
The 1790s was a decade that began on January 1, 1790, and ended on December 31, 1799. Considered as some of the Industrial Revolution's earlier days, the 1790s called for the start of an anti-imperialist world, as new democracies such as the French First Republic and the United States began flourishing at this era. Revolutions – both political and social – forever transformed global politics and art, as wars such as the French Revolutionary Wars and the American Revolutionary War moulded modern-day concepts of liberalism, partisanship, elections, and the political compass.

The Battle of Rivoli was a key military engagement during the War of the First Coalition near the village of Rivoli, then part of the Republic of Venice. In the climax of the Italian campaign of 1796-1797, the outnumbered French Army of Italy commanded by General Napoleon Bonaparte decisively defeated the attacking Austrian army commanded by General of the Artillery Jozsef Alvinczi, who was attempting to march south in a fourth and final attempt to relieve the siege of Mantua. The French victory at Rivoli further demonstrated Bonaparte's capability and deftness as a military commander, and led to the Austrian surrender of Mantua in February, French consolidation of northern Italy, and ultimately France's victory over Austria in the war later that year.

The War of the First Coalition was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797, initially against the constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French Republic that succeeded it. They were only loosely allied and fought without much apparent coordination or agreement; each power had its eye on a different part of France it wanted to appropriate after a French defeat, which never occurred.

The War of the Third Coalition was a European conflict lasting from 1805 to 1806 and was the first conflict of the Napoleonic Wars. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I and its ally Spain opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, which was made up of the United Kingdom, the Austrian Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.

The French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted France against Great Britain, Austria, Prussia, Russia, and several other countries. The wars are divided into two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries, and the Rhineland due to its very large and powerful military, which had been totally mobilized for war against most of Europe with mass conscription of the vast French population. French success in these conflicts ensured military occupation and the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe.

The War of the Second Coalition was the second war targeting revolutionary France by many European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join the coalition, while Spain supported France.
The French Revolutionary Wars continued from 1795, with the French in an increasingly strong position as members of the First Coalition made separate peaces. Austria and Great Britain were the main remaining members of the coalition. The rebellion in the Vendée was also finally terminated by General Hoche.
By 1799, the French Revolutionary Wars had resumed after a period of relative peace in 1798. The Second Coalition had organized against France, with Great Britain allying with Russia, Austria, the Ottoman Empire, and several of the German and Italian states. While Napoleon's army was still embroiled in Egypt, the allies prepared campaigns in Italy, Switzerland, and the Netherlands.
The Napoleonic Wars continued from 1799 with the French fighting the forces of the Second Coalition. Napoleon Bonaparte had returned from Egypt and taken control of the French government, marking the end of the French Revolution. He prepared a new campaign, sending Moreau to the Rhine frontier and personally going to take command in the Alps, where French forces had been driven almost out of Italy in 1799.

The Italian campaigns of the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1801) were a series of conflicts fought principally in Northern Italy between the French Revolutionary Army and a Coalition of Austria, Russia, Piedmont-Sardinia, and a number of other Italian states.

The Battle of Fishguard was a military invasion of Great Britain by Revolutionary France during the War of the First Coalition. The brief campaign, on 22–24 February 1797, is the most recent landing on British soil by a hostile foreign force, and thus is often referred to as the "last invasion of mainland Britain".

The Italian and Swiss expedition of 1799 was a military campaign undertaken by a combined Austro-Russian army under overall command of the Russian Marshal Alexander Suvorov against French forces in Piedmont and Lombardy and the Helvetic Republic. The expedition was part of the Italian campaigns of the French Revolutionary Wars in general, and the War of the Second Coalition in particular. It was one of 'two unprecedented Russian interventions in 1799', the other being the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland.
The siege of Mantua (1799) was a four-month effort by the Austrian army to regain a presence in northern Italy after being excluded from that region by Napoleon Bonaparte through the successful French siege of Mantua in 1797. In April 1799, the Austrians placed a military blockade around Mantua as part of the War of the Second Coalition with the intent of withering the French by attrition. While the diminishing food supplies and losses weakened the French army, the Austrians received reinforcements and attacked on 4 July 1799. By the end of the month, the French agreed to surrender.

