
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Southwestern China, Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, and Jamuna River in Bengali. By itself, it is the 9th largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest.
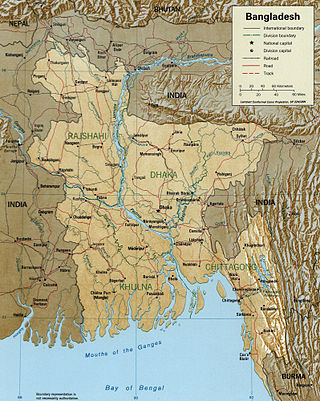
The Meghna is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, the Meghna is formed inside Bangladesh in Kishoreganj District above the town of Bhairab Bazar by the joining of the Surma and the Kushiyara, both of which originate in the hilly regions of eastern India as the Barak River. The Meghna meets its major tributary, the Padma, in Chandpur District. Other major tributaries of the Meghna include the Dhaleshwari, the Gumti, and the Feni. The Meghna empties into the Bay of Bengal in Bhola District via four principal mouths, named Tetulia (Ilsha), Shahbazpur, Hatia, and Bamni.

The Padma is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the eastern and main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for 356 kilometres (221 mi) to its confluence with the Meghna River near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is situated on the banks of the river. Since 1966, over 66,000 hectares of land has been lost to erosion of the Padma.

Tangail is a district (zila) in the central region of Bangladesh. In 1969, Tangail district was created by Tangail Mohokuma from its 237 square kilometers of land and 3177 square kilometers of land acquired from Mymensingh district. It is the largest district of Dhaka division by area and second largest by population. The population of Tangail zila is about 4 million and its area is 3,414.28 square kilometres (1,318.26 sq mi). The main city of the district is Tangail. It is surrounded by Jamalpur District on the north, the Dhaka and Manikganj Districts on the south, Mymensingh and Gazipur on the east, and Sirajganj on the west.

The Jamuna River is one of the three main rivers of Bangladesh. It is the lower stream of the Brahmaputra River, which originates in Tibet as Yarlung Tsangpo, before flowing through India and then southwest into Bangladesh. The Jamuna flows south and joins the Padma River, near Goalundo Ghat, before meeting the Meghna River near Chandpur. It then flows into the Bay of Bengal as the Meghna River.
Tangail is a city of Tangail District in central Bangladesh. A significant city in Bangladesh, Tangail lies on the bank of the Louhajang River, 83 kilometres (52 mi) northwest of Dhaka, the nation's capital. It is the 25th most populous city in Bangladesh.

The Dhaleshwari River is a distributary, 160 kilometres (99 mi) long, of the Jamuna River in central Bangladesh. It branches off the Jamuna near the northwestern tip of Tangail District. After that it divides into two branches: the north branch retains the name Dhaleshwari and merges with the other branch, the Kaliganga River at the southern part of Manikganj District. Finally the merged flow meets the Shitalakshya River near Narayanganj District. This combined flow goes southwards to merge into the Meghna River.

Mymensingh District is a district in Mymensingh Division, Bangladesh, and is bordered on the north by Meghalaya, a state of India and the Garo Hills, on the south by Gazipur District, on the east by the districts of Netrokona and Kishoreganj, and on the west by the districts of Sherpur, Jamalpur and Tangail. Mymensingh is the 8th administrative divisional headquarter and 12th city corporation of Bangladesh. According to Ministry of Public Administration, Mymensingh is ranked 4th in district status. The density of Mymensingh city is 44,458/km2 which is the second most densely populated city in Bangladesh. Mymensingh attracts 25 percent of health tourists visiting Bangladesh. Once known as the largest district of the Indian subcontinent. Mymensingh town is the district headquarters.

The Surma-Meghna River System is a river complex in the Indian Subcontinent, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest on earth. It rises in the Manipur Hills of northeast India as the Barak River and flows west becoming the Surma River and then flows south as the Meghna River, a total of 946 kilometres (588 mi) of which 669 kilometres (416 mi) are within Bangladesh, to the Bay of Bengal.

Chalan Beel is a wetland in the Sirajganj, Natore and Pabna districts of Bangladesh. It is a large inland depression, marshy in character, with rich flora and fauna. Forty-seven rivers and other waterways flow into the Chalan Beel. As silt builds up in the beel, its size is being reduced.

The Bangali River is one of the main rivers in northern Bangladesh. As of 2007, the river is in the news because of the possibility that it might merge with the Jamuna River, which could lead to major changes in the geography of the region.

Karatoya River is a small stream in Rajshahi Division of Bangladesh.

The Bangshi is an important river in central Bangladesh. It originates in Jamalpur, from the course of the old Brahmaputra and flows past the Madhupur tract. It flows through Tangail and meets the Tongi in Ghazipur. It passes near Jatiyo Smriti Soudho in Savar and falls into the Dhaleshwari. About 238 kilometres (148 mi) long, it is not navigable for most of the year except when swelled by the monsoon rains. Louhajang River is a tributary of the Bangshi. Dhamrai on the banks of the Bangshi is famous for its muslin weaving.

Louhajang River is located in central Bangladesh. It branches off from the Jamuna near Gabsain at Bhuapur, Tangail District. Thereafter it bifurcates before the two parts meet up again. It flows past Tangail city, Karotia and Jamurki before joining the Bangshi. The Louhajang is linked with the Dhaleshwari.

The Bhairab is a river in south-western Bangladesh, a distributary of the Ganges. It passes through Khulna, dividing the city into two parts. Bhairab River originates from Tengamari border of Meherpur District and passes through Jessore city. The river is approximately 160 kilometres (100 mi) long and 91 metres (300 ft) wide. Its average depth is 1.2 to 1.5 metres and with minimal water flow, it has plenty of silt.
The Chiknai River, also known as the Dangha, is located in Bangladesh in the beels west of Chatmohor in Pabna District.

The Narayanganj–Bahadurabad Ghat line is a railway line connecting Narayanganj and Bahadurabad Ghat in Bangladesh. There are branch lines to Jagannathganj Ghat and Netrakona-Mohanganj. This track is under the jurisdiction of Bangladesh Railway.

The Old Brahmaputra River is a distributary of the Brahmaputra River in north-central Bangladesh. Historically it constituted the main stem of the Brahmaputra, however, the larger river's primary outflow was redirected via the Jamuna River after the 1762 Arakan earthquake. Today, the Old Brahmaputra has been relegated to a minor river with much less flow than its former self. The river branches off from the Brahmaputra in Jamalpur District and Mymensingh then flows southeasterly for approximately 200 km (120 mi) before meeting the Meghna River in Kishoreganj District.


















