
The Rio Grande in the United States or the Río Bravo in Mexico, also known as P’osoge in Tewa and Tó Ba’áadi in Navajo, is one of the principal rivers in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is 1,896 miles (3,051 km), making it the 4th longest river in the United States and in North America by main stem. It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of 182,200 square miles (472,000 km2); however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to 336,000 square miles (870,000 km2).

Harlingen is a city in Cameron County in the central region of the Rio Grande Valley of the southern part of the U.S. state of Texas, about 30 miles (48 km) from the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. The city covers more than 40 square miles (104 km2) and is the second-largest city in Cameron County, as well as the fourth-largest in the Rio Grande Valley. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 71,892.

Brownsville is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the county seat of Cameron County, located on the western Gulf Coast in South Texas, adjacent to the border with Matamoros, Tamaulipas, Mexico. The city covers 145.2 sq mi (376.066 km2), and had a population of 186,738 at the 2020 census. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, it is the 139th-largest city in the United States and 18th-largest in Texas. It is part of the Matamoros–Brownsville metropolitan area. The city is known for its year-round subtropical climate, deep-water seaport, and Hispanic culture.

South Padre Island is a resort town in Cameron County, Texas, United States. It is part of the Brownsville–Harlingen Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 2,066 at the 2020 census. The town is located on South Padre Island, a barrier island with the Laguna Madre situated to the leeward of the island and the Gulf of Mexico on the windward flank, along the Texas Gulf Coast. South Padre Island is accessible via the Queen Isabella Causeway from the town of Port Isabel. South Padre Island is named after José Nicolás Ballí, a Catholic priest and settler.

The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Massachusetts southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals. It provides a navigable route along its length without many of the hazards of travel on the open sea.

The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW) is the portion of the Intracoastal Waterway located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1,300 mi (2,100 km) from Saint Marks, Florida, to Brownsville, Texas.

South Texas is a geographic and cultural region of the U.S. state of Texas that lies roughly south of—and includes—San Antonio. The southern and western boundary is the Rio Grande, and to the east it is the Gulf of Mexico. The population of this region is more than 5 million according to the 2024 census estimates. The southern portion of this region is often referred to as the Rio Grande Valley. The eastern portion along the Gulf of Mexico is also referred to as the Coastal Bend.

The Texas Mexican Railway was a short line railroad in the U.S. state of Texas operating between Corpus Christi and the Texas Mexican Railway International Bridge in Laredo, Texas. It is often referred to as the Tex Mex, or Tex Mex Railway.

The Houston Ship Channel, in Houston, Texas, is part of the Port of Houston, one of the busiest seaports in the world. The channel is the conduit for ocean-going vessels between Houston-area terminals and the Gulf of Mexico, and it serves an increasing volume of inland barge traffic.

The Port of Beaumont is a deep-water port located in Beaumont, Texas near the mouth of the Neches River.

