Liskeard is an ancient stannary and market town in south-east Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated approximately 20 miles (32 km) west of Plymouth, 14 miles (23 km) west of the Devon border, and 12 miles (20 km) east of Bodmin. The Bodmin Moor lies to the north-west of the town. The total population of the town at the 2011 census was 11,366

Restormel was a borough of Cornwall, England, one of the six administrative divisions that made up the county. Its council was based in St Austell; its other towns included Newquay.

Caradon was a local government district in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It contained five towns: Callington, Liskeard, Looe, Saltash and Torpoint, and over 80 villages and hamlets within 41 civil parishes. Its District Council was based in Liskeard 50.453°N 4.465°W.

A civil parish in England is the lowest unit of local government. There are 284 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Cumbria, with most of the county being parished. At the 2001 census, there were 359,692 people living in those 284 parishes, accounting for 73.8 per cent of the county's population.
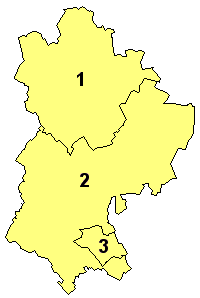
A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 125 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Bedfordshire, most of the county being parished: Luton is completely unparished; Central Bedfordshire is entirely parished. At the 2001 census, there were 312,301 people living in the 125 parishes, which accounted for 55.2 per cent of the county's population.

A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 104 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Berkshire, most of the county being parished; Reading is completely unparished; Bracknell Forest, West Berkshire and Wokingham are entirely parished. At the 2001 census, there were 483,882 people living in the 104 parishes, accounting for 60.5 per cent of the county's population.

A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 264 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, most of the county being parished; Cambridge is completely unparished; Fenland, East Cambridgeshire, South Cambridgeshire and Huntingdonshire are entirely parished. At the 2001 census, there were 497,820 people living in the parishes, accounting for 70.2 per cent of the county's population.

A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 333 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Cheshire, most of the county being parished. Cheshire East unitary authority is entirely parished. At the 2001 census, there were 565,259 people living in 332 parishes, accounting for 57.5 per cent of the county's population.

A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 14 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Greater Manchester, most of the county being unparished; Bury, Rochdale, Salford and Stockport are completely unparished. At the 2001 census, there were 129,325 people living in the civil parishes, accounting for 5.2% of the county's population.
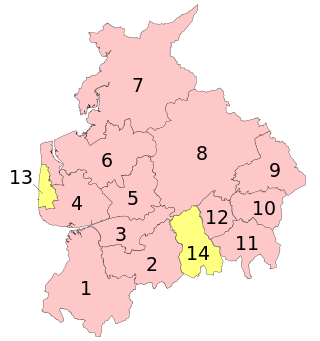
A civil parish is a subnational entity, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 219 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Lancashire; Blackpool is completely unparished; Pendle and Ribble Valley are entirely parished. At the 2001 census, there were 587,074 people living in the 219 parishes, accounting for 41.5 per cent of the county's population.

A civil parish is a subnational entity, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 101 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of West Yorkshire, most of the county being unparished. At the 2001 census, there were 557,369 people living in the parishes, accounting for 26.8 per cent of the county's population.

There are 10 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Tyne and Wear, most of the county being unparished; North Tyneside and South Tyneside are completely unparished. It is the county of England with the lowest number of civil parishes. At the 2001 census, there were 41,044 people living in the 10 parishes, accounting for 3.8 per cent of the county's population. A civil parish is the lowest unit of local government in England.

A civil parish is a subnational entity, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 21 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of West Midlands, most of the county being unparished; Dudley, Sandwell, Walsall and Wolverhampton are completely unparished. At the 2001 census, there were 89,621 people living in the parishes, accounting for 3.5 per cent of the county's population.
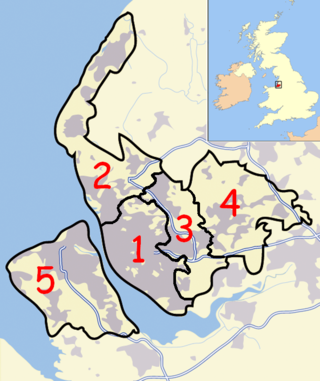
A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 22 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Merseyside, most of the county being unparished; Liverpool and Wirral are completely unparished. At the 2001 census, there were 177,663 people living in the parishes, accounting for 13.0 per cent of the county's population.
St Austell with Fowey was a municipal borough in Cornwall, United Kingdom. It was created in 1968 by a merger of the historic borough of Fowey and the much more populous St Austell urban district. 50.338°N 4.794°W

St Blazey is a small town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.

Cornwall is administered as a county of South West England whose politics are influenced by a number of issues that make it distinct from the general political scene in the wider United Kingdom, and the political trends of neighbouring counties. Its position on the geographical periphery of the island of Great Britain is also a factor.
Bodmin Rural District was a local government division of Cornwall in England, UK, between 1894 and 1934. Established under the Local Government Act 1894, the rural district was abolished in 1934 to create Wadebridge Rural District as well as enlarging Bodmin Municipal Borough, Liskeard Rural District, Lostwithiel Municipal Borough and St Austell Rural District.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Cornwall: Cornwall – ceremonial county and unitary authority area of England within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is a peninsula bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall is also a royal duchy of the United Kingdom. It has an estimated population of half a million and it has its own distinctive history and culture.