
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.

In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding of large proteins or macromolecular protein complexes. There are a number of classes of molecular chaperones, all of which function to assist large proteins in proper protein folding during or after synthesis, and after partial denaturation. Chaperones are also involved in the translocation of proteins for proteolysis.

ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:
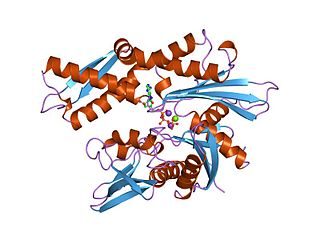
The 70 kilodalton heat shock proteins are a family of conserved ubiquitously expressed heat shock proteins. Proteins with similar structure exist in virtually all living organisms. Intracellularly localized Hsp70s are an important part of the cell's machinery for protein folding, performing chaperoning functions, and helping to protect cells from the adverse effects of physiological stresses. Additionally, membrane-bound Hsp70s have been identified as a potential target for cancer therapies and their extracellularly localized counterparts have been identified as having both membrane-bound and membrane-free structures.
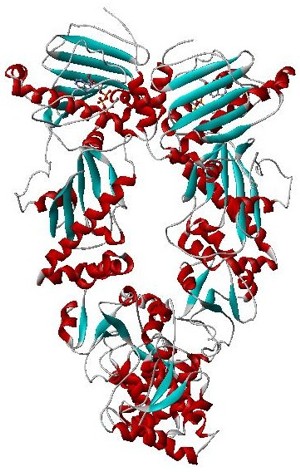
Hsp90 is a chaperone protein that assists other proteins to fold properly, stabilizes proteins against heat stress, and aids in protein degradation. It also stabilizes a number of proteins required for tumor growth, which is why Hsp90 inhibitors are investigated as anti-cancer drugs.
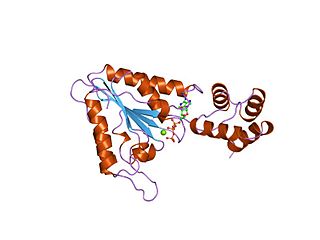
AAA proteins or ATPases Associated with diverse cellular Activities are a protein family sharing a common conserved module of approximately 230 amino acid residues. This is a large, functionally diverse protein family belonging to the AAA+ protein superfamily of ring-shaped P-loop NTPases, which exert their activity through the energy-dependent remodeling or translocation of macromolecules.
In biochemistry, dephosphorylation is the removal of a phosphate (PO43−) group from an organic compound by hydrolysis. It is a reversible post-translational modification. Dephosphorylation and its counterpart, phosphorylation, activate and deactivate enzymes by detaching or attaching phosphoric esters and anhydrides. A notable occurrence of dephosphorylation is the conversion of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate.

Heat shock 70 kDa protein 8 also known as heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein or Hsc70 or Hsp73 is a heat shock protein that in humans is encoded by the HSPA8 gene on chromosome 11. As a member of the heat shock protein 70 family and a chaperone protein, it facilitates the proper folding of newly translated and misfolded proteins, as well as stabilize or degrade mutant proteins. Its functions contribute to biological processes including signal transduction, apoptosis, autophagy, protein homeostasis, and cell growth and differentiation. It has been associated with an extensive number of cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, cell senescence, and aging.

Endopeptidase Clp (EC 3.4.21.92, endopeptidase Ti, caseinolytic protease, protease Ti, ATP-dependent Clp protease, ClpP, Clp protease). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The heat shock proteins HslV and HslU are expressed in many bacteria such as E. coli in response to cell stress. The hslV protein is a protease and the hslU protein is an ATPase; the two form a symmetric assembly of four stacked rings, consisting of an hslV dodecamer bound to an hslU hexamer, with a central pore in which the protease and ATPase active sites reside. The hslV protein degrades unneeded or damaged proteins only when in complex with the hslU protein in the ATP-bound state. HslV is thought to resemble the hypothetical ancestor of the proteasome, a large protein complex specialized for regulated degradation of unneeded proteins in eukaryotes, many archaea, and a few bacteria. HslV bears high similarity to core subunits of proteasomes.
Co-chaperones are proteins that assist chaperones in protein folding and other functions. Co-chaperones are the non-client binding molecules that assist in protein folding mediated by Hsp70 and Hsp90. They are particularly essential in stimulation of the ATPase activity of these chaperone proteins. There are a great number of different co-chaperones however based on their domain structure most of them fall into two groups: J-domain proteins and tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR).
Chaperonin ATPase (EC 3.6.4.9, chaperonin) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP phosphohydrolase (polypeptide-unfolding). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

26S protease regulatory subunit 6A, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt5, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC3 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta also called HSP90beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSP90AB1 gene.

Binding immunoglobulin protein (BiPS) also known as 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP-78) or heat shock 70 kDa protein 5 (HSPA5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSPA5 gene.

STUB1 is a human gene that codes for the protein CHIP.

Caseinolytic peptidase B protein homolog (CLPB), also known as Skd3, is a mitochondrial AAA ATPase chaperone that in humans is encoded by the gene CLPB, which encodes an adenosine triphosphate-(ATP) dependent chaperone. Skd3 is localized in mitochondria and widely expressed in human tissues. High expression in adult brain and low expression in granulocyte is found. It is a potent protein disaggregase that chaperones the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Mutations in the CLPB gene could cause autosomal recessive metabolic disorder with intellectual disability/developmental delay, congenital neutropenia, progressive brain atrophy, movement disorder, cataracts, and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria. Recently, heterozygous, dominant negative mutations in CLPB have been identified as a cause of severe congenital neutropenia (SCN).

In molecular biology, chaperone DnaJ, also known as Hsp40, is a molecular chaperone protein. It is expressed in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to humans.

Acyldepsipeptide or cyclic acyldepsipeptide (ADEP) is a class of potential antibiotics first isolated from bacteria and act by deregulating the ClpP protease. Natural ADEPs were originally found as products of aerobic fermentation in Streptomyces hawaiiensis, A54556A and B, and in the culture broth of Streptomyces species, enopeptin A and B. ADEPs are of great interest in drug development due to their antibiotic properties and thus are being modified in attempt to achieve greater antimicrobial activity.

ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit clpX-like, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CLPX gene. This protein is a member of the family of AAA Proteins and is to form the protein complex of Clp protease.
















