An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis.
In enzymology, a phosphopentomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme L-fuculose-phosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.68) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme guanidinodeoxy-scyllo-inositol-4-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.40) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The haloacid dehydrogenase superfamily is a superfamily of enzymes that include phosphatases, phosphonatases, P-type ATPases, beta-phosphoglucomutases, phosphomannomutases, and dehalogenases, and are involved in a variety of cellular processes ranging from amino acid biosynthesis to detoxification.
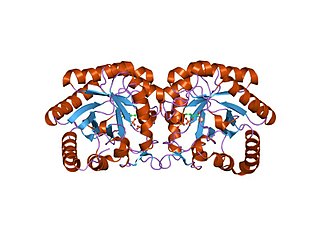
3-Deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase is the first enzyme in a series of metabolic reactions known as the shikimate pathway, which is responsible for the biosynthesis of the amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. Since it is the first enzyme in the shikimate pathway, it controls the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Enzyme inhibition is the primary method of regulating the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Forms of this enzyme differ between organisms, but can be considered DAHP synthase based upon the reaction that is catalyzed by this enzyme.
(KDO)2-lipid IVA (2-8) 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)2-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(KDO)3-lipid IVA (2-4) 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)3-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose-7-phosphate kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 7-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-β-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.82) is an enzyme with systematic name D-glycero-β-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-α-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.83) is an enzyme with systematic name D-glycero-α-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3-Deoxy-2-octulosonidase is an enzyme with systematic name capsular-polysaccharide 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction


