
Glutamate dehydrogenase is an enzyme observed in both prokaryotes and eukaryotic mitochondria. The aforementioned reaction also yields ammonia, which in eukaryotes is canonically processed as a substrate in the urea cycle. Typically, the α-ketoglutarate to glutamate reaction does not occur in mammals, as glutamate dehydrogenase equilibrium favours the production of ammonia and α-ketoglutarate. Glutamate dehydrogenase also has a very low affinity for ammonia, and therefore toxic levels of ammonia would have to be present in the body for the reverse reaction to proceed. However, in brain, the NAD+/NADH ratio in brain mitochondria encourages oxidative deamination. In bacteria, the ammonia is assimilated to amino acids via glutamate and aminotransferases. In plants, the enzyme can work in either direction depending on environment and stress. Transgenic plants expressing microbial GLDHs are improved in tolerance to herbicide, water deficit, and pathogen infections. They are more nutritionally valuable.
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen by catalyzing the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine:
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is a ligase enzyme located in the mitochondria involved in the production of urea. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I transfers an ammonia molecule to a molecule of bicarbonate that has been phosphorylated by a molecule of ATP. The resulting carbamate is then phosphorylated with another molecule of ATP. The resulting molecule of carbamoyl phosphate leaves the enzyme.

Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyzes the ATP-dependent synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate from glutamine or ammonia and bicarbonate. This enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ATP and bicarbonate to produce carboxy phosphate and ADP. Carboxy phosphate reacts with ammonia to give carbamic acid. In turn, carbamic acid reacts with a second ATP to give carbamoyl phosphate plus ADP.
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reactions that produce carbamoyl phosphate in the cytosol. Its systemic name is hydrogen-carbonate:L-glutamine amido-ligase .

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

The enzyme anthranilate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aerobactin synthase (EC 6.3.2.39) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a dihydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate—ethylamine ligase (EC 6.3.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate—methylamine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate-putrescine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate—tRNAGln ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase (EC 6.3.5.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tetrahydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [glutamate—ammonia-ligase] adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

5′-Phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from AIR. It is an intermediate in the adenine pathway and is synthesized from 5′-phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine by AIR synthetase.
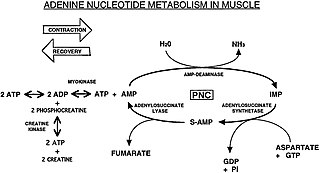
The Purine Nucleotide Cycle is a metabolic pathway in protein metabolism requiring the amino acids aspartate and glutamate. The cycle is used to regulate the levels of adenine nucleotides, in which ammonia and fumarate are generated. AMP coverts into IMP and the byproduct ammonia. IMP converts to S-AMP (adenylosuccinate), which then coverts to AMP and the byproduct fumarate. The fumarate goes on to produce ATP (energy) via oxidative phosphorylation as it enters the Krebs cycle and then the electron transport chain. Lowenstein first described this pathway and outlined its importance in processes including amino acid catabolism and regulation of flux through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Asparagine synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.4, asparagine synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing), glutamine-dependent asparagine synthetase, asparagine synthetase B, AS, AS-B) is an enzyme with systematic name L-aspartate:L-glutamine amido-ligase (AMP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