South Bay is a bay in the Laguna Madre in Texas separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Brazos Island. It is the southernmost bay in Texas, about 1 mi (1.6 km) north of the Texas-Mexico Border.
Port Freeport is the geographically smallest deep-water seaport along the U.S Gulf Coast. Located in Freeport, Texas , it has rail access, and both private and public facilities. It is ranked 10th in the nation for chemicals, 19th in the nation for total tonnage, 26th in the nation for container traffic, and handles over 100,000 vehicles per year and more than 1,000 ships per year. Forbes magazine (2017) ranked Port Freeport as one of the top 10 fastest growing seaports for exports in the U.S.
Chartered on June 6, 1903, the St. Louis, Brownsville & Mexico Railway was a 200-mile (321 km) U.S. railroad that operated from Brownsville, Texas, to Gulf Coast Junction in Houston, Texas. It served numerous towns and cities along its routes and operated a rail bridge between Brownsville and Matamoros, Tamaulipas, in junction with the Mexican government. The Brownie connected the citizens of Brownsville to nearby Corpus Christi for the first time on land rather than using water transportation.
The Port of Corpus Christi is the third-largest port in the United States in total waterborne tonnage, largest crude oil export gateway in the nation, second in the United States in LNG exports and the third-largest gateway in the world for crude oil exports. The Port of Corpus Christi is located on Corpus Christi Bay in the western Gulf of Mexico, with a 36-mile channel that is being widened and deepened to 54 feet MLLW from its current depth of 45 feet.
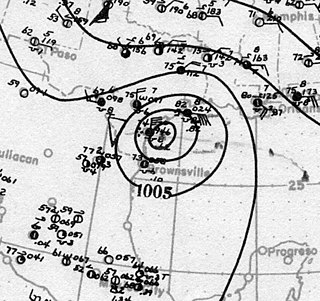
The effects of the 1919 Florida Keys hurricane in Texas were the deadliest of any tropical cyclone in the Texas Coastal Bend, killing at least 284 people. The hurricane produced a widespread swath of devastation across the region, exacerbated by the large extent of its winds. The city of Corpus Christi bore the brunt of the hurricane's impacts, contributing to the largest portion of the damage toll in Texas; nearly all of the confirmed fatalities were residents of the city. The storm originated from the Leeward Islands early in September 1919 and took a generally west-northwestward course, devastating the Florida Keys en route to the Gulf of Mexico. On the afternoon of September 14, the center of the hurricane made landfall upon the Texas coast at Baffin Bay. The storm's winds were estimated at 115 mph (185 km/h) at landfall, making it a Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. After slowly moving ashore, it weakened and straddled the Rio Grande before dissipating on September 16 over West Texas.

The U.S. state of Texas has a series of estuaries along its coast on the Gulf of Mexico, most of them bounded by the Texas barrier islands. Estuaries are coastal bodies of water in which freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the sea. Twenty-one drainage basins terminate along the Texas coastline, forming a chain of seven major and five minor estuaries: listed from southwest to northeast, these are the Rio Grande Estuary, Laguna Madre, the Nueces Estuary, the Mission–Aransas Estuary, the Guadalupe Estuary, the Colorado–Lavaca Estuary, East Matagorda Bay, the San Bernard River and Cedar Lakes Estuary, the Brazos River Estuary, Christmas Bay, the Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary, and the Sabine–Neches Estuary. Each estuary is named for its one or two chief contributing rivers, excepting Laguna Madre, East Matagorda Bay, and Christmas Bay, which have no major river sources. The estuaries are also sometimes referred to by the names of their respective primary or central water bodies, though each also includes smaller secondary bays, inlets, or other marginal water bodies.
Boca Chica is an area on the eastern portion of a subdelta peninsula of Cameron County, at the far south of the US State of Texas along the Gulf Coast. It is bordered by the Brownsville Ship Channel to the north, the Rio Grande and Mexico to the south, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. The area extends about 25 miles (40 km) east of the city of Brownsville. The peninsula is served by Texas State Highway 4—also known as the Boca Chica Highway, or Boca Chica Boulevard within Brownsville city limits—which runs east–west, terminating at the Gulf and Boca Chica Beach.

Port Mansfield Channel or Mansfield Cut is an artificial waterway encompassing the Laguna Madre positioned at the 97th meridian west on the earth's longest barrier island known as Padre Island. During Post–World War II, the tidal inlet was dredged as a private channel differentiating North Padre Island better known as Padre Island National Seashore and South Padre Island. The navigable waterway was channeled during the late 1950s ceremoniously cresting the intertidal zone of the Gulf of Mexico by September 1957 on the Texas Gulf Coast.

Brazos Santiago Pass is a natural coastal landform located in the Lower Laguna Madre and Lower Rio Grande Valley on the furthest southern beach terrain of the Texas Gulf Coast. The seacoast passage is interpolated by barrier islands encompassing the southern Brazos Island and the northern South Padre Island.
















