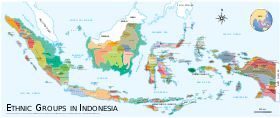
The demographics of Malaysia are represented by the multiple ethnic groups that exist in the country. Malaysia's population, according to the 2010 census, is 28,334,000 including non-citizens, which makes it the 42nd most populated country in the world. Of these, 5.72 million live in East Malaysia and 22.5 million live in Peninsular Malaysia. The population distribution is uneven, with some 79% of its citizens concentrated in Peninsular Malaysia, which has an area of 131,598 square kilometres (50,810.27 sq mi), constituting under 40% of the total area of Malaysia.

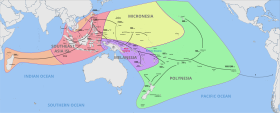
Southeast Asia is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia which is part of Oceania. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the parts of Southeast Asia that lie south of the Equator.

The Peranakan Chinese are an ethnic group defined by their genealogical descent from the first waves of Southern Chinese settlers to maritime Southeast Asia, known as Nanyang, namely the British Colonial ruled ports in the Malay Peninsula and the Indonesian Archipelago, as well as Singapore. Peranakan culture, especially in the dominant Peranakan centres of Malacca, Singapore, Penang, Phuket and Tangerang, is characterized by its unique hybridization of ancient Chinese culture with the local cultures of the Nusantara region, the result of a centuries-long history of transculturation and interracial marriage.

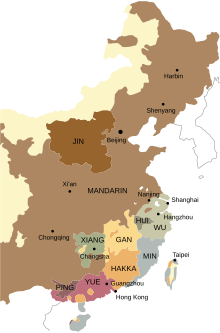
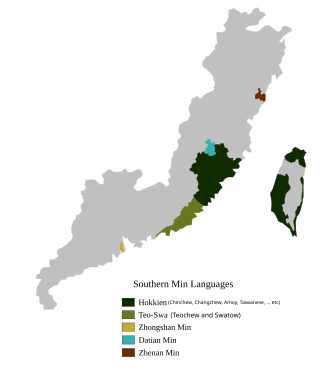
Min is a broad group of Sinitic languages with about 70 million native speakers. These languages are spoken in Fujian province as well as by the descendants of Min-speaking colonists on the Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan and by the assimilated natives of Chaoshan, parts of Zhongshan, three counties in southern Wenzhou, the Zhoushan archipelago, Taiwan and scattered in pockets or sporadically across Hong Kong, Macau, and several countries in Southeast Asia, particularly Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, Brunei. The name is derived from the Min River in Fujian, which is also the abbreviated name of Fujian Province. Min varieties are not mutually intelligible with one another nor with any other variety of Chinese.

Southern Min, Minnan or Banlam, is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Chinese languages that form a branch of Min Chinese spoken in Fujian, most of Taiwan, Eastern Guangdong, Hainan, and Southern Zhejiang. Southern Min dialects are also spoken by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora, most notably in Southeast Asia, such as Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Brunei, Southern Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Southern and Central Vietnam, San Francisco, Los Angeles and New York City. Minnan is the most widely-spoken branch of Min, with approximately 48 million speakers as of 2017–2018.

Chinese Malaysians, also commonly called locally as Malaysian Chinese, are Malaysian citizens of Han Chinese ethnicity. They form the second-largest ethnic group, after the Malay majority, and are 22.8% of the Malaysian population. Most of them are descendants of Southern Chinese immigrants who arrived in Malaysia between the early 19th and the mid-20th centuries. Malaysian Chinese form the second largest community of Overseas Chinese in the world, after Thai Chinese. Malaysian Chinese are traditionally dominant in the business sector of the Malaysian economy.

Chinatowns in Asia are widespread with large concentrations of overseas Chinese in East Asia and Southeast Asia, and ethnic Chinese whose ancestors came from southern China — particularly the provinces of Guangdong, Fujian, and Hainan — and settled in countries such as Brunei, Cambodia, East Timor, Indonesia, India, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam, Japan and Korea centuries ago — starting as early as the Tang dynasty, but mostly notably in the 17th–19th centuries, and well into the 20th century. Today the Chinese diaspora in Asia is primarily concentrated in Southeast Asia; however, the legacy of the once widespread overseas Chinese communities in Asia is evident in the many Chinatowns found across East, South and Southeast Asia.
Eurasian Singaporeans are Singaporeans of mixed European and Asian descent. Their Asian ancestry trace from colonial India to other colonies while their European ancestry trace back to western Europe primarily, although Eurasian settlers to Singapore in the 19th century came largely from other European colonies. These included British Malaya and British Sarawak, part of the former British Raj India, of the former Portuguese India and Chittagong, the Dutch East Indies and French Indochina. When the European maritime powers colonised Asian countries, such as colonial India, Ceylon, Malaya, Singapore, Indonesia and Indochina, from the 16th to 20th century, they brought into being a new group of commingled ethnicities known historically as Eurasians.

Chinese Singaporeans are Singaporeans of Han Chinese ancestry. Chinese Singaporeans constitute 75.9% of the Singaporean citizen population according to the official census, making them the largest ethnic group in Singapore.

