
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The opponens digiti minimi is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the three hypothenar muscles that control the little finger.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
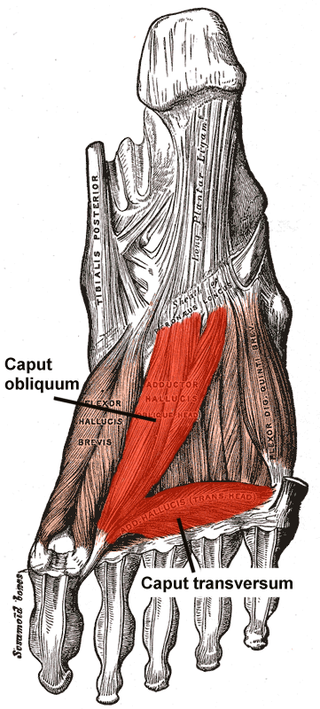
The Adductor hallucis arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.
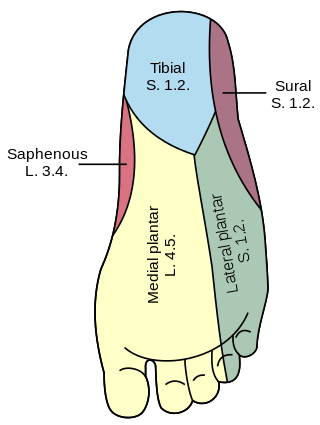
The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.
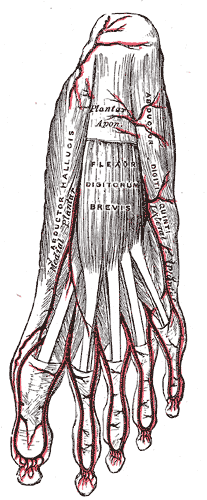
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

The flexor digiti minimi brevis is a hypothenar muscle in the hand that flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. It lies lateral to the abductor digiti minimi when the hand is in anatomical position.

The sole is the bottom of the foot.

The lateral plantar nerve is a branch of the tibial nerve, in turn a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the skin of the fifth toe and lateral half of the fourth, as well as most of the deep muscles, its distribution being similar to that of the ulnar nerve in the hand.

The lateral plantar artery, much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.

The superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve:
In human anatomy, a brevis muscle derives its name from the Latin brevis meaning "short", and can refer to:


















