
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever.

Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin salix for willow tree, from which it was initially identified and derived. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.
An antipyretic is a substance that reduces fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature. The body then works to lower the temperature, which results in a reduction in fever.

Reye syndrome is a rapidly worsening brain disease. Symptoms of Reye syndrome may include vomiting, personality changes, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness. While liver toxicity typically occurs in the syndrome, jaundice usually does not. Death occurs in 20–40% of those affected with Reye syndrome, and about a third of those who survive are left with a significant degree of brain damage.
Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.

URB597 (KDS-4103) is a relatively selective and irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). FAAH is the primary degradatory enzyme for the endocannabinoid anandamide and, as such, inhibition of FAAH leads to an accumulation of anandamide in the CNS and periphery where it activates cannabinoid receptors. URB597 has been found to elevate anandamide levels and have activity against neuropathic pain in a mouse model.
An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis.

Monoacylglycerol lipase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the MGLL gene. MAGL is a 33-kDa, membrane-associated member of the serine hydrolase superfamily and contains the classical GXSXG consensus sequence common to most serine hydrolases. The catalytic triad has been identified as Ser122, His269, and Asp239.

Aloxiprin is a medical drug used for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with muscular skeletal and joint disorders. It is used for its properties as an anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic drug. It is a chemical compound of aluminium hydroxide and aspirin.
The enzyme acylcarnitine hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.28) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme arylesterase (EC 3.1.1.2) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme carboxylesterase (or carboxylic-ester hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.1; systematic name carboxylic-ester hydrolase) catalyzes reactions of the following form:
The enzyme feruloyl esterase (EC 3.1.1.73) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme sterol esterase (EC 3.1.1.13) catalyzes the reaction
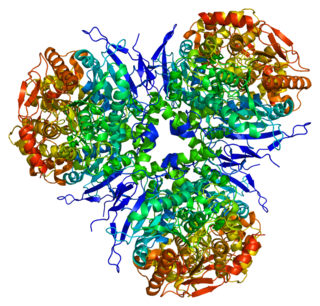
Liver carboxylesterase 1 also known as carboxylesterase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES1 gene. The protein is also historically known as serine esterase 1 (SES1), monocyte esterase and cholesterol ester hydrolase (CEH). Three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene. The various protein products from isoform a, b and c range in size from 568, 567 and 566 amino acids long, respectively.

Aspirin causes several different effects in the body, mainly the reduction of inflammation, analgesia, the prevention of clotting, and the reduction of fever. Much of this is believed to be due to decreased production of prostaglandins and TXA2. Aspirin's ability to suppress the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes is due to its irreversible inactivation of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. Cyclooxygenase is required for prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis. Aspirin acts as an acetylating agent where an acetyl group is covalently attached to a serine residue in the active site of the COX enzyme. This makes aspirin different from other NSAIDs, which are reversible inhibitors. However, other effects of aspirin, such as uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, and the modulation of signaling through NF-κB, are also being investigated. Some of its effects are like those of salicylic acid, which is not an acetylating agent.

The enzyme triacylglycerol lipase (also triglyceride lipase, EC 3.1.1.3;systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of ester linkages of triglycerides:
The enzyme mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide esterase (EC 3.1.1.93, mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide deglucuronidase; AcMPAG deglucuronidase; systematic name mycophenolic acid O-acyl-glucuronide-ester hydrolase), is in humans encoded by the ABHD10 gene, and catalyses the reaction

Estradiol acetylsalicylate, or estradiol 3-acetylsalicylate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) ester of estradiol – which was described in the late 1980s and was never marketed. In dogs, the oral bioavailability of estradiol acetylsalicylate was found to be 17-fold higher than that of unmodified estradiol. However, a subsequent study found that the oral bioavailability of estradiol and estradiol acetylsalicylate did not differ significantly in rats, suggestive of a major species difference.

Lysine acetylsalicylate, also known as aspirin DL-lysine or lysine aspirin, is a more soluble form of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). As with aspirin itself, it is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic and antipyretic properties. It is composed of the ammonium form of the amino acid lysine paired with the conjugate base of aspirin.











