Voting Results
The result of the voting was the following: [1]
| UN General Assembly Resolution 1631 | |
|---|---|
| Date | October 27 1961 |
| Code | A/RES/1631 |
| Subject | Admission of Mauritania to the United Nations |
Voting summary |
|
| Result | Adopted |
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1631 was adopted on October 27, 1961 to admit Mauritania to membership in the United Nations.
The resolution was adopted by a majority of 68 members with 13 opposing, 20 abstaining and Cyprus didn't vote.
The result of the voting was the following: [1]

The United Nations General Assembly is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its 78th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter.

A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, adopted on 10 November 1975, "Determines that Zionism is a form of racism and racial discrimination" with 72 votes in favour, 35 votes against, and 32 abstentions. It was revoked by Resolution 46/86, adopted on 16 December 1991 with 111 votes in favour, 25 votes against, and 13 abstentions. The vote for Resolution 3379 was held nearly one year after the adoption of Resolution 3236 and Resolution 3237: the former recognized the "Question of Palestine" and invited the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) to participate in international diplomacy; and the latter designated the PLO as a non-member Assembly observer following the "Olive Branch Speech" by Palestinian political leader Yasser Arafat.

United Nations Security Council resolution 497, adopted unanimously on 17 December 1981, declared that the Israeli Golan Heights Law, which effectively annexed the Golan Heights, is "null and void and without international legal effect" and further calls on Israel to rescind its action.

Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter defines a non-self-governing territory (NSGT) as a territory "whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government". In practice, an NSGT is a territory deemed by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) to be "non-self-governing". Chapter XI of the UN Charter also includes a "Declaration on Non-Self-Governing Territories" that the interests of the occupants of dependent territories are paramount and requires member states of the United Nations in control of such territories to submit annual information reports concerning the development of those territories. Since 1946, the UNGA has maintained a list of non-self governing territories under member states' control. Since its inception, dozens of territories have been removed from the list, typically when they attained independence or internal self-government, while other territories have been added as new administering countries joined the United Nations or the General Assembly reassessed the status of certain territories.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 339 was adopted on 23 October 1973 in order to bring a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War where Resolution 338 two days before had failed.
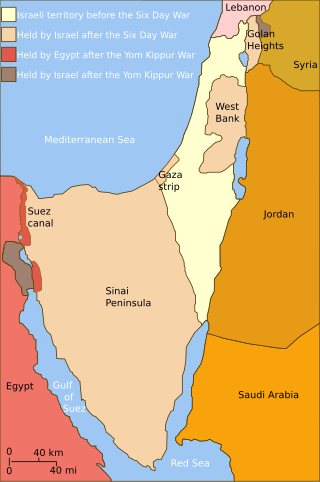
United Nations Security Council Resolution 350, adopted on 31 May 1974, established the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force, to monitor the ceasefire between Israel and Syria in the wake of the Yom Kippur War. UNDOF was initially established for a period of six months, but has had its mandate renewed by subsequent resolutions.

At Italy's instigation, a resolution for a moratorium on the death penalty was presented by the European Union in partnership with eight co-author member States to the General Assembly of the United Nations, calling for general suspension of capital punishment throughout the world. It was approved on 15 November 2007 by the Third Committee, and then subsequently adopted on 18 December by the United Nations General Assembly resolution 62/149. New Zealand played a central role facilitating agreement between the co-author group and other supporters.
Israel – Micronesia relations are diplomatic and other relations between the State of Israel and the Federated States of Micronesia. Israel was among the first countries to establish formal diplomatic relations with Micronesia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1631, adopted unanimously on 17 October 2005, after recalling Chapter VIII of the United Nations Charter, the council addressed co-operation between the United Nations and regional organisations in the maintenance of international peace and security.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1653, adopted unanimously on January 27, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions concerning the situations in the African Great Lakes region, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Burundi, particularly resolutions 1625 (2005), 1631 (2005), 1649 (2005) and 1650 (2005), the Council addressed the stability of the Great Lakes region in Africa.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2016 was unanimously adopted on 27 October 2011 on the situation of Libya during the Libyan Civil War.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution 68/262 was adopted on 27 March 2014 by the sixty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly in response to the Russian annexation of Crimea and entitled "territorial integrity of Ukraine". The nonbinding resolution, which was supported by 100 United Nations member states, affirmed the General Assembly's commitment to the territorial integrity of Ukraine within its internationally recognized borders and underscored the invalidity of the 2014 Crimean referendum. Eleven nations voted against the resolution, while 58 abstained, and a further 24 states were absent when the vote took place.

The eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly opened on 28 February 2022 at the United Nations headquarters. It addresses the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Maldivian politician Abdulla Shahid served as President of the body during this time.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2623 called for the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly on the subject of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Albania and the United States introduced the resolution before the United Nations Security Council, which adopted it on 27 February 2022. Russia voted against while China, India and the United Arab Emirates abstained. As this was a procedural resolution, no permanent member could exercise their veto power.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/1 is a resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 2 March 2022. It deplored Russia's invasion of Ukraine and demanded a full withdrawal of Russian forces and a reversal of its decision to recognise the self-declared People's Republics of Donetsk and Luhansk.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/3 is a resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 7 April 2022. The resolution suspended the membership of Russia in the United Nations Human Rights Council over "grave concern at the ongoing human rights and humanitarian crisis in Ukraine [...] including gross and systematic violations and abuses of human rights" committed by Russia, and was passed with 93 votes in favour, 24 against, and 58 abstentions.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/4 is the fourth resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 12 October 2022, following Resolution ES-11/3 which was adopted on 7 April 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)