Platelet-activating factor, also known as PAF, PAF-acether or AGEPC (acetyl-glyceryl-ether-phosphorylcholine), is a potent phospholipid activator and mediator of many leukocyte functions, platelet aggregation and degranulation, inflammation, and anaphylaxis. It is also involved in changes to vascular permeability, the oxidative burst, chemotaxis of leukocytes, as well as augmentation of arachidonic acid metabolism in phagocytes.

In an organic chemistry general sense, an ether lipid implies an ether bridge between an alkyl group and an unspecified alkyl or aryl group, not necessarily glycerol. If glycerol is involved, the compound is called a glyceryl ether, which may take the form of an alkylglycerol, an alkyl acyl glycerol, or in combination with a phosphatide group, a phospholipid.
Alkylglycerol monooxygenase (AGMO) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of alkylglycerols, a specific subclass of ether lipids. This enzyme was first described in 1964 as a pteridine-dependent ether lipid cleaving enzyme. In 2010 finally, the gene coding for alkylglycerol monooxygenase was discovered as transmembrane protein 195 (TMEM195) on chromosome 7. In analogy to the enzymes phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, tryptophan hydroxylase and nitric oxide synthase, alkylglycerol monooxygenase critically depends on the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin and iron.
The enzyme 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase (EC 3.1.1.47) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme 6-acetylglucose deacetylase (EC 3.1.1.33) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme alkylacetylglycerophosphatase (EC 3.1.3.59) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme cephalosporin-C deacetylase (EC 3.1.1.41) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme N-acetylgalactosaminoglycan deacetylase (EC 3.1.1.58) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.33) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylglucosaminylphosphatidylinositol deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.89) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerol O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-alkylglycerophosphocholine O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkylglycerophosphate 2-O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a platelet-activating factor acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a geranylgeranylglycerol-phosphate geranylgeranyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-mimosine synthase (EC 2.5.1.52) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an uracilylalanine synthase (EC 2.5.1.53) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a zeatin 9-aminocarboxyethyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkylglycerol kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
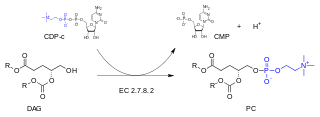
In enzymology, a diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction


