
ATPases (EC 3.6.1.3, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life.

In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding of large proteins or macromolecular protein complexes. There are a number of classes of molecular chaperones, all of which function to assist large proteins in proper protein folding during or after synthesis, and after partial denaturation. Chaperones are also involved in the translocation of proteins for proteolysis.

ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:

Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme involved in light-independent part of photosynthesis, including the carbon fixation by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants and other photosynthetic organisms to energy-rich molecules such as glucose. It emerged approximately four billion years ago in primordial metabolism prior to the presence of oxygen on earth. It is probably the most abundant enzyme on Earth. In chemical terms, it catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate.
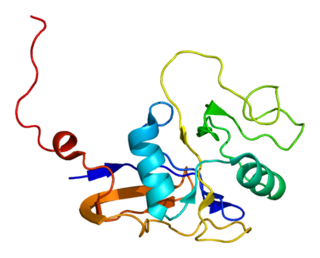
The 70 kilodalton heat shock proteins are a family of conserved ubiquitously expressed heat shock proteins. Proteins with similar structure exist in virtually all living organisms. Intracellularly localized Hsp70s are an important part of the cell's machinery for protein folding, performing chaperoning functions, and helping to protect cells from the adverse effects of physiological stresses. Additionally, membrane-bound Hsp70s have been identified as a potential target for cancer therapies and their extracellularly localized counterparts have been identified as having both membrane-bound and membrane-free structures.
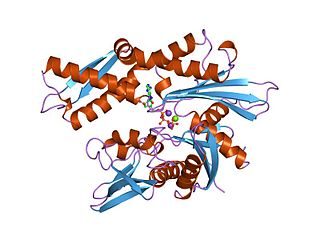
Hsp90 is a chaperone protein that assists other proteins to fold properly, stabilizes proteins against heat stress, and aids in protein degradation. It also stabilizes a number of proteins required for tumor growth, which is why Hsp90 inhibitors are investigated as anti-cancer drugs.
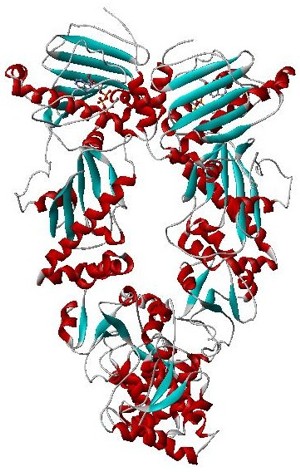
GroEL is a protein which belongs to the chaperonin family of molecular chaperones, and is found in many bacteria. It is required for the proper folding of many proteins. To function properly, GroEL requires the lid-like cochaperonin protein complex GroES. In eukaryotes the organellar proteins Hsp60 and Hsp10 are structurally and functionally nearly identical to GroEL and GroES, respectively, due to their endosymbiotic origin.
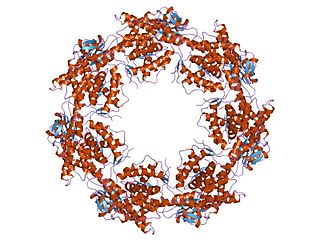
HSP60, also known as chaperonins (Cpn), is a family of heat shock proteins originally sorted by their 60kDa molecular mass. They prevent misfolding of proteins during stressful situations such as high heat, by assisting protein folding. HSP60 belong to a large class of molecules that assist protein folding, called molecular chaperones.

Prefoldin (GimC) is a superfamily of proteins used in protein folding complexes. It is classified as a heterohexameric molecular chaperone in both archaea and eukarya, including humans. A prefoldin molecule works as a transfer protein in conjunction with a molecule of chaperonin to form a chaperone complex and correctly fold other nascent proteins. One of prefoldin's main uses in eukarya is the formation of molecules of actin for use in the eukaryotic cytoskeleton.
Non-chaperonin molecular chaperone ATPase (EC 3.6.4.10, molecular chaperone Hsc70 ATPase) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP phosphohydrolase (polypeptide-polymerizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

26S protease regulatory subunit 6A, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt5, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC3 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta also called HSP90beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSP90AB1 gene.
In enzymology, a chloroplast protein-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.52) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
26S protease regulatory subunit 6B, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt3, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC4 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

26S protease regulatory subunit S10B, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC6 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial is an enzyme subunit that in humans is encoded by the ATP5PF gene.
Reginald John Ellis is a British scientist.

In molecular biology, chaperone DnaJ, also known as Hsp40, is a molecular chaperone protein. It is expressed in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to humans.

ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit clpX-like, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CLPX gene. This protein is a member of the family of AAA Proteins and is to form the protein complex of Clp protease.

GrpE is a bacterial nucleotide exchange factor that is important for regulation of protein folding machinery, as well as the heat shock response. It is a heat-inducible protein and during stress it prevents unfolded proteins from accumulating in the cytoplasm. Accumulation of unfolded proteins in the cytoplasm can lead to cell death.

















