
The Indigenous languages of Australia number in the hundreds, the precise number being quite uncertain, although there is a range of estimates from a minimum of around 250 up to possibly 363. The Indigenous languages of Australia comprise numerous language families and isolates, perhaps as many as 13, spoken by the Indigenous peoples of mainland Australia and a few nearby islands. The relationships between the language families are not clear at present although there are proposals to link some into larger groupings. Despite this uncertainty, the Indigenous Australian languages are collectively covered by the technical term "Australian languages", or the "Australian family".

Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands.
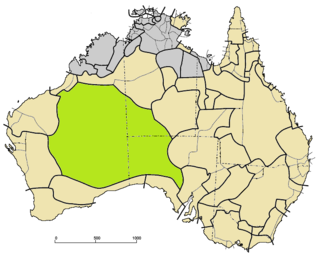
The Western Desert language, or Wati, is a dialect cluster of Australian Aboriginal languages in the Pama–Nyungan family.

The Iwaidjan or Yiwaidjan languages are a small family of non-Pama–Nyungan Australian Aboriginal languages spoken in the Cobourg Peninsula region of Western Arnhem Land.

The Adnyamathanha language, also known as yura ngarwala natively and Kuyani, also known as Guyani and other variants, are two closely related Australian Aboriginal languages. They are traditional languages of the Adnyamathanha of and the Kuyani peoples, of the Flinders Ranges and to the west of the Flinders respectively, in South Australia.
Pitta Pitta is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language. It was spoken around Boulia, Queensland.

The Shire of Cook is a local government area in Far North Queensland, Australia. The Shire covers most of the eastern and central parts of Cape York Peninsula, the most northerly section of the Australian mainland.
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, and/or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of present day Australia prior to British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups, which include many ethnic groups: the Aboriginal Australians of the mainland and many islands, including Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islanders of the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea, located in Melanesia.
Bidjara, also spelt Bidyara or Pitjara, is an Australian Aboriginal language. In 1980, it was spoken by 20 elders in Queensland between the towns of Tambo and Augathella, or the Warrego and Langlo Rivers. There are many dialects of the language, including Gayiri and Gunggari. Some of them are being revitalised and are being taught in local schools in the region. The various dialects are not all confirmed or agreed by linguists.
Aboriginal Australian kinship comprises the systems of Aboriginal customary law governing social interaction relating to kinship in traditional Aboriginal cultures. It is an integral part of the culture of every Aboriginal group across Australia, and particularly important with regard to marriages between Aboriginal people.

The Paakantyi language, also spelt Paakantji, Barkindji, Barkandji, and Baagandji, and is also known as the Darling language, is a nearly extinct Australian Aboriginal language spoken along the Darling River in New South Wales from the present-day Queensland border to Bourke, then along the river to Wentworth. It includes much of the backcountry around the Paroo River, plus an area along Coopers Creek into Queensland and also through the Broken Hill district.

Marrgu (Marrku) is an extinct Aboriginal language of northern Australia. Additional names include Ajokoot, Croker Island, Raffles Bay, Terrutong (Terutong), Yaako.

Worrorra, also written Worora and other variants, and also known as Western Worrorran, is a moribund Australian Aboriginal language of northern Western Australia. It encompasses a number of dialects, which are spoken by a group of people known as the Worrorra people.
Mbariman-Gudhinma, one of several languages labelled Gugu Warra 'unintelligible speech' as opposed to Gugu Mini 'intelligible speech', is an extinct dialect cluster of Aboriginal Australian languages of the Cape York Peninsula in northern Queensland, Australia. Another one in the group is Wurangung, also known as Yadaneru or Jeteneru.
Mbara, and Yanga are mutually intelligible but separate Aboriginal language of Queensland, both now extinct. Glottolog assigns a code to a group level as Mbara-Yanga (mbar1254). Yanga is not to be confused with the Yangga language, a dialect of Biri.
Biri, also known as Biria, Birri Gubba, Birigaba, Wiri, Perembba and other variants, is an Australian Aboriginal language of the Mackay area of Queensland spoken by the Birri Gubba people. There are at least eight languages regarded as dialects of Biri, and two which are related but whose status is not yet fully determined. All are covered in this article.
The Morrobolam language, formerly known as Morrobalama and Umbuygamu, is a possibly extinct Paman language from Princess Charlotte Bay in far-north Queensland in Australia which was spoken by a group the Lamalama people.
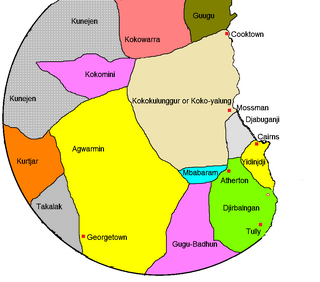
Wamin, also known as Agwamin or Ewamian, is an Australian Aboriginal language of North Queensland spoken by the Ewamian people. Wamin was traditionally spoken in the Etheridge region, in the areas around Einasliegh, Georgetown, and Mount Surprise.
The Marrku–Wurrugu languages are a possible language family of Australian Aboriginal languages spoken in the Cobourg Peninsula region of Western Arnhem Land. They are the extinct Marrgu and Wurrugu languages. They were once classified as distant relatives of the Iwaidjan languages, until Nicholas Evans found the evidence for Marrgu's membership insufficient, concluding that similarities were due to borrowing.
The Wurango or Wurrugu are an indigenous Australian people of the Northern Territory.










