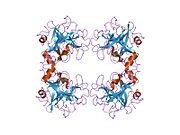
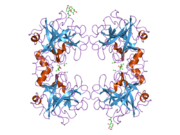
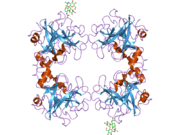
Tryptase is the most abundant secretory granule-derived serine proteinase contained in mast cells and has been used as a marker for mast cell activation. Club cells contain tryptase, which is believed to be responsible for cleaving the hemagglutinin surface protein of influenza A virus, thereby activating it and causing the symptoms of flu.

Interleukin 9, also known as IL-9, is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the group of interleukins. IL-9 is produced by variety of cells like mast cells, NKT cells, Th2, Th17, Treg, ILC2, and Th9 cells in different amounts. Among them, Th9 cells are regarded as the major CD4+ T cells that produce IL-9.

Granzyme A is an enzyme. that in humans is encoded by the GZMA gene, and is one of the five granzymes encoded in the human genome. This enzyme is present in cytotoxic T lymphocyte granules.

CD1D is the human gene that encodes the protein CD1d, a member of the CD1 family of glycoproteins expressed on the surface of various human antigen-presenting cells. They are non-classical MHC proteins, related to the class I MHC proteins, and are involved in the presentation of lipid antigens to T cells. CD1d is the only member of the group 2 CD1 molecules.
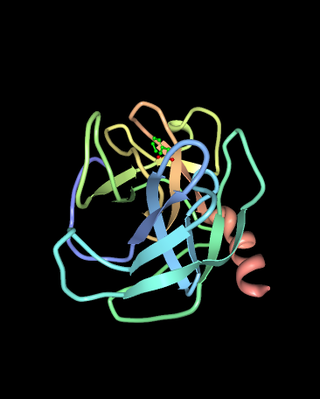
Chymases are a family of serine proteases found primarily in mast cells, though also present in basophil granulocytes. Recently, Derakhshan et al. reported that a specific mast cell population expressed trascripts for Mcpt8. They show broad peptidolytic activity and are involved in a variety of functions. For example, chymases are released by connective tissue-type mast cells upon challenge with parasites and parasite antigens promoting an inflammatory response, and chymase mcp1 and mcp2 are used for marker for mast cell degranulation in parasite infection such as Nematode, Trichuris muris Chymases are also known to convert angiotensin I to angiotensin II and thus play a role in hypertension and atherosclerosis.

Chymase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CMA1 gene.

Tryptase alpha-1 and tryptase beta-1 are enzymes that in humans are encoded by the same TPSAB1 gene. Beta tryptases appear to be the main isoenzymes expressed in mast cells; whereas in basophils, alpha tryptases predominate.

Protease activated receptor 2 (PAR2) also known as coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 1 (F2RL1) or G-protein coupled receptor 11 (GPR11) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the F2RL1 gene. PAR2 modulates inflammatory responses, obesity, metabolism, cancers and acts as a sensor for proteolytic enzymes generated during infection. In humans, we can find PAR2 in the stratum granulosum layer of epidermal keratinocytes. Functional PAR2 is also expressed by several immune cells such as eosinophils, neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells and T cells.

CD3e molecule, epsilon also known as CD3E is a polypeptide which in humans is encoded by the CD3E gene which resides on chromosome 11.
Kallikrein-5, formerly known as stratum corneum tryptic enzyme (SCTE), is a serine protease expressed in the epidermis. In humans it is encoded by the KLK5 gene. This gene is one of the fifteen kallikrein subfamily members located in a cluster on chromosome 19. Its expression is up-regulated by estrogens and progestins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein.

Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KLK4 gene.

Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 is a immunoglobulin gene with symbol IGHA1. It encodes a constant (C) segment of Immunoglobulin A heavy chain. Immunoglobulin A is an antibody that plays a critical role in immune function in the mucous membranes. IgA shows the same typical structure of other antibody classes, with two heavy chains and two light chains, and four distinct domains: one variable region, and three variable regions. As a major class of immunoglobulin in body secretions, IgA plays a role in defending against infection, as well as preventing the access of foreign antigens to the immunologic system.

Serpin B6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINB6 gene.

Prostasin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS8 gene.

Granzyme H is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GZMH gene.

Granzyme K (GrK) is a protein that is encoded by the GZMK gene on chromosome 5 in humans. Granzymes are a family of serine proteases which have various intracellular and extracellular roles. GrK is found in granules of natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), and is traditionally described as cytotoxic towards targeted foreign, infected, or cancerous cells. NK cells and CTLs can induce apoptosis through the granule secretory pathway, which involves the secretion of granzymes along with perforin at immunological synapses.

Carboxypeptidase A3 (mast cell carboxypeptidase A), also known as CPA3, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the CPA3 gene. The "CPA3" gene expression has only been detected in mast cells and mast-cell-like lines, and CPA3 is located in secretory granules. CPA3 is one of 8-9 members of the A/B subfamily that includes the well-studied pancreatic enzymes carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1), carboxypeptidase A2 (CPA2), and carboxypeptidase B. This subfamily includes 6 carboxypeptidase A-like enzymes, numbered 1-6. The enzyme now called CPA3 was originally named mast cell carboxypeptidase A, and another protein was initially called CPA3. A gene nomenclature committee renamed mast cell carboxypeptidase A as CPA3, and the original CPA3 reported by Huang et al. became CPA4 to reflect the order of their discovery.

Tryptase delta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TPSD1 gene.

Tryptase gamma, also known as serine protease 31 or transmembrane tryptase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TPSG1 gene.

Brain-specific serine protease 4 (BSSP-4), also known as serine protease 22 or tryptase epsilon, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRSS22 gene.