A gumma is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis. It is a form of granuloma. Gummas are most commonly found in the liver, but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues, leading to a variety of potential problems including neurological disorders or heart valve disease.

A granuloma is a structure formed during inflammation that is found in many diseases. It is a collection of immune cells known as macrophages. Granulomas form when the immune system attempts to wall off substances it perceives as foreign but is unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as keratin and suture fragments.

Leukoplakia generally refers to a firmly attached white patch on a mucous membrane which is associated with an increased risk of cancer. The edges of the lesion are typically abrupt and the lesion changes with time. Advanced forms may develop red patches. There are generally no other symptoms. It usually occurs within the mouth, although sometimes mucosa in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or genitals may be affected.

A chest radiograph, colloquially called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
Epulis fissuratum is a benign hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue which develops as a reactive lesion to chronic mechanical irritation produced by the flange of a poorly fitting denture. More simply, epulis fissuratum is where excess folds of firm tissue form inside the mouth, as a result of rubbing on the edge of dentures that do not fit well. It is a harmless condition and does not represent oral cancer. Treatment is by simple surgical removal of the lesion, and also by adjustment of the denture or provision of a new denture.
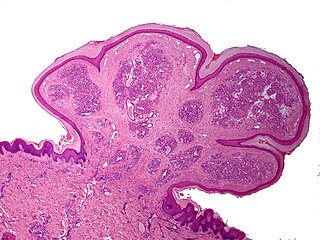
Pyogenic granuloma is a vascular lesion that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, the skin and nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head such as in the thigh.
Peripheral ossifying fibroma “a gingival nodule which is composed of a cellular fibroblastic connective tissue stroma which is associated with the formation of randomly dispersed foci of mineralised products, which consists of bone, cementum-like tissue, or a dystrophic calcification. The lesion is considered part of an ossifying fibroma, but that is usually considered to be a jaw tumor. Because of its overwhelming incidence on the gingiva, the condition is associated with two other diseases, though not because they occur together. Instead, the three are associated with each other because they appear frequently on gingiva: pyogenic granuloma and peripheral giant cell granuloma. Some researchers believe peripheral ossifying fibromas to be related to pyogenic fibromas and, in some instances, are the result of a pyogenic granuloma which has undergone fibrosis and calcification.
Oral medicine is a specialty focused on the mouth and nearby structures. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry.

Granuloma annulare is a fairly rare, chronic skin condition which presents as reddish bumps on the skin arranged in a circle or ring. It can initially occur at any age and is four times more common in females.

Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is a severe bone disease (osteonecrosis) that affects the jaws. Various forms of ONJ have been described over the last 160 years, and a number of causes have been suggested in the literature.
Giant-cell fibroma is a type of fibroma not associated with trauma or irritation. It can occur at any age and on a mucous membrane surface. The most common oral locations are on the gingiva of the mandible, tongue, and palate. It is a localized reactive proliferation of fibrous connective tissue.
Desquamative gingivitis is an erythematous (red), desquamatous (shedding) and ulcerated appearance of the gums. It is a descriptive term and can be caused by several different disorders.

Central giant-cell granuloma (CGCG) is a localised benign condition of the jaws. It is twice as common in females and is more likely to occur before age 30. Central giant-cell granulomas are more common in the anterior mandible, often crossing the midline and causing painless swellings.
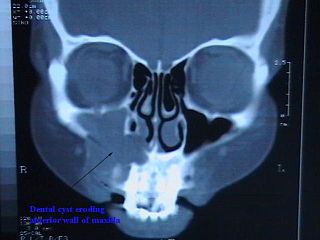
The periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. Periapical is defined as "the tissues surrounding the apex of the root of a tooth" and a cyst is "a pathological cavity lined by epithelium, having fluid or gaseous content that is not created by the accumulation of pus." Most frequently located in the maxillary anterior region, it is caused by pulpal necrosis secondary to dental caries or trauma. The cyst has lining that is derived from the epithelial cell rests of Malassez which proliferate to form the cyst. Highly common in the oral cavity, the periapical cyst is asymptomatic, but highly significant because a secondary infection can cause pain and damage. In radiographs, it appears a radiolucency around the apex of a tooth's root.

Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor on the gingiva.

Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa is a condition characterized by an ulcer with an indurated and elevated border. The lesion might be tender, fast-growing and the patient often not be aware of any trauma in the area.
Epulis is any tumor like enlargement situated on the gingival or alveolar mucosa. The word literally means "(growth) on the gingiva", and describes only the location of the mass and has no further implications on the nature of the lesion. There are three types: fibromatous, ossifying and acanthomatous. The related term parulis refers to a mass of inflamed granulation tissue at the opening of a draining sinus on the alveolus over the root of an infected tooth. Another closely related term is gingival enlargement, which tends to be used where the enlargement is more generalized over the whole gingiva rather than a localized mass.
A cyst is a pathological epithelial lined cavity that fills with fluid or soft material and usually grows from internal pressure generated by fluid being drawn into the cavity from osmosis. The bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla, are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body. This is due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse together, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.

Amalgam tattoo is a grey, blue or black area of discoloration on the mucous membranes of the mouth, typically on the gums of the lower jaw. It is a healthcare caused lesion, is due to entry of dental amalgam into the soft tissues. It is common, painless, and benign, but it can be mistaken for melanoma.