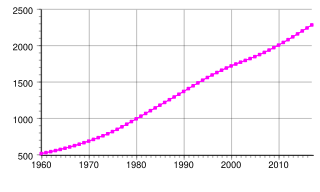
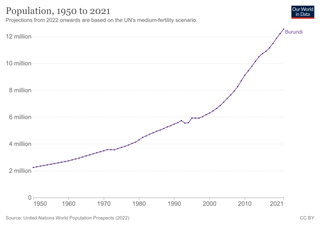
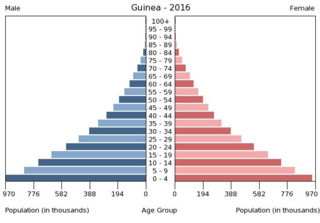
It has been requested that the title of this article be changed to Demographics of eSwatini . Please see the relevant discussion on the discussion page. Do not move the page until the discussion has reached consensus for the change and is closed. |
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Swaziland, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

In biology, a population is the number of all the organisms of the same group or species, which live in a particular geographical area, and have the capability of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is potentially possible between any pair within the area, and where the probability of interbreeding is greater than the probability of cross-breeding with individuals from other areas.
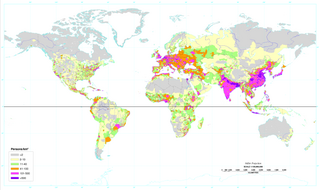
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume; it is a quantity of type number density. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and most of the time to humans. It is a key geographical term. In simple terms population density refers to the number of people living in an area per kilometer square.

An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a category of people who identify with each other based on similarities such as common ancestry, language, history, society, culture or nation. Ethnicity is usually an inherited status based on the society in which one lives. Membership of an ethnic group tends to be defined by a shared cultural heritage, ancestry, origin myth, history, homeland, language or dialect, symbolic systems such as religion, mythology and ritual, cuisine, dressing style, art or physical appearance.
Contents
- Population
- Vital statistics
- Fertility and Births
- Life expectancy at birth
- CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
- Population 2
- Median age
- Age structure
- Sex ratio
- Population growth rate
- Birth rate
- Death rate
- Net migration rate
- Urbanization
- Maternal mortality rate
- Infant mortality rate
- Life expectancy at birth 2
- Total fertility rate
- Education expenditures
- Health expenditures
- Obesity - adult prevalence rate
- Children under the age of 5 years underweight
- Physicians density
- Hospital bed density
- HIV/AIDS
- Major infectious diseases
- Nationality
- Ethnic groups
- Religions[5]
- Languages[5]
- Literacy
- See also
- Notes

The majority of Swaziland's population is ethnic Swazi, mixed with a small number of Zulus and white Africans, predominantly of British and Afrikaner origin. This population also includes a small segment within it that is mixed with any number of these ancestries.

The Swazi or Swati are a Bantu ethnic group of Southern Africa, predominantly inhabiting modern Eswatini and South Africa's Mpumalanga province. The Swati are part of the Nguni family that can be archaeologically traced in East Africa where the same tradition, beliefs and cultural practices are found. The Swati share a unique experience, culture and Royal lineage. This lineage is exclusive to the inhabitants of Eswatini, even though there have been more Swazi people that have moved to South Africa and the United Kingdom in the 20th century. The original inhabitants of Eswatini no longer reside in Eswatini as a majority population while some remain in the land. The Swazi people and the Kingdom of Eswatini today are named after Mswati II, who became king in 1839 after the death of his father King Sobhuza who strategically defeated the British who occupied Swaziland. The Kingdom of Swaziland was a region occupied by the San people of Southern Africa and the current Swazis came in from North Eastern regions through to Mozambique and eventually Swaziland in the 15th century. Mixtures with the San people and other Nguni tribes occurred. Their royal lineage can be traced to a chief named Dlamini I; this is still the royal clan name. About three-quarters of the clan groups are Nguni; the remainder are Sotho, Tsonga, others North East African and San descendants. These groups have intermarried freely. There are slight differences among Swazis as a nation with varying features and skin tones yet Swazi identity extends to all those with allegiance to the twin monarchs Ingwenyama "the Lion" and Indlovukati "the She-Elephant". The dominant Swati language and culture are factors that unify Swazis as a nation since there is no other language spoken except for English.
The Zulu are a Bantu ethnic group of Southern Africa and the largest ethnic group in South Africa, with an estimated 10–12 million people living mainly in the province of KwaZulu-Natal. Small numbers also live in Zimbabwe, Zambia, Tanzania and Mozambique.
The British diaspora in Africa is a population group broadly defined as English-speaking white Africans of mainly British descent who live in or come from Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority live in South Africa and other Southern African countries including Zimbabwe, Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Lesotho (Basutoland) and Swaziland. There are also sizable numbers in Kenya, Nigeria and Ghana. Their first language is usually English. The majority of white Africans who speak English as a first language are of British and Irish descent.
Traditionally Swazis have been subsistence farmers and herders, but most now work in the growing urban formal economy and in government. Some Swazis work in the mines in South Africa. Swaziland also received Portuguese settlers and black refugees from Mozambique. Christianity in Swaziland is sometimes mixed with traditional beliefs and practices. Most Swazis ascribe a special spiritual role to the Swazi Royal Family.

South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by 2,798 kilometres (1,739 mi) of coastline of Southern Africa stretching along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini (Swaziland); and it surrounds the enclaved country of Lesotho. South Africa is the largest country in Southern Africa and the 25th-largest country in the world by land area and, with over 57 million people, is the world's 24th-most populous nation. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World or the Eastern Hemisphere. About 80 percent of South Africans are of Sub-Saharan African ancestry, divided among a variety of ethnic groups speaking different African languages, nine of which have official status. The remaining population consists of Africa's largest communities of European (White), Asian (Indian), and multiracial (Coloured) ancestry.

Portuguese people are a Romance ethnic group indigenous to Portugal that share a common Portuguese culture and speak Portuguese. Their predominant religion is Christianity, mainly Roman Catholicism, though vast segments of the population, especially the younger generations, have no religious affiliation. Historically, the Portuguese people's heritage includes the pre-Celts and Celts. A number of Portuguese descend from converted Jewish and North Africans as a result of the Moorish occupation of the Iberian Peninsula.

Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini (Swaziland) and South Africa to the southwest. The sovereign state is separated from the Comoros, Mayotte and Madagascar by the Mozambique Channel to the east. The capital of Mozambique is Maputo while Matola is the largest city, being a suburb of Maputo.
The country's official languages are Siswati (a language related to Zulu) and English. Government and commercial business is conducted mainly in English. Asians, Afrikaners, Portuguese, and black Mozambicans speak their own languages.

English is a West Germanic language that was first spoken in early medieval England and eventually became a global lingua franca. It is named after the Angles, one of the Germanic tribes that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, as England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula in the Baltic Sea. The language is closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, and its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Norse, and to a greater extent by Latin and French.