During the siege of Mantua, which lasted from 4 June 1796 to 2 February 1797 with a short break, French forces under the overall command of Napoleon Bonaparte besieged and blockaded a large Austrian garrison at Mantua for many months until it surrendered. This eventual surrender, together with the heavy losses incurred during four unsuccessful relief attempts, led indirectly to the Austrians suing for peace in 1797. The siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, which is part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Mantua, a city in the Lombardy region of Italy, lies on the Mincio River.

Franz von Lauer entered the Imperial Army as a military engineer in 1755 and ended his career as Feldzeugmeister. After serving in the Seven Years' War, by 1783 he had reached the rank of oberst, or colonel. He fought against Ottoman Turkey at Belgrade and became a general officer for his distinguished effort as a siege specialist.

The Battle of Tarvis was fought during 21–23 March 1797 near present-day Tarvisio in far northeast Italy, about 12 kilometres (7 mi) west-by-southwest of the three-border conjunction with Austria and Slovenia, and was the final battle before the end of the War of the First Coalition. In the battle, three divisions of a First French Republic army commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte attacked several columns of the retreating Habsburg Austrian army led by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. In three days of confused fighting, French divisions directed by André Masséna, Jean Joseph Guieu, and Jean-Mathieu-Philibert Sérurier succeeded in blocking the Tarvis Pass and capturing 3,500 Austrians led by Adam Bajalics von Bajahaza. The engagement occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars.

In the siege of Hüningen, the Austrians captured the city from the French. Hüningen is in the present-day Department of Haut-Rhin, France. Its fortress lay approximately 2.5 miles (4.0 km) north of the Swiss city of Basel and .5 miles (0.80 km) north of the spot where the present-day borders of Germany, France and Switzerland meet. During the time of this siege, the village was part of the Canton of Basel City and the fortress lay in area contested between the German states and the First French Republic.

The Piedmontese Republic was a revolutionary, provisional and internationally unrecognized government established in Turin between 1798 and 1799 on the territory of Piedmont during its military rule by the French First Republic.
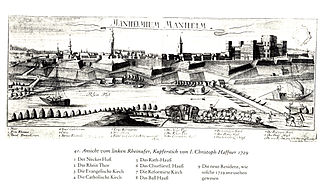
The action at Mannheim began in April 1795 when two French armies crossed the Rhine and converged on the confluence of the Main and the Rhine. Initial action at Mannheim resulted in a minor skirmish, but the Bavarian commander negotiated a quick truce with the French and withdrew. On 17 October 1795, 17,000 Habsburg Austrian troops under the command of Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser engaged 12,000 soldiers, led by Jean-Charles Pichegru in the grounds outside the city of Mannheim. In a combination of maneuvers, the Habsburg army forced 10,000 of the French forces to withdraw into the city itself; other French troops fled to join neighboring Republican armies. First Coalition forces then laid siege to Mannheim. Subsequent action at neighboring cities forced the French to withdraw further westward toward France; after a month's siege, the 10,000-strong Republican French garrison now commanded by Anne Charles Basset Montaigu surrendered to 25,000 Austrians commanded by Wurmser. This surrender brought the 1795 campaign in Germany to an end. The battle and siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Situated on the Rhine River at its confluence with the Neckar River, Mannheim lies in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in modern-day Germany.

The Italian campaign of 1796–1797, also known as the First Italian Campaign, was a series of military operations in Italy during the War of the First Coalition. Led by Napoleon Bonaparte, the First French Republic's Army of Italy fought and defeated the armies of the Kingdom of Sardinia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Papal States, as well as various revolts, notably in the Republic of Venice.















