus of phasmids belonging to the family Diapheromeridae.

Campsiura is a genus of beetles in the scarab beetle family Scarabaeidae. There are more than 30 described species in Campsiura, found in Africa and Asia.

















