
The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences is an organization dedicated to the advancement of science and literature in the Netherlands. The academy is housed in the Trippenhuis in Amsterdam.
E-Science or eScience is computationally intensive science that is carried out in highly distributed network environments, or science that uses immense data sets that require grid computing; the term sometimes includes technologies that enable distributed collaboration, such as the Access Grid. The term was created by John Taylor, the Director General of the United Kingdom's Office of Science and Technology in 1999 and was used to describe a large funding initiative starting in November 2000. E-science has been more broadly interpreted since then, as "the application of computer technology to the undertaking of modern scientific investigation, including the preparation, experimentation, data collection, results dissemination, and long-term storage and accessibility of all materials generated through the scientific process. These may include data modeling and analysis, electronic/digitized laboratory notebooks, raw and fitted data sets, manuscript production and draft versions, pre-prints, and print and/or electronic publications." In 2014, IEEE eScience Conference Series condensed the definition to "eScience promotes innovation in collaborative, computationally- or data-intensive research across all disciplines, throughout the research lifecycle" in one of the working definitions used by the organizers. E-science encompasses "what is often referred to as big data [which] has revolutionized science... [such as] the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN... [that] generates around 780 terabytes per year... highly data intensive modern fields of science...that generate large amounts of E-science data include: computational biology, bioinformatics, genomics" and the human digital footprint for the social sciences.

The European University Institute (EUI) is an international postgraduate and post-doctoral research-intensive university and an intergovernmental organisation with juridical personality, established by its founding member states to contribute to cultural and scientific development in the social sciences, in a European perspective. Its main campus is located in the hills above Florence in Fiesole, Italy.

The Netherlands Institute for Advanced Study in the Humanities and Social Sciences (NIAS) in Amsterdam, Netherlands, is an independent research institute in the field of the humanities and social and behavioural sciences founded in 1970. The institute offers advanced research facility for international scholars of all of the humanities and social sciences. It is a member of Some Institutes for Advanced Study (SIAS) and the Network of European Institutes for Advanced Studies (NetIAS).
The University College Dublin Library, composed of five separate bodies, holds varied ranges of digital and printed books on a wide range of topics, including architecture, arts and humanities, business studies, engineering, law, medicine, science, social sciences and veterinary medicine. In 2015 UCD Archives and the National Folklore Collection UCD came under the administrative umbrella of UCD Library. University College Dublin (UCD) is the Republic of Ireland's largest university. It is located in Dublin, Ireland.

The Dutch Research Council is the national research council of the Netherlands. NWO funds thousands of top researchers at universities and institutes and steers the course of Dutch science by means of subsidies and research programmes. NWO promotes quality and innovation in science. NWO is an independent administrative body under the auspices of the Dutch Ministry of Education, Culture and Science. NWO directs its approximate budget of 1 billion euros towards Dutch universities and institutes, often on a project basis. Also, NWO has its own research institutes and facilitates international cooperation. Current president of NWO since April 1, 2021 is Marcel Levi. Former NWO presidents include Stan Gielen, Peter Nijkamp and Jos Engelen.
The LISS panel is an online household panel. The panel consists of some 5000 households in the Netherlands, comprising approximately 7500 individuals over the age of 16. The panel is based on a true probability sample of households drawn from the population register by Statistics Netherlands. Households without prior Internet access are equipped with a computer and broadband Internet.

Franklin Gerardus "Frank" Grosveld, FRS is a Dutch molecular biologist whose research interests are in the regulation of transcription during development with a particular emphasis on mammalian erythroid differentiation. He is a professor and former Head of the Department of Cell Biology at the Erasmus MC, Rotterdam.

University of Cape Town Libraries is the library system of the University of Cape Town in Cape Town, South Africa.

OPUS is an open-source software package under the GNU General Public License used for creating Open Access repositories that are compliant with the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting. It provides tools for creating collections of digital resources, as well as for their storage and dissemination. It is usually used at universities, libraries and research institutes as a platform for institutional repositories.

