The Time from NPL is a radio signal broadcast from the Anthorn Radio Station near Anthorn, Cumbria, which serves as the United Kingdom's national time reference. The time signal is derived from three atomic clocks installed at the transmitter site, and is based on time standards maintained by the UK's National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in Teddington. The service is provided by Babcock International, under contract to the NPL. It was funded by the former Department for Business, Innovation and Skills; as of 2017 NPL Management Limited (NPLML) was owned by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS), and NPL operated as a public corporation.
The Greenwich Time Signal (GTS), popularly known as the pips, is a series of six short tones broadcast at one-second intervals by many BBC Radio stations. The pips were introduced in 1924 and have been generated by the BBC since 1990 to mark the precise start of each hour. Their utility in calibration is diminishing as digital broadcasting entails time lags.

WWV is a shortwave radio station, located near Fort Collins, Colorado. It has broadcast a continuous time signal since 1945, and implements United States government frequency standards, with transmitters operating on 2.5, 5, 10, 15, and 20 MHz. WWV is operated by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), under the oversight of its Time and Frequency Division, which is part of NIST's Physical Measurement Laboratory based in Gaithersburg, Maryland.
WWVB is a time signal radio station near Fort Collins, Colorado and is operated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Most radio-controlled clocks in North America use WWVB's transmissions to set the correct time. The 70 kW ERP signal transmitted from WWVB is a continuous 60 kHz carrier wave, the frequency of which is derived from a set of atomic clocks located at the transmitter site, yielding a frequency uncertainty of less than 1 part in 1012. A one-bit-per-second time code, which is based on the IRIG "H" time code format and derived from the same set of atomic clocks, is then modulated onto the carrier wave using pulse-width modulation and amplitude-shift keying. A single complete frame of time code begins at the start of each minute, lasts one minute, and conveys the year, day of year, hour, minute, and other information as of the beginning of the minute.
RWM is the callsign of a high frequency (shortwave) standard frequency and time signal radio station in Moscow, Russia. It is controlled by All-Russian Scientific Research Institute for Physical-Engineering and Radiotechnical Metrology, and operated by Russian Television and Radio Broadcasting Network. Transmitting frequencies are 4.996 MHz with 5 kW and on 9.996 and 14.996 MHz with 8 kW.

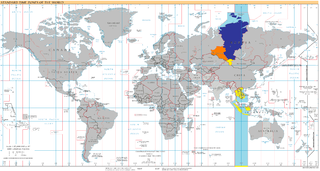
Moscow Time is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011.

DUT1 is a time correction equal to the difference between Universal Time (UT1), which is defined by Earth's rotation, and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is defined by a network of precision atomic clocks.

UTC+08:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +08:00.
UTC+07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +07:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2023-11-25T05:07:55+07:00. It is 7 hours ahead of UTC, meaning that when the time in UTC areas is midnight (00:00), the time in UTC+07:00 areas would be 7:00 in the morning.

Radio Poland is the official international broadcasting station of Poland and is a part of Poland’s public radio network, Polish Radio.

Voice of Korea is the international broadcasting service of North Korea. It broadcasts primarily information in Chinese, Spanish, German, English, French, Russian, Japanese and Arabic. Until 2002 it was known as Radio Pyongyang. The interval signal is identical to that of Korean Central Television.

There are eleven time zones in Russia, which currently observe times ranging from UTC+02:00 to UTC+12:00. Daylight saving time (DST) has not been used in Russia since 26 October 2014. From 27 March 2011 to 26 October 2014, permanent DST was used.

Irkutsk Time (IRKT) is the time zone eight hours ahead of UTC (UTC+08:00) and 5 hours ahead of Moscow Time (MSK+5).

Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time at 0° longitude and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
RBU is a time code radio station located in Moscow. It transmits a continuous 10 kW time code on 66⅔ kHz. This is commonly written as 66.66 or 66.666 kHz, but is actually 200/3 kHz. Until 2008, the transmitter site was near Kupavna 55°44′04″N38°9′0″E and used as antenna three T-antennas spun between three 150 metres tall grounded masts. In 2008, it has been transferred to the Taldom transmitter at 56°44′00″N37°39′48″E.
BPC is the callsign of a time signal broadcasting from the BPC Shangqiu Low-Frequency Time-Code Radio Station, cooperatively constructed by the National Time Service Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Xi’an Gaohua Technology Co., Ltd., beginning April 25, 2002.
JN53dv is the Maidenhead grid square of an experimental shortwave time signal station in Italy. It is located in the town of Corsanico-Bargecchia near Massarosa and operated by Italcable

The 2014 Bandy World Championship was held between 26 January and 2 February 2014, in Irkutsk and Shelekhov, Russia. 17 nations participated in the tournament, playing in two divisions partitioned into two subdivisions. A team representing Somalia took part, the first squad from Africa to play in the Bandy World Championship.

All-Russian Scientific Research Institute for Physical-Engineering and Radiotechnical Metrology was founded in 1955. It is located in the settlement of Mendeleyevo of Solnechnogorsky District, Moscow Oblast, Russia, and also it includes West-Siberian, East-Siberian, Far-Eastern and Kamchatka branches.











