
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura. The oldest fossil "proto-frog" appeared in the early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their origins may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforests. There are over 6,300 recorded species, accounting for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history.

Xenopus is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis, which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects.

The American bullfrog, often simply known as the bullfrog in Canada and the United States, is an amphibious frog, a member of the family Ranidae, or "true frogs". This frog has an olive green back and sides blotched with brownish markings and a whitish belly spotted with yellow or grey. The upper lip is often bright green and males have yellow throats. It inhabits large, permanent water bodies, such as swamps, ponds, and lakes, where it is usually found along the water's edge. The male bullfrog defends a territory during the breeding season. His call is reminiscent of the roar of a bull, which gives the frog its common name. This frog is native to southern and eastern parts of the United States and Canada, but has been widely introduced across other parts of North, Central and South America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia, and in some areas is regarded as a pest and an invasive species.

Ribonuclease H is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria to archaea to eukaryotes.
Maturation-promoting factor (abbreviated MPF, also called mitosis-promoting factor or M-Phase-promoting factor) is the cyclin-Cdk complex that was discovered first in frog eggs. It stimulates the mitotic and meiotic phases of the cell cycle. MPF promotes the entrance into mitosis (the M phase) from the G2 phase by phosphorylating multiple proteins needed during mitosis. MPF is activated at the end of G2 by a phosphatase, which removes an inhibitory phosphate group added earlier.

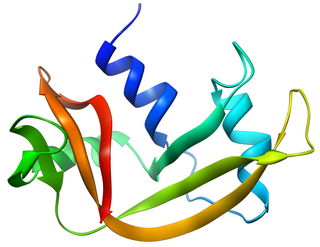
Ranpirnase is a ribonuclease enzyme found in the oocytes of the Northern Leopard Frog. Ranpirnase is a member of the pancreatic ribonuclease protein superfamily and degrades RNA substrates with a sequence preference for uracil and guanine nucleotides. Along with amphinase, another leopard frog ribonuclease, ranpirnase has been studied as a potential cancer treatment due to its unusual mechanism of cytotoxicity tested against tumor cells.

Rana is a genus of frogs commonly known as the Holarctic true frogs, pond frogs or brown frogs. Members of this genus are found through much of Eurasia and western North America. Many other genera were formerly included here. These true frogs are usually largish species characterized by their slim waists and wrinkled skin; many have thin ridges running along their backs, but they generally lack "warts" as in typical toads. They are excellent jumpers due to their long, slender legs. The typical webbing found on their hind feet allows for easy movement through water. Coloration is mostly greens and browns above, with darker and yellowish spots.

Angiogenin (Ang) also known as ribonuclease 5 is a small 123 amino acid protein that in humans is encoded by the ANG gene. Angiogenin is a potent stimulator of new blood vessels through the process of angiogenesis. Ang hydrolyzes cellular RNA, resulting in modulated levels of protein synthesis and interacts with DNA causing a promoter-like increase in the expression of rRNA. Ang is associated with cancer and neurological disease through angiogenesis and through activating gene expression that suppresses apoptosis.

Ribonuclease inhibitor (RI) is a large, acidic, leucine-rich repeat protein that forms extremely tight complexes with certain ribonucleases. It is a major cellular protein, comprising ~0.1% of all cellular protein by weight, and appears to play an important role in regulating the lifetime of RNA.
Pancreatic ribonucleases are pyrimidine-specific endonucleases found in high quantity in the pancreas of certain mammals and of some reptiles.

Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASE2 gene.

Rev-ErbA beta (Rev-erbβ) also known as NR1D2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1D2 gene.

Ribonuclease pancreatic is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASE1 gene.

Ribonuclease inhibitor is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNH1 gene.

Ranavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Iridoviridae. There are four other genera of viruses within the family Iridoviridae, but Ranavirus is the only one that includes viruses that are infectious to amphibians and reptiles. Additionally, it is one of the three genera within this family which infect teleost fishes, along with Lymphocystivirus and Megalocytivirus. The family Iridoviridae is one of the five families of nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses.

Morpheeins are proteins that can form two or more different homo-oligomers, but must come apart and change shape to convert between forms. The alternate shape may reassemble to a different oligomer. The shape of the subunit dictates which oligomer is formed. Each oligomer has a finite number of subunits (stoichiometry). Morpheeins can interconvert between forms under physiological conditions and can exist as an equilibrium of different oligomers. These oligomers are physiologically relevant and are not misfolded protein; this distinguishes morpheeins from prions and amyloid. The different oligomers have distinct functionality. Interconversion of morpheein forms can be a structural basis for allosteric regulation. A mutation that shifts the normal equilibrium of morpheein forms can serve as the basis for a conformational disease. Features of morpheeins can be exploited for drug discovery. The dice image represents a morpheein equilibrium containing two different monomeric shapes that dictate assembly to a tetramer or a pentamer. The one protein that is established to function as a morpheein is porphobilinogen synthase, though there are suggestions throughout the literature that other proteins may function as morpheeins.

In the field of molecular biology, enterotoxin type B, also known as Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), is an enterotoxin produced by the gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is a common cause of food poisoning, with severe diarrhea, nausea and intestinal cramping often starting within a few hours of ingestion. Being quite stable, the toxin may remain active even after the contaminating bacteria are killed. It can withstand boiling at 100 °C for a few minutes. Gastroenteritis occurs because SEB is a superantigen, causing the immune system to release a large amount of cytokines that lead to significant inflammation.
Ranid herpesvirus 1 (RaHV-1), also known as the Lucké tumor herpesvirus (LTHV), is a double-stranded DNA virus within the order Herpesvirales. The virus was initially observed within renal tumors in 1934 by Baldwin Lucké, and more recently has become identifiable through the use of PCR in samples isolated from frog tumors. RaHV-1 causes renal tumors within the northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens. The virus has not yet been isolated in vitro within cell lines, meaning that while its existence and symptoms are fairly evident, its methods of transmission, cell infection, and reproduction are largely unknown.



