INFLIBNET Centre is an Inter-University Centre of the University Grants Commission (India) under the Ministry of Education (India). The organisation promotes and facilitates libraries and information resources for Indian further education. Its premises are in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
E-Theses Online Service (EThOS) is a bibliographic database and union catalogue of electronic theses provided by the British Library, the National Library of the United Kingdom. As of February 2022 EThOS provides access to over 500,000 doctoral theses awarded by over 140 UK higher education institutions, with around 3,000 new thesis records added every month.

Scholarly communication of the Netherlands published in open access form can be found by searching the National Academic Research and Collaboration Information System (NARCIS). The web portal was developed in 2004 by the Data Archiving and Networked Services of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research and Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.

In India, the Open Access movement started in May 2004, when two workshops were organized by the M S Swaminathan Research Foundation, Chennai. In 2006, the National Knowledge Commission in its recommendations proposed that "access to knowledge is the most fundamental way of increasing the opportunities and reach of individuals and groups". In 2011, the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) began requiring that its grantees provide open access to funded research, the Open Access India forum formulated a draft policy on Open Access for India. The Shodhganga, a digital repository for theses, was also established in 2011 with the aim of promoting and preserving academic research. The University Grants Commission (UGC) made it mandatory for scholars to deposit their theses in Shodhganga, as per the Minimum Standards and Procedure for Award of M. Phil./Ph.D. Degrees Regulations, 2016. Currently, the Directory of Open Access Journals lists 326 open access journals published in India, of which 233 have no fees.
NARCIS (National Academic Research and Collaboration Information System) of the Netherlands was an online portal for searching Dutch scientific research publications and data. As of July 2018, NARCIS indexed 268,989 data sets and 1,707,486 publications, including a significant proportion of open access works.
The National Documentation Centre is a Greek public organisation that promotes knowledge, research, innovation and digital transformation. It was established in 1980 with funding from the United Nations Development Programme with the aim to strengthen the collection and distribution of research-related material, and to ensure full accessibility to it. It has been designated as a National Scientific Infrastructure, a National Authority of the Hellenic Statistical System, and National Contact Point for European Research and Innovation Programmes. Since August 2019, it has been established as a discrete public-interest legal entity under private law, and is supervised by the Ministry of Digital Governance. The management bodies of EKT are the Administrative Board and the Director who, since 2013, has been Dr. Evi Sachini.

Katja Loos is professor at the Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials of the University of Groningen, The Netherlands holding the chair of Macromolecular Chemistry and New Polymeric Materials.
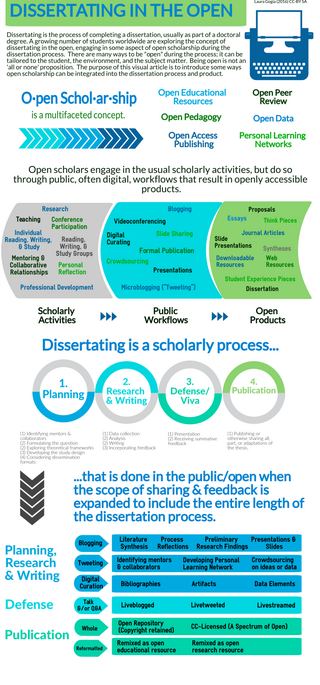
An open thesis, also known as an open dissertation, is a thesis that is freely available for members of the public to access upon publication, and often also during the planning and writing process. The decision to write an open thesis is made by the author, who will usually explain their rationale for creating an open thesis as part of the final published work or while developing it. Writing an open thesis is a process with many decision points regarding where and when to share information openly - from the planning stage, through research and writing, the defense/ voce viva and ultimate publication. Open theses are usually created and located in digital and multimodal formats.
The VSNU Elsevier contract is a legal agreement between Dutch research organisations and the scientific publishers Elsevier. Lasting from 2020 - 2024, the agreement has been portrayed as a significant shift in scholarly publishing, offering individual researchers at Dutch universities unlimited right to freely publish articles in Elsevier journals. While informally known as the VSNU contract, it is signed on behalf of a number of umbrella organisations for research in the Netherlands - the Association of Universities in the Netherlands (VSNU), the Netherlands Federation of University Medical Centres (NFU) and the Dutch Research Council (NWO). The Dutch ICT organisation SURF acted as legal signatories for the contract.











