
Marietta is a city in, and the county seat of, Washington County, Ohio, United States. It is located in southeastern Ohio at the confluence of the Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, 11 miles (18 km) northeast of Parkersburg, West Virginia. As of the 2020 census, Marietta has a population of 13,385 people. It is the principal city of the Marietta micropolitan area, which includes all of Washington County, and is the second-largest city in the Parkersburg–Marietta–Vienna combined statistical area.
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial organized incorporated territory.
The Treaty of Fort McIntosh was a treaty between the United States government and representatives of the Wyandotte, Delaware, Chippewa and Ottawa nations of Native Americans. The treaty was signed at Fort McIntosh on January 21, 1785. It contained 10 articles and an addendum.

Coal Run is an unincorporated community in northeastern Waterford Township, Washington County, Ohio, United States. It has a post office with the ZIP code 45721. It is located along State Route 60 between the villages of Beverly and Lowell. The Muskingum River flows past the community.

The Huffman Historic District is a historic section of the Historic Inner East neighborhood in Dayton, Ohio, United States. Formed at the end of the nineteenth century primarily by a wealthy businessman, it has long been home to people of many different occupations and numerous places on the social ladder. After seeing very few changes throughout the twentieth century, it was named a historic site in the 1980s.

The Kenilworth Avenue Historic District is a historic district in the northwestern portion of Dayton, Ohio, United States. Composed largely of houses constructed after the Great Flood of 1913, the district features examples of several prominent architectural styles, and it has received both local and federal recognition.

The Drake Park Neighborhood Historic District is located adjacent to Drake Park near the historic downtown area in Bend, Oregon, United States. Because of the unique and varied architecture in the Drake Park neighborhood and its close association with the early development of the city of Bend, the area was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2005.

The Putnam Street Bridge, also known as the Marietta Bridge, is a historic United States river crossing that connects Marietta, Ohio, with its Fort Harmar district. The original 1880 bridge was the first free crossing of the Muskingum River. The 1913 bridge was a contributing structure to the Harmar Historic District. The bridge crosses the Muskingum, just above its confluence with the Ohio River.

Fort Harmar was an early United States frontier military fort, built in pentagonal shape during 1785 at the confluence of the Ohio and Muskingum rivers, on the west side of the mouth of the Muskingum River. It was built under the orders of Colonel Josiah Harmar, then commander of the United States Army, and took his name. The fort was intended for the protection of Indians, i.e., to prevent pioneer squatters from settling in the land to the northwest of the Ohio River. "The position was judiciously chosen, as it commanded not only the mouth of the Muskingum, but swept the waters of the Ohio, from a curve in the river for a considerable distance both above and below the fort." It was the first frontier fort built in Ohio Country.

The Marietta Historic District is a historic district in Marietta, Ohio, United States that is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Among the buildings in the district are ones dating back to 1788, the year in which Marietta was founded as the first white settlement in what is now Ohio. Among its most significant buildings are the Rufus Putnam House and the Ohio Company Land Office, which are also separately listed on the Register.

The Putnam House is a historic building in the Harmar neighborhood of Marietta, Washington County, Ohio, United States, on the National Register of Historic Places. The house overlooks the Muskingum River.

The Ohio Company Land Office is one of the original buildings of the city of Marietta, Ohio, United States. The Office is listed individually in the National Register of Historic Places and as a contributing property to the Marietta Historic District.
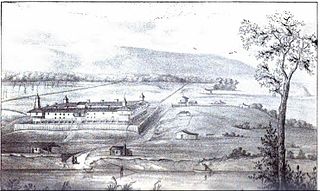
Campus Martius was a defensive fortification at the Marietta, Ohio settlement, and was home to Rufus Putnam, Benjamin Tupper, Arthur St. Clair, and other pioneers from the Ohio Company of Associates during the Northwest Indian War. Major Anselm Tupper was commander of the Campus Martius during the war. Construction began in 1788 and was fully completed in 1791. The Campus Martius was located on the east side of the Muskingum River, and upriver from its confluence with the Ohio River. A firsthand description of the fort is provided in Hildreth's Pioneer History,
Campus Martius is the handsomest pile of buildings on this side of the Alleghany mountains, and in a few days will be the strongest fortification in the territory of the United States. It stands on the margin of the elevated plain on which are the remains of the ancient works [mounds], mentioned in my letter of May last, thirty feet above the high bank of the Muskingum, twenty-nine perches distant from the river, and two hundred and seventy-six from the Ohio. It consists of a regular square, having a block house at each angle, eighteen feet square on the ground, and two stories high; the upper story on the outside or face, jutting over the lower one, eighteen inches. These block houses serve as bastions to a regular fortification of four sides. The curtains are composed of dwelling houses two stories high, eighteen feet wide, and of different lengths.

