An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships, gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons.

The Tesla turbine is a bladeless centripetal flow turbine invented by Nikola Tesla in 1913. It functions as nozzles apply a moving fluid to the edges of a set of discs. The engine uses smooth discs rotating in a chamber to generate rotational movement due to the momentum exchange between the fluid and the discs. The discs are arranged in an orientation similar to a stack of CDs on a pole.

An autogyro, or gyroplane, is a class of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift. While similar to a helicopter rotor in appearance, the autogyro's unpowered rotor disc must have air flowing upward across it to make it rotate.

A tiltrotor is an aircraft that generates lift and propulsion by way of one or more powered rotors mounted on rotating shafts or nacelles usually at the ends of a fixed wing. Almost all tiltrotors use a transverse rotor design, with a few exceptions that use other multirotor layouts.

A model aircraft is a physical model of an existing or imagined aircraft, and is built typically for display, research, or amusement. Model aircraft are divided into two basic groups: flying and non-flying. Non-flying models are also termed static, display, or shelf models.

An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.

Wingtip devices are intended to improve the efficiency of fixed-wing aircraft by reducing drag. Although there are several types of wing tip devices which function in different manners, their intended effect is always to reduce an aircraft's drag. Wingtip devices can also improve aircraft handling characteristics and enhance safety for following aircraft. Such devices increase the effective aspect ratio of a wing without greatly increasing the wingspan. Extending the span would lower lift-induced drag, but would increase parasitic drag and would require boosting the strength and weight of the wing. At some point, there is no net benefit from further increased span. There may also be operational considerations that limit the allowable wingspan.
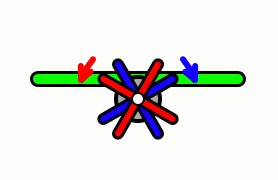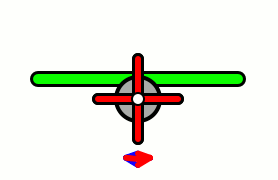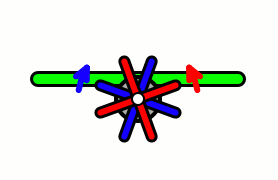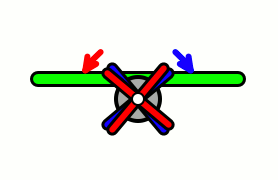
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers (CRP) coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston engine or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propellers in contra-rotation. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via a planetary gear or spur gear transmission. Contra-rotating propellers are also known as counter-rotating propellers, although the term counter-rotating propellers is much more widely used when referring to airscrews on separate non-coaxial shafts turning in opposite directions.

A hybrid airship is a powered aircraft that obtains some of its lift as a lighter-than-air (LTA) airship and some from aerodynamic lift as a heavier-than-air aerodyne.

A coaxial-rotor aircraft is an aircraft whose rotors are mounted one above the other on concentric shafts, with the same axis of rotation, but turning in opposite directions (contra-rotating).
A jet engine performs by converting fuel into thrust. How well it performs is an indication of what proportion of its fuel goes to waste. It transfers heat from burning fuel to air passing through the engine. In doing so it produces thrust work when propelling a vehicle but a lot of the fuel is wasted and only appears as heat. Propulsion engineers aim to minimize the degradation of fuel energy into unusable thermal energy. Increased emphasis on performance improvements for commercial airliners came in the 1970s from the rising cost of fuel.

A quadcopter, also called quadrocopter, or quadrotor is a type of helicopter or multicopter that has four rotors.

A rotorcraft or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings or rotor blades, which generate lift by rotating around a vertical mast. Several rotor blades mounted on a single mast are referred to as a rotor. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines a rotorcraft as "supported in flight by the reactions of the air on one or more rotors".
A convertiplane is defined by the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale as an aircraft which uses rotor power for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and converts to fixed-wing lift in normal flight. In the US it is further classified as a sub-type of powered lift. In popular usage it sometimes includes any aircraft that converts in flight to change its method of obtaining lift.

In aeronautics, an aircraft propeller, also called an airscrew, converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type.

A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway.

Unconventional wind turbines are those that differ significantly from the most common types in use.

The Kline–Fogleman airfoil or KF airfoil is a simple airfoil design with single or multiple steps along the length of the wing. It was originally devised in the 1960s for paper airplanes.

A multirotor or multicopter is a rotorcraft with more than two lift-generating rotors. An advantage of multirotor aircraft is the simpler rotor mechanics required for flight control. Unlike single- and double-rotor helicopters which use complex variable pitch rotors whose pitch varies as the blade rotates for flight stability and control, multirotors often use fixed-pitch blades; control of vehicle motion is achieved by varying the relative speed of each rotor to change the thrust and torque produced by each.

A cyclorotor, cycloidal rotor, cycloidal propeller or cyclogiro, is a fluid propulsion device that converts shaft power into the acceleration of a fluid using a rotating axis perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. It uses several blades with a spanwise axis parallel to the axis of rotation and perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. These blades are cyclically pitched twice per revolution to produce force in any direction normal to the axis of rotation. Cyclorotors are used for propulsion, lift, and control on air and water vehicles. An aircraft using cyclorotors as the primary source of lift, propulsion, and control is known as a cyclogyro or cyclocopter. A unique aspect is that it can change the magnitude and direction of thrust without the need of tilting any aircraft structures. The patented application, used on ships with particular actuation mechanisms both mechanical or hydraulic, is named after German company Voith Turbo.