
Glucose 6-phosphate is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way.
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycle, in the liver, and also activated by insulin in response to high glucose levels.

Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is a nucleotide diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.
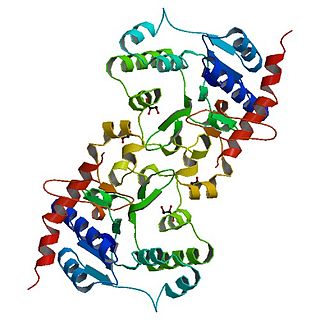
Glycogenin is an enzyme involved in converting glucose to glycogen. It acts as a primer, by polymerizing the first few glucose molecules, after which other enzymes take over. It is a homodimer of 37-kDa subunits and is classified as a glycosyltransferase.
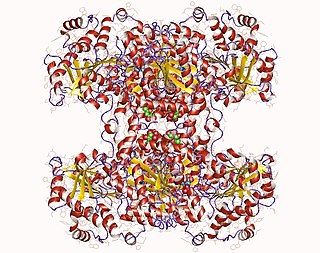
Glycogen synthase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and n to yield UDP and n+1.
1,3-Beta-glucan synthase is a glucosyltransferase enzyme involved in the generation of beta-glucan in fungi. It serves as a pharmacological target for antifungal drugs such as caspofungin, anidulafungin, and micafungin, deemed 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase inhibitors. Under the CAZy classification system, fungi and plant members fall in the glycosyltransferase 48 family (GT48). Some members of the glycosyltransferase 2 family, such as the curdlan synthase CrdS, also has a similar activity.
In enzymology, an alpha-1,3-glucan synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-1,4-glucan-protein synthase (ADP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diglucosyl diacylglycerol synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hydroquinone glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indole-3-acetate beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a linamarin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methyl-ONN-azoxymethanol beta-D-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a starch synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sucrose-phosphate synthase (SPS) is a plant enzyme involved in sucrose biosynthesis. Specifically, this enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a hexosyl group from uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) to D-fructose 6-phosphate to form UDP and D-sucrose-6-phosphate. This reversible step acts as the key regulatory control point in sucrose biosynthesis, and is an excellent example of various key enzyme regulation strategies such as allosteric control and reversible phosphorylation.

In enzymology, a sucrose synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Alpha,alpha-trehalose synthase is an enzyme with systematic name ADP-glucose:D-glucose 1-alpha-D-glucosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