The Hoklo people are a Han Chinese subgroup who speak Hokkien, a Southern Min language, or trace their ancestry to southeastern Fujian in China, and known by various related terms such as Banlam people, Minnan people, or more commonly in Southeast Asia as the Hokkien people. The Hokkien people are found in significant numbers in mainland China, Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, Indonesia, Brunei, Myanmar, the United States, Hong Kong, and Macau. The Hokkien people have a distinct culture and architecture, including Hokkien shrines and temples with tilted sharp eaves, high and slanted top roofs, and finely detailed decorative inlays of wood and porcelain. The Hokkien language, which includes Taiwanese Hokkien, is the mainstream Southern Min, which is partially mutually intelligible to the Teochew language, Hainanese, Leizhou Min, and Haklau Min.

The languages of Singapore are English, Chinese, Malay and Tamil, with the lingua franca between Singaporeans of different races being English, the de facto main language. Singaporeans often speak Singlish among themselves, an English creole arising from centuries of contact between Singapore's internationalized society and its legacy of being a British colony. Linguists formally define it as Singapore Colloquial English. A multitude of other languages are also used in Singapore. They consist of several varieties of languages under the families of the Austronesian, Dravidian, Indo-European and Sino-Tibetan languages. The Constitution of Singapore states that the national language of Singapore is Malay. This plays a symbolic role, as Malays are constitutionally recognised as the indigenous peoples of Singapore, and it is the government's duty to protect their language and heritage.
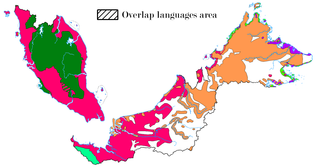
The indigenous languages of Malaysia belong to the Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian families. The national, or official, language is Malay which is the mother tongue of the majority Malay ethnic group. The main ethnic groups within Malaysia are the Malay people, Han Chinese people and Tamil people, with many other ethnic groups represented in smaller numbers, each with its own languages. The largest native languages spoken in East Malaysia are the Iban, Dusunic, and Kadazan languages. English is widely understood and spoken within the urban areas of the country; the English language is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary education. It is also the main medium of instruction within most private colleges and private universities. English may take precedence over Malay in certain official contexts as provided for by the National Language Act, especially in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, where it may be the official working language. Furthermore, the law of Malaysia is commonly taught and read in English, as the unwritten laws of Malaysia continue to be partially derived from pre-1957 English common law, which is a legacy of past British colonisation of the constituents forming Malaysia. In addition, authoritative versions of constitutional law and statutory law are continuously available in both Malay and English.
Hokkien is a variety of the Southern Min languages, native to and originating from the Minnan region, in the southeastern part of Fujian in southeastern mainland China. It is also referred to as Quanzhang, from the first characters of the urban centers of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou.
Min-speaking peoples are a major subgroup of ethnic Han Chinese people, speaking Min Chinese languages. They mainly live or trace roots from Fujian, Hainan, Southern Zhejiang and Guangdong province's Leizhou and Chaoshan regions. In the Chinese diaspora, they form the majority of people in Taiwan and the majority of Han Chinese in Southeast Asian countries, like Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines. The first two countries have majority Teochew-speaking Chinese minorities, whereas the last four house Hokkien-speaking Chinese minorities.

Singaporeans are the citizens and nationals of the sovereign island city-state of Singapore. Singapore is home to a people of a variety of ethno-racial origins, with the city-state itself being a multi-racial, multi-cultural, multi-religious, and multi-lingual country. Singaporeans of Chinese, Malay, Indian and Eurasian descent have made up the overwhelming majority of the population since the 19th century. The Singaporean diaspora is also far-reaching worldwide.

Chinese folk religion plays a dynamic role in the lives of the overseas Chinese who have settled in the countries of this geographic region, particularly Burmese Chinese, Singaporean Chinese, Malaysian Chinese, Thai Chinese and Hoa. The Indonesian Chinese, by contrast, were forced to adopt en masse either Buddhism or Christianity in the 1950s and 1960s, abandoning traditional worship, due to Indonesia's religious policies which at the time forbade Chinese traditional religion or did not recognize it as a "religion," thus making it vulnerable to discrimination. Some Chinese Filipinos also still practice some Chinese traditional religions, besides Christianity of either Roman Catholicism or Protestantism, with which some have also varyingly syncretized traditional Chinese religious practices. Chinese folk religion, the ethnic religion of Han Chinese, "Shenism" was especially coined referring to its Southeast Asian expression; another Southeast Asian name for the religion is the Sanskrit expression Satya Dharma.

Penangite Chinese are ethnic Chinese Malaysians of full or partial Chinese ancestry who either hail from or live within the State of Penang. As of 2020, 45% of Penang's population belonged to the Chinese ethnic group, making ethnic Chinese the largest ethnic community within the state.
The usage of Chinese by the Chinese diaspora and their descendants has been determined by a large number of factors, including their ancestry, their migrant ancestors' "regime of origin", assimilation through generational changes, and official policies of their country of residence. The general trend is that more established Chinese populations in the Western world and in many regions of Asia have Cantonese as either the dominant variety or as a common community vernacular, while Mandarin is much more prevalent among new arrivals, making it increasingly common in many Chinatowns, though still not dominant.

Sabah is the third most populous state in Malaysia, with a population of 3,418,785 according to the 2020 Malaysian census. It also has the highest non-citizen population, at 810,443. Although Malaysia is one of the least densely populated countries in Asia, Sabah is particularly sparsely populated. Most of the population is concentrated along coastal areas, with towns and urban centers seeing the most population growth.

Eastern culture, also known as Eastern civilization and historically as Oriental culture, is an umbrella term for the diverse cultural heritages of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, artifacts and technologies of the Eastern world.