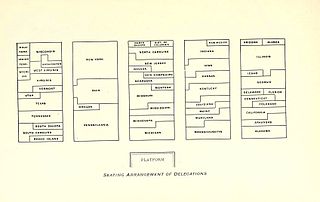
The 1896 Democratic National Convention, held at the Chicago Coliseum from July 7 to July 11, was the scene of William Jennings Bryan's nomination as the Democratic presidential candidate for the 1896 U.S. presidential election.

The 1896–97 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1896 and 1897, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.
"As Maine goes, so goes the nation" was once a maxim in United States politics. The phrase described Maine's reputation as a bellwether state for presidential elections. Maine's September election of a governor predicted the party outcome of the November presidential election in 23 out of the 29 presidential election years from 1820 to 1932: namely 1820–1844, 1852, 1860–1880, 1888, 1896–1908 and 1920–1932; more importantly, as Maine was a generally Republican-leaning state, the margin of the September elections compared to expectations could predict national November results more than the identity of the winning party in Maine. A contest still won by the Republicans but with a narrower margin than usual would still predict good Democratic results nationally.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Connecticut took place on November 8, 1988, as part of the 1988 United States presidential election, which was held throughout all 50 states and D.C. Voters chose eight representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1896 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1896. Incumbent Republican Governor Charles H. Sheldon declined to run for re-election to a third term. Former Secretary of State Amund O. Ringsrud was nominated as Sheldon's replacement at the Republican convention. Ringrud's main opponent was businessman Andrew E. Lee, who was nominated by a makeshift coalition of Populists, Free Silver Republicans, and Democrats. In the general election, Lee narrowly defeated Ringsrud, the first defeat for the Republican Party in a gubernatorial election since statehood.

The 1976 United States presidential election in Virginia took place on November 2, 1976. All 50 states and the District of Columbia were part of the 1976 United States presidential election. Virginia voters chose twelve electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president of the United States.
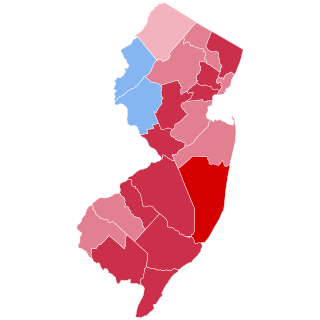
The 1896 United States presidential election in New Jersey took place on November 3, 1896. Voters chose 10 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1896 United States presidential election in Maryland took place on November 3, 1896. All contemporary 45 states were part of the 1896 United States presidential election. States voters chose eight electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

In the Chicago mayoral election of 1897, Democratic nominee Carter Harrison Jr. was elected, winning a majority of the vote and defeating independent Republican John Maynard Harlan, Republican nominee Nathaniel C. Sears, independent Democrat Washington Hesing, as well as several minor candidates. Harrison carried a 26.7 point lead over second-place finisher Harlan, a margin greater than Harlan's vote share itself.

The 1872 United States presidential election in Maryland took place on November 5, 1872. All contemporary 37 states were part of the 1872 United States presidential election. The state voters chose eight electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 1894 New Hampshire gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1894. Republican nominee Charles A. Busiel defeated Democratic nominee Henry O. Kent with 55.98% of the vote.

The 1896 Rhode Island gubernatorial election was held on April 1, 1896. Incumbent Republican Charles W. Lippitt defeated Democratic nominee George L. Littlefield with 56.40% of the vote.

The 1885 Rhode Island gubernatorial election was held on April 1, 1885. Republican nominee George P. Wetmore defeated Democratic nominee Ziba O. Slocum with 55.97% of the vote.

Elections were held in Illinois on Tuesday, November 3, 1936.

A general election was held in the U.S. state of Wyoming on Tuesday, November 6, 1894. All of the state's executive officers—the Governor, Secretary of State, Auditor, Treasurer, and Superintendent of Public Instruction—were up for election. The Republican Party, helped by the strong performance of the Populist Party, which operated as a spoiler to the Democratic Party, won back the governorship and improved its margin of victory in all other statewide offices.

The 1896 Delaware gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1896. Shortly after his victory in the 1894 gubernatorial election, Republican Governor Joshua H. Marvil died. State Senate Speaker William T. Watson, a Democrat, became Governor and a new election for a full four-year term was scheduled in 1896. Though Watson was considered a potential candidate for re-election, the Democratic convention instead nominated Ebe W. Tunnell, the 1894 nominee for Governor; despite his protests that he would decline the nomination, Tunnell ultimately accepted it.
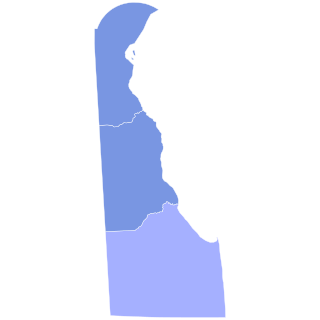
The 1936 Delaware gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1936. Incumbent Republican Governor C. Douglass Buck was barred from seeking re-election to a third term, creating an open race. A challenging contest developed on the Republican side to succeed Buck, with Harry L. Cannon, former State Senator I. Dolphus Short and Assistant Motor Vehicle Commissioner George S. Williams all emerging as frontrunners. Cannon, a longtime figure in state politics who served as a member of the State Board of Agriculture and on the University of Delaware Board of Trustees, ultimately won the nomination. Short walked out of the convention, however, and shortly thereafter organized a slate of statewide candidates as Independent Republicans, dividing the party.

The 1896 Wisconsin gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1896.

The 1900 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1900.

The 1896 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1896, and featured Populist and Democratic fusion nominee James E. Harris defeating his major rival, Republican nominee Orlando Tefft. Other candidates who received two percent of the vote or less included Gold Democratic nominee Owen F. Biglin, Prohibition nominee Lucius O. Jones, Socialist Labor nominee Fred Herman, and National Silver nominee Oscar Kent. Incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor Robert E. Moore did not seek reelection.




