Picketed Point Stockade was the last of three fortifications built at Marietta, Ohio. This defensive stockade was built by pioneers during the Northwest Indian War in 1791 on the east side of the mouth of the Muskingum River at its confluence with the Ohio River, and directly across the Muskingum from Fort Harmar. Colonel William Stacy superintended the construction of the stockade under direction of Colonel Ebenezer Sproat. Palisades or pickets were set from the Muskingum River eastward, meeting in the northeast corner of the fortification with another line of pickets built from the Ohio River northward, enclosing about four acres.
Three block houses were immediately built: one on the Muskingum bank, at the western termination of the pickets; one in the northeast corner of the inclosure; and one on the Ohio bank. Near to the latter, and by that on the Muskingum, were strong gates, of a size to admit teams, the approaches to which were commanded by the block houses. These block houses were surmounted by sentry boxes, or turrets, the sides of which were secured with thick planks for the defense of the men when on guard.
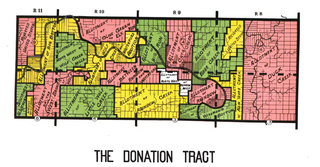
The Donation Tract was a land tract in southern Ohio that was established by the Congress late in the 18th century to buffer Ohio Company lands against local indigenous people. Congress gave 100-acre (0.40 km2) lots to men who settled on the land. This marked the first time that federal land was given without charge to specified settlers, predating the more famous Homestead Act of 1862 by seventy years.

Fort Steuben was a fortification erected in Feb. 1787 on the Ohio River in eastern Ohio Country at the northern end of the Seven Ranges land tract to be surveyed. It was at the location of the modern city of Steubenville, Ohio. The fort was built by Major John Hamtramck and named for Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben, a Prussian army officer who had served under General Washington. The original purpose was to provide protection from Indians for the first surveyors to venture into the Northwest Territory.

Fort Frye was a triangular defensive fortification built by a group of pioneers from the Ohio Company of Associates who moved about twenty miles up the Muskingum River from the settlement of Marietta, Ohio to a location near the mouth of Wolf Creek. During 1789 the pioneers established settlements now known as Waterford and Beverly on the southwest and northeast banks of the Muskingum, respectively. The settlements were located about 13 miles downriver from a small group of pioneers at Big Bottom. During January and February 1791, following the massacre at Big Bottom and the start of the Northwest Indian War, the settlers built Fort Frye at Beverly.
The form of the fort was triangular, which is rather uncommon in military defenses. But as they were in a hurry, and it saved them one line of curtains, while the block houses at the angles defended the sides just as well as in any other form, it was adopted. The base of the triangle rested on the river, distant only a few paces from the bank, and was about two hundred feet in length. One of the other sides was somewhat longer, so that the work was not a regular triangle. At each corner, was a two story block house, twenty feet square below, and a foot or two more above. The two longer sides were filled in with dwelling houses, some of which were two stories high, and others of a lesser height, while a considerable portion were built barrack fashion, with only one roof, pitched inward, so that the rain from it fell within the garrison. The spaces not occupied by buildings were filled in with stout pickets. Broad, substantial gates, near the northern block house, led out through the palisades into the highway and fields, while a smaller one in the curtain on the bank, called the water gate, afforded an opening to the river. A line of palisades, twelve feet high, at the distance of thirty feet, inclosed the whole, and descended to the river.

The First Unitarian Church of Marietta is a historic Unitarian Universalist church in the city of Marietta, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1869, it uses a building constructed in 1858 for one of its two predecessor churches; this building's high-quality architecture has led to its designation as a historic site.

The Marietta Earthworks is an archaeological site located at the confluence of the Muskingum and Ohio Rivers in Washington County, Ohio, United States. Most of this Hopewellian complex of earthworks is now covered by the modern city of Marietta. Archaeologists have dated the ceremonial site's construction to approximately 100 BCE to 500 CE.

Putnam Historic District, located in Zanesville, Ohio, was an important center of Underground Railroad traffic and it home to a number of abolitionists. The district, with private residences and other key buildings important in the fight against slavery, lies between the Pennsylvania Central Railroad, Van Buren Street, and Muskingum River. It became a historic district of the National Register of Historic Places in 1975.

























