
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.

HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia.
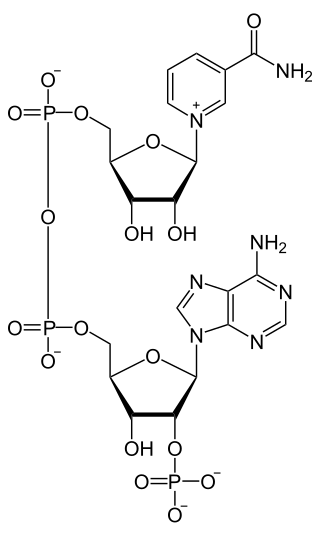
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP+ or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+, the oxidized form. NADP+ is used by all forms of cellular life.

Glutathione reductase (GR) also known as glutathione-disulfide reductase (GSR) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSR gene. Glutathione reductase catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to the sulfhydryl form glutathione (GSH), which is a critical molecule in resisting oxidative stress and maintaining the reducing environment of the cell. Glutathione reductase functions as dimeric disulfide oxidoreductase and utilizes an FAD prosthetic group and NADPH to reduce one molar equivalent of GSSG to two molar equivalents of GSH:

In enzymology, aldose reductase is a cytosolic NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase that catalyzes the reduction of a variety of aldehydes and carbonyls, including monosaccharides. It is primarily known for catalyzing the reduction of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism.
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase is an enzyme (EC 4.1.3.4 that in human is encoded by the HMGCL gene located on chromosome 1. It is a key enzyme in ketogenesis. It is a ketogenic enzyme in the liver that catalyzes the formation of acetoacetate from HMG-CoA within the mitochondria. It also plays a prominent role in the catabolism of the amino acid leucine.

Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion pathway, it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA as a product or as a reactant.
GMP reductase EC 1.7.1.7 is an enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible and NADPH-dependent reductive deamination of GMP into IMP.
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
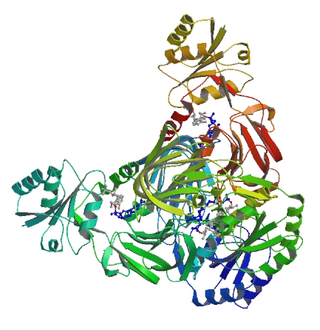
NAD+ kinase (EC 2.7.1.23, NADK) is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) into NADP+ through phosphorylating the NAD+ coenzyme. NADP+ is an essential coenzyme that is reduced to NADPH primarily by the pentose phosphate pathway to provide reducing power in biosynthetic processes such as fatty acid biosynthesis and nucleotide synthesis. The structure of the NADK from the archaean Archaeoglobus fulgidus has been determined.
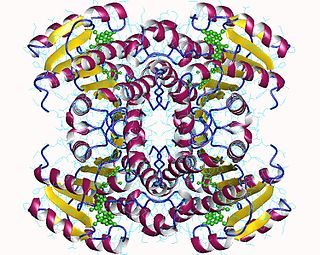
In enzymology, a carbonyl reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.184) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.34) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.3.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH, B-specific) (EC 1.3.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase (EC 1.2.1.38) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CoA-glutathione reductase (EC 1.8.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
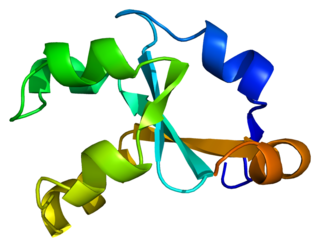
Cytochrome b5, form A, is a human microsomal cytochrome b5.
In enzymology, a dephospho-[reductase kinase] kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme with systematic name short-chain acyl-CoA:electron-transfer flavoprotein 2,3-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
















