Perranporth is a seaside resort town on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is 2.1 miles east of the St Agnes Heritage Coastline, and around 7 miles south-west of Newquay. Perranporth and its 2 miles (3 km) long beach face the Atlantic Ocean. It has a population of 3,066, and is the largest settlement in the civil parish of Perranzabuloe. It has an electoral ward in its own name whose population was 4,270 in the 2011 census.
Godrevy is an area on the eastern side of St Ives Bay, west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, which faces the Atlantic Ocean. It is popular with both the surfing community and walkers. It is part owned by the National Trust, and offshore on Godrevy Island is a lighthouse maintained by Trinity House which is said to be the inspiration for Virginia Woolf's novel To the Lighthouse. Godrevy lies within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) and the South West Coast Path runs around the whole promontory. There are several public car parks on the western side where the National Trust owns and operates a café.

Porthtowan is a small village in Cornwall, England, UK, which is a popular summer tourist destination. Porthtowan is on Cornwall's north Atlantic coast about 3.5 km (2.2 mi) southwest of St Agnes, 6 km (3.7 mi) north of Redruth, 16 km (9.9 mi) west of Truro and 24 km (15 mi) southwest of Newquay in the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape, a World Heritage Site.

Aire Point to Carrick Du SSSI is a Site of Special Scientific Interest on the Penwith Peninsula, Cornwall, England. It is 5.98 square kilometres in extent, stretching from grid reference SW360279 to grid reference SW513410. The site is designated both for its biological and its geological interest.

Lower Bostraze And Leswidden SSSI is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest, located on the Penwith Peninsula, Cornwall, England, a little to the east of St Just, approximately 8 km west of Penzance.

Gugh could be described as the sixth inhabited island of the Isles of Scilly, but is usually included with St Agnes with which it is joined by a sandy tombolo known as "The Bar" when exposed at low tide. The island is only about 1 km (0.62 mi) long and about 0.5 km (0.31 mi) wide, with the highest point, Kittern Hill at 34 m (112 ft). The geology consists of Hercynian granite with shallow podzolic soils on the higher ground and deeper sandy soils on the lower ground. The former Gugh farm is just north of the neck across the middle of the island between the two hills. The two houses were designed and built in the 1920s by Charles Hamlet Cooper.

Teän is an uninhabited island to the north of the Isles of Scilly archipelago between Tresco, 1.5 kilometres (0.9 mi) to the west, and St Martin's, 300 metres (330 yd) to the east. Approximately 16 hectares in area, the island consists of a series of granite tors with the highest point, Great Hill, rising to 40 metres (130 ft) at its eastern end. The low-lying land is overlain with glacial till and outwash gravels with glacial erratics abundant on the north coast beaches, which indicates the southern limit of outwash from an ice sheet for which it is designated a Geological Conservation Review site.

Cornwall is the county that forms the tip of the southwestern peninsula of England; this area has a mild and warm climate regulated by the Gulf Stream. The mild climate allows rich plant cover, such as palm trees in the far south and west of the county and in the Isles of Scilly, due to sub-tropical conditions in the summer.

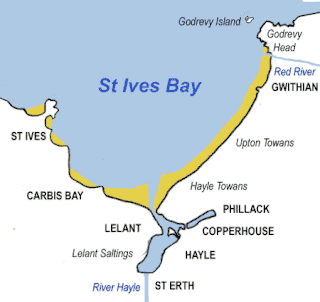
St Ives Bay is a bay on the Atlantic coast of north-west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in the form of a shallow crescent, some 4 miles or 6 km across, between St Ives in the west and Godrevy Head in the east.

Decoy Pit, Pools and Woods is a 17.7-hectare (44-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest south of Aldermaston in Berkshire. An area of 8 hectares is a nature reserve called Decoy Heath, which is managed by the Berkshire, Buckinghamshire and Oxfordshire Wildlife Trust.

Treen Cliff is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) located on the Penwith Peninsula in Cornwall, England, UK, 6 miles (9.7 km) south-west of Penzance. First notified in 1951, with a revision in 1973, and a further notification on 1 July 1986, it is 49.3 hectares in area, stretching from grid reference SW387220 to SW402225. Designated for both for its biological and geological interest, part of the site, Treryn Dinas, is a Scheduled Ancient Monument consisting of a "cliff castle" with four ramparts and ditches and the Logan Rock. It is within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), the Penwith Heritage Coast and is part owned and managed by the National Trust.

Caerthillian to Kennack is a coastal Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) on the Lizard Peninsula in Cornwall, UK, noted for both its biological and geological characteristics. It is of great botanical importance, with several Red Data Book of rare and endangered plant species being found on the site, as well as a breeding site for Cornish choughs.

Steeple Point to Marsland Mouth is a coastal Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Cornwall, England, UK, noted for its biological characteristics.

Wingletang Down is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) on the southern side of the island of St Agnes in the Isles of Scilly, England, UK, which is noted for its biological characteristics. All of the land designated as Wingletang Down SSSI is owned by the Duchy of Cornwall. The site is managed by the Isles of Scilly Wildlife Trust and is within the Isles of Scilly Heritage Coast and the Isles of Scilly Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is the only site in Great Britain and Ireland for the small fern, least adder's–tongue. As of 11 September 2009 the SSSI was considered to be in ″unconditional recovering″ condition because European gorse and bramble are at unacceptable levels.

The Eastern Isles are a group of twelve small uninhabited islands within the Isles of Scilly Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, part of the Scilly Heritage Coast and a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) first designated in 1971 for its flora and fauna. They have a long period of occupation from the Bronze Age with cairns and entrance graves through to Iron Age field systems and a Roman shrine on Nornour. Before the 19th century, the islands were known by their Cornish name, which had also become the name of the largest island in the group after the submergence of the connecting lands.

Polruan to Polperro is a coastal Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and Special Area of Conservation (SAC) in south-east Cornwall, England, UK, noted for its biological interest. It contains a wide variety of plant species and is a site for populations of breeding birds.

Peninnis Head is the southernmost point of St Mary's, Isles of Scilly. The headland is within the Isles of Scilly Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and part of the Heritage Coast. It is also a Geological Conservation Review site for its Quaternary geomorphology and was first designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in 1971 for both its biological and geological interests. All of the land designated as Peninnis Head SSSI is owned by the Duchy of Cornwall. On the tip of the headland is a squat lighthouse built in 1911 by Trinity House as a replacement for the 17th century lighthouse on St Agnes.

Penhale Sands, or Penhale Dunes, is a complex of sand dunes and a protected area for its wildlife, on the north Cornwall coast in England, UK. It is the most extensive system of sand dunes in Cornwall and is believed to be the landing site of Saint Piran. Dating from the 6th century, St Piran's Oratory is thought to be one of the oldest Christian sites in Britain. The remains were discovered in the late 18th century, and in 2014 the covering sand was removed to reveal a building more than a thousand years old, in a reasonable state of preservation. A restricted military area dating from 1939, Penhale Camp, is found on the northern part of the dunes.
Ventongimps Moor is a moorland nature reserve and Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), noted for its biological characteristics, in mid Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The site, important for the occurrence of the plant Dorset heath, was the first reserve to be purchased by the Cornwall Wildlife Trust.