
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme.

Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement.

ATPases (EC 3.6.1.3, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life.

ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:
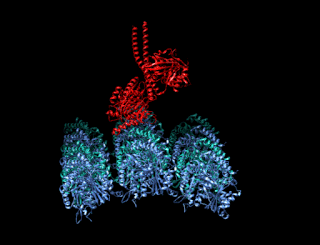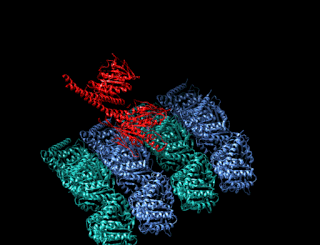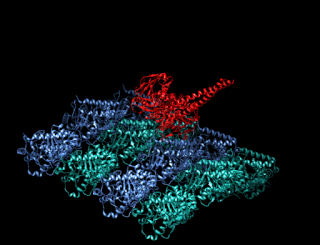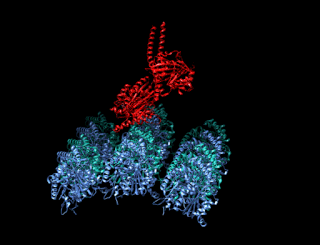
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The active movement of kinesins supports several cellular functions including mitosis, meiosis and transport of cellular cargo, such as in axonal transport, and intraflagellar transport. Most kinesins walk towards the plus end of a microtubule, which, in most cells, entails transporting cargo such as protein and membrane components from the center of the cell towards the periphery. This form of transport is known as anterograde transport. In contrast, dyneins are motor proteins that move toward the minus end of a microtubule in retrograde transport.

Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport.
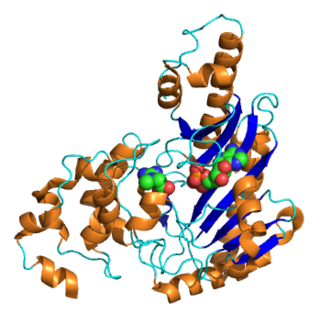
Creatine kinase (CK), also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phosphocreatine kinase, is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This CK enzyme reaction is reversible and thus ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP.
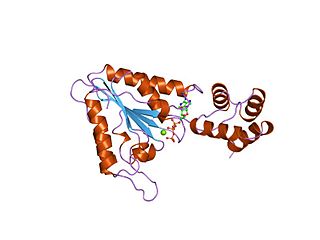
AAA proteins or ATPases Associated with diverse cellular Activities are a protein family sharing a common conserved module of approximately 230 amino acid residues. This is a large, functionally diverse protein family belonging to the AAA+ protein superfamily of ring-shaped P-loop NTPases, which exert their activity through the energy-dependent remodeling or translocation of macromolecules.

An axoneme, also called an axial filament is the microtubule-based cytoskeletal structure that forms the core of a cilium or flagellum. Cilia and flagella are found on many cells, organisms, and microorganisms, to provide motility. The axoneme serves as the "skeleton" of these organelles, both giving support to the structure and, in some cases, the ability to bend. Though distinctions of function and length may be made between cilia and flagella, the internal structure of the axoneme is common to both.

Molecular motors are natural (biological) or artificial molecular machines that are the essential agents of movement in living organisms. In general terms, a motor is a device that consumes energy in one form and converts it into motion or mechanical work; for example, many protein-based molecular motors harness the chemical free energy released by the hydrolysis of ATP in order to perform mechanical work. In terms of energetic efficiency, this type of motor can be superior to currently available man-made motors. One important difference between molecular motors and macroscopic motors is that molecular motors operate in the thermal bath, an environment in which the fluctuations due to thermal noise are significant.

Motor proteins are a class of molecular motors that can move along the cytoplasm of cells. They convert chemical energy into mechanical work by the hydrolysis of ATP. Flagellar rotation, however, is powered by a proton pump.
Gastric hydrogen potassium ATPase, also known as H+/K+ ATPase, is an enzyme which functions to acidify the stomach. It is a member of the P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases due to its two states.
Minus-end-directed kinesin ATPase (EC 3.6.4.5) is an enzyme with systematic name kinesin ATP phosphohydrolase (minus-end-directed). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, a microtubule-severing ATPase (EC 3.6.4.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
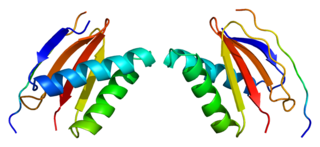
Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNLL1 gene.

Dynein light chain Tctex-type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNLT1 gene.

Cytoplasmic dynein 1 light intermediate chain 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNC1LI2 gene.

Ronald David Vale ForMemRS is an American biochemist and cell biologist. He is a professor at the Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology, University of California, San Francisco. His research is focused on motor proteins, particularly kinesin and dynein. He was awarded the Canada Gairdner International Award for Biomedical Research in 2019, the Shaw Prize in Life Science and Medicine in 2017 together with Ian Gibbons, and the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research in 2012 alongside Michael Sheetz and James Spudich. He is a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and a member of the National Academy of Sciences. He was the president of the American Society for Cell Biology in 2012. He has also been an investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute since 1995. In 2019, Vale was named executive director of the Janelia Research Campus and a vice president of HHMI, his appointment began in early 2020.

Ian Read Gibbons, was a biophysicist and cell biologist. He discovered and named dynein, and demonstrated energy source as ATP is sufficient for dynein to walk on microtubules. In 2017, he and Ronald Vale received the Shaw Prize for their research on microtubule motor proteins.
Edwin W. Taylor is an adjunct professor of cell and developmental biology at Northwestern University. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2001. Taylor received a BA in physics and chemistry from the University of Toronto in 1952; an MSc in physical chemistry from McMaster University in 1955, and a PhD in biophysics from the University of Chicago in 1957. In 2001 Taylor was elected to the National Academy of Scineces in Cellular and Developmental Biology and Biochemistry.















