
Acetoacetic acid is the organic compound with the formula CH3COCH2COOH. It is the simplest beta-keto acid, and like other members of this class, it is unstable. The methyl and ethyl esters, which are quite stable, are produced on a large scale industrially as precursors to dyes. Acetoacetic acid is a weak acid.
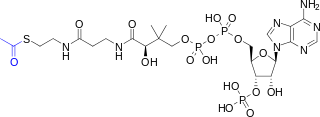
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid (B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol).
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase is an enzyme (EC 4.1.3.4 that in human is encoded by the HMGCL gene located on chromosome 1. It is a key enzyme in ketogenesis. It is a ketogenic enzyme in the liver that catalyzes the formation of acetoacetate from HMG-CoA within the mitochondria. It also plays a prominent role in the catabolism of the amino acid leucine.

Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion pathway, it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA as a product or as a reactant.

Thiolases, also known as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferases (ACAT), are enzymes which convert two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate pathway.

In enzymology, a 3-oxoacid CoA-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a butyrate-acetoacetate CoA-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.4) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme acetyl-CoA hydrolase catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme ADP-dependent medium-chain-acyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.19) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme ADP-dependent short-chain-acyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.18) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme choloyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.27) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.5) catalyzes the reaction
Palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.2) is an enzyme in the family of hydrolases that specifically acts on thioester bonds. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of long chain fatty acyl thioesters of acyl carrier protein or coenzyme A to form free fatty acid and the corresponding thiol:
The enzyme S-formylglutathione hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.12) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.17) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme succinyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.3) catalyzes the reaction

In enzymology, an acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase or HMG-CoA synthase EC 2.3.3.10 is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction in which acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). This reaction comprises the second step in the mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. HMG-CoA is an intermediate in both cholesterol synthesis and ketogenesis. This reaction is overactivated in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 if left untreated, due to prolonged insulin deficiency and the exhaustion of substrates for gluconeogenesis and the TCA cycle, notably oxaloacetate. This results in shunting of excess acetyl-CoA into the ketone synthesis pathway via HMG-CoA, leading to the development of diabetic ketoacidosis.
3-oxoacid CoA-transferase 1 (OXCT1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OXCT1 gene. It is also known as succinyl-CoA-3-oxaloacid CoA transferase (SCOT). Mutations in the OXCT1 gene are associated with succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase deficiency. This gene encodes a member of the 3-oxoacid CoA-transferase gene family. The encoded protein is a homodimeric mitochondrial matrix enzyme that plays a central role in extrahepatic ketone body catabolism by catalyzing the reversible transfer of coenzyme A (CoA) from succinyl-CoA to acetoacetate.










