Crater Lake is a crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a nearly 2,148-foot-deep (655 m) caldera that was formed around 7,700 years ago by the collapse of the volcano Mount Mazama. There are no rivers flowing into or out of the lake; the evaporation is compensated for by rain and snowfall at a rate such that the total amount of water is replaced every 250 years. With a depth of 1,949 feet (594 m), the lake is the deepest in the United States. In the world, it ranks ninth for maximum depth, and third for mean (average) depth.
Crater Lake National Park is an American national park located in southern Oregon. Established in 1902, Crater Lake is the fifth-oldest national park in the United States and the only national park in Oregon. The park encompasses the caldera of Crater Lake, a remnant of Mount Mazama, a destroyed volcano, and the surrounding hills and forests.
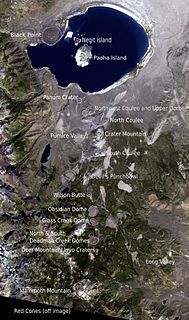
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.

Crater of Diamonds State Park is a 911-acre (369 ha) Arkansas state park in Pike County, Arkansas, in the United States. The park features a 37.5-acre plowed field, the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public. Diamonds have continuously been discovered in the field since 1906, including the Strawn-Wagner Diamond. The site became a state park in 1972 after the Arkansas Department of Parks and Tourism purchased the site from the Arkansas Diamond Company and Ozark Diamond Mines Corporation, who had operated the site as a tourist attraction previously.

Sunset Crater is a cinder cone located north of Flagstaff in the U.S. state of Arizona. The crater is within the Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument.

Tenoumer is considered to be an impact crater in Mauritania.

Masaya is a caldera located in Masaya, Nicaragua, 20 km south of the capital Managua. It is Nicaragua's first and largest national park, and one of 78 protected areas of Nicaragua. The complex volcano is composed of a nested set of calderas and craters, the largest of which is Las Sierras shield volcano and caldera. Within this caldera lies a sub-vent, which is Masaya Volcano sensu stricto. The vent is a shield type composing of basaltic lavas and tephras and includes a summit crater. This hosts Masaya caldera, formed 2,500 years ago by an 8-km³ basaltic ignimbrite eruption. Inside this caldera a new basaltic complex has grown from eruptions mainly on a semi-circular set of vents that include the Masaya and Nindiri cones. The latter host the pit craters of Masaya, Santiago, Nindiri and San Pedro. Observations in the walls of the pit craters indicate that there have been several episodes of cone and pit crater formation.

Taal Volcano is a large caldera filled by Taal Lake in the Philippines. Located in the province of Batangas, the volcano is one of the most active volcanoes in the country, with 34 recorded historical eruptions, all of which were concentrated on Volcano Island, near the middle of Taal Lake. The caldera was formed by prehistoric eruptions between 140,000 and 5,380 BP.

Ubehebe Crater is a large volcanic crater of the Ubehebe Craters volcanic field in the northern half of Death Valley, in Death Valley National Park, California, United States.

Mount Schank is a 100 m (330 ft) high dormant volcano in the southeast corner of South Australia, near Mount Gambier. It was sighted by James Grant on 3 December 1800 and named after Admiral John Schank, designer of Grant's ship, HMS Lady Nelson.

Kerið is a volcanic crater lake located in the Grímsnes area in south Iceland, along the Golden Circle. It is one of several crater lakes in the area, known as Iceland's Western Volcanic Zone, which includes the Reykjanes peninsula and the Langjökull Glacier, created as the land moved over a localized hotspot, but it is the one that has the most visually recognizable caldera still intact. The caldera, like the other volcanic rock in the area, is composed of a red volcanic rock. The caldera itself is approximately 55 m (180 ft) deep, 170 m (560 ft) wide, and 270 m (890 ft) across. Kerið's caldera is one of the three most recognizable volcanic craters because at approximately 3,000 years old, it is only half the age of most of the surrounding volcanic features. The other two are Seyðishólar and Kerhóll.

Aram Chaos, centered at 2.6°N, 21.5°W, is a heavily eroded impact crater on Mars. It lies at the eastern end of the large canyon Valles Marineris and close to Ares Vallis. Various geological processes have reduced it to a circular area of chaotic terrain. Aram Chaos takes its name from Aram, one of the classical albedo features observed by Giovanni Schiaparelli, who named it after the Biblical land of Aram. Spectroscopic observation from orbit indicates the presence of the mineral hematite, likely a signature of a once aqueous environment.

Roden Crater is a cinder cone type of volcanic cone from an extinct volcano, with a remaining interior volcanic crater. It is located approximately 50 miles northeast of the city of Flagstaff in northern Arizona, United States.

Al Wahbah Crater, also Maqlaʿ Ṭamiyyah, is a volcanic crater, which is about 250 kilometres away from Ta'if, on the western edge of the Harrat Kishb basalt plateau in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia. The Harrat Kishb plateau contains many volcanic cones. It is 250 m (820 ft) deep and 2 km (1.2 mi) in diameter. The bottom of the crater is covered with white sodium phosphate crystals.

Endeavour is an impact crater located in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. Endeavour is about 22 kilometers (14 mi) in diameter. Using Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter data, phyllosilicate-bearing outcrops have been detected along its rim. These minerals may have formed under wet conditions in a low-acidic environment during the early history of Mars. There are raised rim segments to the north, east, and southwest. The rim has become worn, rounded and degraded, with infilling of plains material in a manner similar to the Victoria crater.

Strawberry Crater is a cinder cone volcano, more than 1,000 feet (300 m) high, in the San Francisco volcanic field, 20 miles (32 km) north of Flagstaff, Arizona. It is along Forest Road 545 between the Wupatki National Monument and Sunset Crater National Monument in the Strawberry Crater Wilderness. The crater lies in a volcanic field at a base elevation of about 5,500 feet (1,700 m), and prominence heights of about 6,526 feet (1,989 m). The northwestern end of the crater is covered with lava flows, while the southern end is filled with low cinder cones. Several of the surrounding cones include the better known, taller and younger Sunset Crater in the adjacent Sunset Crater National Monument.

Orcus Patera is a region on the surface of the planet Mars first photographed by Mariner 4. Of unknown formation, whether by volcanic, tectonic, or cratering causes, the region includes a depression about 380 kilometres long, 140 kilometres wide, surrounded by a rim up to 1.8 kilometres high.

Patera is an irregular crater, or a complex crater with scalloped edges on a celestial body. Paterae can have any origin, although majority of them were created by volcanism. The term comes from Latin language, where it refers to a shallow bowl used in antique culture.

A volcanic crater lake is a lake in a crater that was formed from explosive activity or collapse during a volcanic eruption.