
The Lechuguilla Desert is a small desert located in southwestern Arizona near the U.S.-Mexico border. It is considered to be part of the Lower Colorado Valley region of the Sonoran Desert. It lies in a north–south direction between the Gila Mountains and the Cabeza Prieta Mountains, and almost entirely in the Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range. The desert is named after the Lechuguilla plant, known scientifically as Agave lecheguilla, which occurs exclusively in the Chihuahuan desert many hundreds of miles to the east. The desert is also on the north border of the Gran Desierto de Altar of Sonora, Mexico.

Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge (CPNWR) is located in southwestern Arizona in the United States, along 56 miles (90 km) of the Mexico–United States border. It is bordered to the north and to the west by the Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range, to the south by Mexico's El Pinacate y Gran Desierto de Altar Biosphere Reserve, to the northeast by the town of Ajo, and to the southeast by Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument.

The Kofa National Wildlife Refuge is located in Arizona in the southwestern United States, northeast of Yuma and southeast of Quartzsite. The refuge, established in 1939 to protect desert bighorn sheep, encompasses over 665,400 acres (2,693 km2) of the Yuma Desert region of the Sonoran Desert. Broad, gently sloping foothills as well as the sharp, needlepoint peaks of the Kofa Mountains are found in the rugged refuge. The small, widely scattered waterholes attract a surprising number of water birds for a desert area. A wide variety of plant life is also found throughout the refuge.

The Kofa Mountains of Yuma and La Paz counties in Arizona is the central mountain range of the Kofa National Wildlife Refuge. The range lies about 60 miles northeast of Yuma in the southwestern part of the state. Kofa Wilderness takes up 547,719 acres of the refuge, making it the second largest wilderness area in Arizona. The equally extensive Castle Dome Mountains comprise the southern refuge border; the western end of the Tank Mountains are in the southeast of the wildlife refuge, and the New Water Wilderness in the New Water Mountains ends the extension of the Kofa National Wildlife Refuge to the north. Scenic "King Valley" is south of the Kofa Mountains between the Castle Dome Mountains.
The Copper Mountains is a minor north–south trending mountain range, only 8 miles long in southwestern Arizona in the southwestern Sonoran Desert.

The Tinajas Altas Mountains are an extremely arid northwest-southeast trending mountain range in southern Yuma County, Arizona, approximately 35 mi southeast of Yuma, Arizona. The southern end of the range extends approximately one mile into the northwestern Mexican state of Sonora on the northern perimeter of the Gran Desierto de Altar. The range is about 22 mi in length and about 4 mi wide at its widest point. The highpoint of the range is unnamed and is 2,766 feet above sea level and is located at 32°16'26"N, 114°02'48"W. Aside from the portion of the range in Mexico, the entirety of the range lies within the Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range. They lie at the heart of the traditional homeland of the Hia C-eḍ O'odham people.

The Muggins Mountains is a mountain range in southwest Arizona east of Yuma, Arizona, northeast of the Gila Mountains, and east of the Laguna Mountains. The Castle Dome Mountains lie to the northeast across the broad Castle Dome Plain. The Muggins Mountains Wilderness occupies the southwest portion of the range.

The Bryan Mountains are a small mountain range in the northwestern Sonoran Desert of southwestern Arizona. The range is located in southeastern Yuma County, about 75 mi southeast of Yuma and about 35 mi west of Ajo. The range is approximately ten miles long and about three miles wide at its widest point. The highpoint of the range is 1,794 feet above sea level and is located at 32°18'27"N, 113°22'46"W. The range is located entirely within the Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge.
The San Cristobal Valley is a valley in the lower regions of the western Gila River Valley in southwestern Arizona in the western Sonoran Desert. The San Cristobal Wash drains northwest, but exists only in the southern half of the valley.

The Mohawk Mountains is a mountain range in the northwest Sonoran Desert of southwest Arizona. It abuts the western Gila River valley to the north, and is located in southern Yuma County. The Mohawk Valley lies adjacent and southwest of the range; the San Cristobal Valley is northeast.
The Granite Mountains of Arizona is a mountain range in the Sonoran Desert of southern Arizona. It is located in extreme western Pima County, Arizona, bordering southeast Yuma County.

The Gila Mountains of Yuma County are a 26-mile (42 km) long mountain range in southwestern Arizona in the northwest Sonoran Desert.

The Sierra Pinta or Sierra Pintas are a narrow remote block faulted northwest-southeast trending mountain range, about 22 miles (35 km) long located in southwestern Arizona in the arid northwestern Sonoran Desert, just north of the Pinacate Reserve of northern Sonora, Mexico. The mountains derive their name from visitor descriptions of its multicolored hues when viewed at sunrise and sunset.
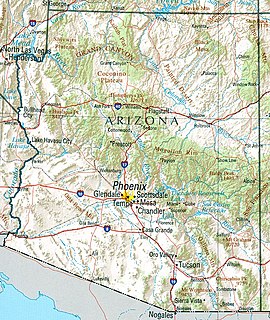
Arizona is a landlocked state situated in the southwestern region of the United States of America. It has a vast and diverse geography famous for its deep canyons, high- and low-elevation deserts, numerous natural rock formations, and volcanic mountain ranges. Arizona shares land borders with Utah to the north, the Mexican state of Sonora to the south, New Mexico to the east, and Nevada to the northwest, as well as water borders with California and the Mexican state of Baja California to the southwest along the Colorado River. Arizona is also one of the Four Corners states and is diagonally adjacent to Colorado.

The Growler Mountains is a 23-mile, (37-km) long north-south trending mountain range of far western Pima County, Arizona that lies 12 miles (19 km) west of Ajo, Arizona. This desert region of southern Arizona lies in the north and central Sonoran Desert, and is one of the drier desert areas of North America.

The Little Ajo Mountains is a mountain range in southern Arizona, in extreme western Pima County, Arizona. The city of Ajo sits on the northeast of this small mountain range. Both the mountain range and city take their name from the Spanish word for garlic.

The Harcuvar Mountains are a narrow mountain range in western-central Arizona, United States. The range lies just east of the north-south Colorado River, and south of the east-west, west-flowing Bill Williams River, from Alamo Lake.

The West Silver Bell Mountains are a small 10 mile (16 km) long mountain range of south-central Arizona, United States. The range lies in the north-central arid Sonoran Desert; the Madrean Sky Islands region of southeast Arizona, around Tucson is adjacent to the southeast.

The Painted Rocks Mountains are a short 15-mile (24 km) long mountain range of the north-central Sonoran Desert southwest of Phoenix, Arizona and in southwest Maricopa County. The Gila River flows through the central-north end of the range.












