The following is a timeline of the French Revolution.
Contents
- Pre-1788 – The pre-revolution; challenging absolutism
- 1788 – The royal treasury is empty; prelude to revolution
- 1789 – The Revolution Begins; the Estates-General and the Constituent Assembly
- July 14, 1789 – The Siege and Surrender of the Bastille
- August 27, 1789 – Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen
- October 4, 1789 – Women's March on Versailles
- 1790 – the Rise of the Political Clubs
- July 14, 1790 – Fête de la Fédération
- 1791 – The unsuccessful flight of the Royal Family from Paris
- June 20–21, 1791 – The Royal Family flees Paris
- 1792 – War and the overthrow of the monarchy
- August 10, 1792 – Storming of the Tuileries; Downfall of the King
- September 2–7, 1792 – Massacres in Paris prisons
- September 20, 1792 – French victory at Valmy; Debut of the Convention
- December 10, 1792 – January 21, 1793 – Trial and Execution of Louis XVI
- 1793 – France at war against Europe; The Jacobins seize power; The Terror begins
- Uprising in the Vendée
- April 6 – May 30, 1793 - Committee on Public Safety takes control of government
- May 31 – June 2, 1793 – The Montagnard Coup d'État
- July 13, 1793 – Assassination of Jean-Paul Marat by Charlotte Corday
- September 17, 1793 – The Reign of Terror begins
- October 16, 1793 – The execution of Marie-Antoinette
- 1794 – The fury of the Terror, the Cult of the Supreme Being, and the Downfall of Robespierre
- March 30, 1794 – The arrest and trial of Danton and Desmoulins
- June 8, 1794 – Festival of the Supreme Being; Acceleration of the Terror
- July 26–28, 1794 – Arrest and execution of Robespierre; End of the Terror
- 1795 – The Directory Replaces the Convention
- May 20–24, 1795 – Last Paris uprising by the Jacobins and sans-culottes
- June 25 – July 27, 1795 – Renewed uprisings in the Vendée and a royalist invasion of Brittany
- August 22 – September 23, 1795 – The new Constitution is approved: the Directory takes power
- October 5, 1795 – "A whiff of grapeshot": General Bonaparte suppresses a royalist rebellion in Paris
- 1796 – Napoleon's campaign in Italy; Defeat of the royalists in the Vendée; a failed uprising in Paris
- 1797 – Bonaparte chases the Austrians from Italy; a republican coup d'état against the royalists in Paris
- September 4, 1797 – A republican coup d'état against the royalists
- 1798 – New republics in Switzerland and Italy; an election annulled; Bonaparte invades Egypt
- 1799 – France at War in Italy and Germany; Bonaparte returns from Egypt; the Consulate seizes power; End of the Revolution
- Conflicts between the Directory and the Legislature (June 1799)
- Bonaparte returns to France (October 9, 1799)
- The Coup d'État of November 9–10
- See also
- References
- Notes and citations
- Bibliography
- In French
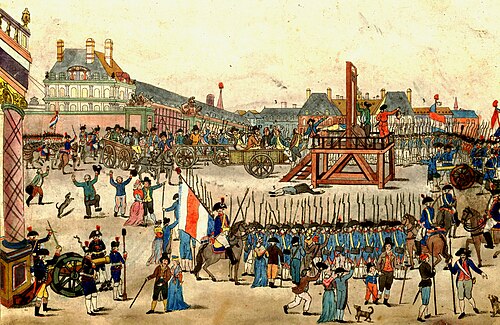
 The execution of Louis XVI on the Place de la Révolution (now Place de la Concorde) (January 21, 1793) | |
| Date | 1789–1799 |
|---|---|
| Location | France |
| Participants | French society |
| Outcome |
|