
Armenia is a landlocked country in the South Caucasus region of the Caucasus. The country is geographically located in West Asia, within the Armenian plateau. Armenia is bordered on the north and east by Georgia and Azerbaijan and on the south and west by Iran, Azerbaijan's exclave Nakhchivan, and Turkey.

The Murrumbidgee River is a major tributary of the Murray River within the Murray–Darling basin and the second longest river in Australia. It flows through the Australian state of New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, descending 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) over 1,485 kilometres (923 mi), generally in a west-northwesterly direction from the foot of Peppercorn Hill in the Fiery Range of the Snowy Mountains towards its confluence with the Murray River near Boundary Bend.

The Kura is an east-flowing river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus, while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, the Kura flows through Turkey to Georgia, then to Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and enters the Caspian Sea at Neftçala. The total length of the river is 1,515 kilometres (941 mi).

The Aras is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, finally, through Azerbaijan where it flows into the Kura river. It drains the south side of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains, while the Kura drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus. The river's total length is 1,072 km (666 mi) and its watershed covers an area of 102,000 km2 (39,000 sq mi). The Aras is one of the longest rivers in the Caucasus.

The Eastern Continental Divide, Eastern Divide or Appalachian Divide is a hydrological divide in eastern North America that separates the easterly Atlantic Seaboard watershed from the westerly Gulf of Mexico watershed. The divide nearly spans the United States from south of Lake Ontario through the Florida peninsula, and consists of raised terrain including the Appalachian Mountains to the north, the southern Piedmont Plateau and lowland ridges in the Atlantic Coastal Plain to the south. Water including rainfall and snowfall, lakes, streams and rivers on the eastern/southern side of the divide drains to the Atlantic Ocean; water on the western/northern side of the divide drains to the Gulf of Mexico. The ECD is one of six continental hydrological divides of North America which define several drainage basins, each of which drains to a particular body of water.

The Huron River is a 130-mile-long (210 km) river in southeastern Michigan, rising out of the Huron Swamp in Springfield Township in northern Oakland County and flowing into Lake Erie, as it forms the boundary between present-day Wayne and Monroe counties. Thirteen parks, game areas, and recreation areas are associated with the river, which passes through the cities of Dexter, Ann Arbor, Ypsilanti, Belleville, Flat Rock and Rockwood that were developed along its banks.

The Owyhee River is a tributary of the Snake River located in northern Nevada, southwestern Idaho and southeastern Oregon in the United States. It is 280 miles (450 km) long. The river's drainage basin is 11,049 square miles (28,620 km2) in area, one of the largest subbasins of the Columbia Basin. The mean annual discharge is 995 cubic feet per second (28.2 m3/s), with a maximum of 50,000 cu ft/s (1,400 m3/s) recorded in 1993 and a minimum of 42 cu ft/s (1.2 m3/s) in 1954.

Lake Sevan is the largest body of water in both Armenia and the Caucasus region. It is one of the largest freshwater high-altitude (alpine) lakes in Eurasia. The lake is situated in Gegharkunik Province, at an altitude of 1,900 m (6,234 ft) above sea level. The total surface area of its basin is about 5,000 km2 (1,900 sq mi), which makes up 1⁄6 of Armenia's territory. The lake itself is 1,242 km2 (480 sq mi), and the volume is 32.8 km3 (7.9 cu mi). It is fed by 28 rivers and streams. Only 10% of the incoming water is drained by the Hrazdan River, while the remaining 90% evaporates.

The Hrazdan is a major river and the second largest in Armenia. It originates at the northwest extremity of Lake Sevan and flows south through the Kotayk Province and Armenia's capital, Yerevan; the lake in turn is fed by several streams. In the Ararat plain it joins the Aras river along the border with Turkey. Its waters join the Kura river, before flowing into the Caspian Sea.

The Bois de Sioux River drains Lake Traverse, the southernmost body of water in the Hudson Bay watershed of North America. It is a tributary of the Red River of the North and defines part of the western border of the U.S. state of Minnesota, and the eastern borders of North Dakota and South Dakota. It is about 41 miles (66 km) in length.
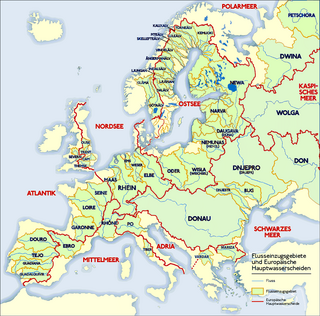
The main European watershed is the drainage divide ("watershed") which separates the basins of the rivers that empty into the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Baltic Sea from those that feed the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea and the Black Sea. It stretches from the tip of the Iberian Peninsula at Gibraltar in the southwest to the endorheic basin of the Caspian Sea in Russia in the northeast.
Yellow Creek is a tributary of the Pecatonica River in Stephenson County, in the US state of Illinois. The 50-mile (80 km) stream also flows through a small part of Jo Daviess County. The waters of Yellow Creek were assessed for water quality in 1996, with 28 miles (45 km) being listed as "fair" and 22 miles (35 km) being listed as "good". During the 1832 Black Hawk War, the Battle of Waddams Grove was fought along Yellow Creek.

Salmon Falls Creek is a tributary of the Snake River, flowing from northern Nevada into Idaho in the United States. Formed in high mountains at the northern edge of the Great Basin, Salmon Falls Creek flows northwards 121 miles (195 km), draining an arid and mountainous basin of 2,103 square miles (5,450 km2). The Salmon Falls Creek valley served as a trade route between the Native American groups of the Snake River Plain and Great Basin. Today, most of its water is used for irrigation.

The geology of Armenia was shaped by geological upheaval that pushed up the Earth's crust to form the Armenian plateau 25 million years ago. This created the complex topography of Armenia.

Sevan–Hrazdan Cascade is a complex of hydroelectric power plants on the Hrazdan River and its tributaries between the Lake Sevan and Yerevan in Armenia. They use irrigation water flow from the Lake Sevan and streams waters of Hrazdan River. The cascade is owned by the International Energy Corporation (IEC), a subsidiary of Tashir Group owned by Samvel Karapetyan.

The Saint Lawrence River Divide is a continental divide in central and eastern North America that separates the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River Basin from the southerly Atlantic Ocean watersheds. Water, including rainfall and snowfall, lakes, rivers and streams, north and west of the divide, drains into the Gulf of St. Lawrence or the Labrador Sea; water south and east of the divide drains into the Atlantic Ocean or Gulf of Mexico. The divide is one of six continental divides in North America that demarcate several watersheds that flow to different gulfs, seas or oceans.

Rivers and creeks in Lake County, California are listed below by river basin and alphabetically. Unless otherwise stated, the information is taken from the Geographic Names Information System maintained by the United States Geological Survey. Coordinates, elevations and lengths from this source are approximate.




















