
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybeans, from which they are mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane. They are also a member of the lecithin group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (lecithin) is a major component of the pulmonary surfactant, and is often used in the lecithin–sphingomyelin ratio to calculate fetal lung maturity. While phosphatidylcholines are found in all plant and animal cells, they are absent in the membranes of most bacteria, including Escherichia coli. Purified phosphatidylcholine is produced commercially.
Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.

Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid. Deoxycholic acid is one of the secondary bile acids, which are metabolic byproducts of intestinal bacteria. The two primary bile acids secreted by the liver are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. Bacteria metabolize chenodeoxycholic acid into the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid, and they metabolize cholic acid into deoxycholic acid. There are additional secondary bile acids, such as ursodeoxycholic acid. Deoxycholic acid is soluble in alcohol and acetic acid. When pure, it exists in a white to off-white crystalline powder form.
In enzymology, a 5'-acylphosphoadenosine hydrolase (EC 3.6.1.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenylylsulfatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.4) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a carboxymethylenebutenolidase (EC 3.1.1.45, also known as CMBL and dienelactone hydrolase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme choloyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.27) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme sterol esterase (EC 3.1.1.13) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
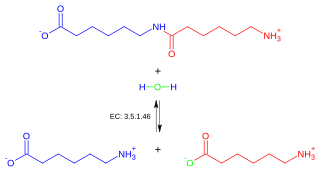
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.46) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate + H2O 2 6-aminohexanoate. Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate and H2O, whereas its product is two molecules of 6-aminohexanoate.

In enzymology, an amidase (EC 3.5.1.4, acylamidase, acylase (misleading), amidohydrolase (ambiguous), deaminase (ambiguous), fatty acylamidase, N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide. In this way, the two substrates of this enzyme are an amide and H2O, whereas its two products are monocarboxylate and NH3.
In enzymology, a chenodeoxycholoyltaurine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.74) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a choloylglycine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.24) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an imidazolonepropionase (EC 3.5.2.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a maleimide hydrolase (EC 3.5.2.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, Nα-benzyloxycarbonylleucine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.64) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-benzyloxycarbonylglycine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.58) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoyl-D-amino acid hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.77) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Bile-acid 7alpha-dehydroxylase (EC 1.17.99.5, cholate 7alpha-dehydroxylase, 7alpha-dehydroxylase, bile acid 7-dehydroxylase) was thought to be an enzyme with systematic name deoxycholate:NAD+ oxidoreductase.






