
Spiro Theodore Agnew was the 39th vice president of the United States, serving from 1969 until his resignation in 1973. He is the second of two vice presidents to resign, the first being John C. Calhoun in 1832.

The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon which began in 1972 and ultimately led to Nixon's resignation in 1974. It revolved around members of a group associated with Nixon's 1972 re-election campaign breaking into and planting listening devices in the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate Office Building in Washington, D.C., on June 17, 1972, and Nixon's later attempts to hide his administration's involvement.

Archibald Cox Jr. was an American legal scholar who served as U.S. Solicitor General under President John F. Kennedy and as a special prosecutor during the Watergate scandal. During his career, he was a pioneering expert on labor law and was also an authority on constitutional law. The Journal of Legal Studies has identified Cox as one of the most cited legal scholars of the 20th century.

United States v. Nixon, 418 U.S. 683 (1974), was a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States in which the Court unanimously ordered President Richard Nixon to deliver tape recordings and other subpoenaed materials related to the Watergate scandal to a federal district court. Decided on July 24, 1974, the ruling was important to the late stages of the Watergate scandal, amidst an ongoing process to impeach Richard Nixon. United States v. Nixon is considered a crucial precedent limiting the power of any U.S. president to claim executive privilege.

Leonidas "Leon" Jaworski was an American attorney and law professor who served as the second special prosecutor during the Watergate scandal. He was appointed to that position on November 1, 1973, soon after the "Saturday Night Massacre" of October 19–20, 1973, which included the dismissal of his predecessor Archibald Cox.

The "Saturday Night Massacre" was a series of resignations over the dismissal of special prosecutor Archibald Cox that took place in the United States Department of Justice during the Watergate scandal in 1973. The events followed the refusal by Cox to drop a subpoena for the Nixon White House tapes at President Richard Nixon's request.
In the United States, a special counsel is a lawyer appointed to investigate, and potentially prosecute, a particular case of suspected wrongdoing for which a conflict of interest exists for the usual prosecuting authority. Other jurisdictions have similar systems. For example, the investigation of an allegation against a sitting president or attorney general might be handled by a special prosecutor rather than by an ordinary prosecutor who would otherwise be in the position of investigating his or her own superior. Special prosecutors also have handled investigations into those connected to the government but not in a position of direct authority over the Justice Department's prosecutors, such as cabinet secretaries or election campaigns.

William Doyle Ruckelshaus was an American attorney and government official.

William BartSaxbe was an American diplomat and politician affiliated with the Republican Party, who served as a U.S. Senator for Ohio, and was the Attorney General for Presidents Richard M. Nixon and Gerald R. Ford, and as the U.S. Ambassador to India.

Richard Gordon Kleindienst was an American lawyer, politician, and U.S. Attorney General during the early stages of Watergate political scandal. He resigned his post in disgrace for his involvement in the Watergate cover-up.

The Watergate scandal refers to the burglary and illegal wiretapping of the headquarters of the Democratic National Committee, in the Watergate complex by members of President Richard Nixon's re-election campaign, and the subsequent cover-up of the break-in resulting in Nixon's resignation on August 9, 1974, as well as other abuses of power by the Nixon White House that were discovered during the course of the scandal.
Audio recordings of conversations between U.S. President Richard Nixon and Nixon administration officials, Nixon family members, and White House staff surfaced during the Watergate scandal in 1973 and 1974, leading to Nixon's resignation.
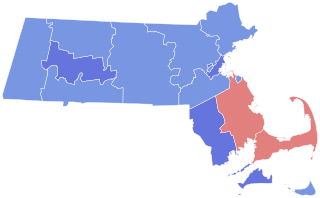
The 1984 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held on November 6, to elect a member of the U.S. Senate from the State of Massachusetts. The election was won by Democrat John Kerry, the Lieutenant Governor of Massachusetts, who remained Senator until 2013, when he resigned to become United States Secretary of State. One-term incumbent Democratic Senator Paul Tsongas declined to seek re-election after developing cancer.

Philip Benjamin Heymann was an American legal scholar and federal prosecutor who headed the Criminal Division of the Justice Department as Assistant Attorney General during the Carter administration and was briefly Deputy Attorney General in the Clinton administration before he resigned over management and policy differences as well as perceived interference by the White House. He was involved internationally in supporting the rule of law in criminal justice systems. In domestic politics he was a vocal supporter of civil and political liberties and, as such, was actively critical of the George W. Bush administration, particularly its warrantless domestic spying program. Even before the September 11 attacks, Heymann studied and published on how prosecution of antiterror policies can be done consistent with the rule of law in a democratic society. He was later James Bar Ames Professor of Law, Emeritus at Harvard Law School, where he began teaching in 1969.
Joseph Edward Lumbard Jr. was a United States circuit judge of the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit.

Richard Nixon's tenure as the 37th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1969, and ended when he resigned on August 9, 1974, in the face of almost certain impeachment and removal from office, the only U.S. president ever to do so. He was succeeded by Gerald Ford, whom he had appointed vice president after Spiro Agnew became embroiled in a separate corruption scandal and was forced to resign. Nixon, a prominent member of the Republican Party from California who previously served as vice president for two terms under president Dwight D. Eisenhower from 1953 to 1961, took office following his narrow victory over Democratic incumbent vice president Hubert Humphrey and American Independent Party nominee George Wallace in the 1968 presidential election. Four years later, in the 1972 presidential election, he defeated Democratic nominee George McGovern, to win re-election in a landslide. Although he had built his reputation as a very active Republican campaigner, Nixon downplayed partisanship in his 1972 landslide re-election.

The 1972 United States presidential election in Massachusetts took place on November 7, 1972, as part of the 1972 United States presidential election, which was held throughout all 50 states and D.C. Voters chose 14 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The impeachment process against Richard Nixon was initiated by the United States House of Representatives on October 30, 1973, during the course of the Watergate scandal, when multiple resolutions calling for the impeachment of President Richard Nixon were introduced immediately following the series of high-level resignations and firings widely called the "Saturday Night Massacre". The House Committee on the Judiciary soon began an official investigation of the president's role in Watergate, and, in May 1974, commenced formal hearings on whether sufficient grounds existed to impeach Nixon of high crimes and misdemeanors under Article II, Section 4, of the United States Constitution. This investigation was undertaken one year after the United States Senate established the Select Committee on Presidential Campaign Activities to investigate the break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate office complex during the 1972 presidential election, and the Republican Nixon administration's attempted cover-up of its involvement; during those hearings the scope of the scandal became apparent and the existence of the Nixon White House tapes was revealed.
Henry Swartley "Hank" Ruth Jr., was an American lawyer who served as the third special prosecutor during the Watergate Scandal. He was appointed after the October 1974 resignation of Leon Jaworski, and served until his own resignation in October 1975. He was succeeded by Charles F. Ruff.
Philip A. Lacovara is an American lawyer and legal scholar. He is best known as counsel to special prosecutor Archibald Cox during the Watergate Scandal.




















