
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure, or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring.

Walden inversion is the inversion of a stereogenic center in a chiral molecule in a chemical reaction. Since a molecule can form two enantiomers around a stereogenic center, the Walden inversion converts the configuration of the molecule from one enantiomeric form to the other. For example, in an SN2 reaction, Walden inversion occurs at a tetrahedral carbon atom. It can be visualized by imagining an umbrella turned inside-out in a gale. In the Walden inversion, the backside attack by the nucleophile in an SN2 reaction gives rise to a product whose configuration is opposite to the reactant. Therefore, during SN2 reaction, 100% inversion of product takes place. This is known as Walden inversion.
L-Gulonolactone oxidase is an enzyme that produces vitamin C, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini, in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone (2-keto-gulono-γ-lactone) and hydrogen peroxide. It uses FAD as a cofactor. The L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone then converts to ascorbic acid spontaneously, without enzymatic action.

6-Phosphogluconolactonase (EC 3.1.1.31, 6PGL, PGLS, systematic name 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone lactonohydrolase) is a cytosolic enzyme found in all organisms that catalyzes the hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconic acid in the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway:
Iodolactonization is an organic reaction that forms a ring by the addition of an oxygen and iodine across a carbon-carbon double bond. It is an intramolecular variant of the halohydrin synthesis reaction. The reaction was first reported by M. J. Bougalt in 1904 and has since become one of the most effective ways to synthesize lactones. Strengths of the reaction include the mild conditions and incorporation of the versatile iodine atom into the product.
In enzymology, a glucuronolactone reductase (EC 1.1.1.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an uronate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.203) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-galactonolactone oxidase (EC 1.3.3.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of Camptotheca acuminata, a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically more recently in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today: topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also been found in other plants including Chonemorpha fragrans.
The enzyme limonin-D-ring-lactonase (EC 3.1.1.36) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme xylono-1,4-lactonase (EC 3.1.1.68) catalyzes the reaction

Lactonase (EC 3.1.1.81, acyl-homoserine lactonase; systematic name N-acyl-L-homoserine-lactone lactonohydrolase) is a metalloenzyme, produced by certain species of bacteria, which targets and inactivates acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs). It catalyzes the reaction
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by Masaru Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.
Streptogramin A is a group of antibiotics within the larger family of antibiotics known as streptogramins. They are synthesized by the bacteria Streptomyces virginiae. The streptogramin family of antibiotics consists of two distinct groups: group A antibiotics contain a 23-membered unsaturated ring with lactone and peptide bonds while group B antibiotics are depsipeptides. While structurally different, these two groups of antibiotics act synergistically, providing greater antibiotic activity than the combined activity of the separate components. These antibiotics have until recently been commercially manufactured as feed additives in agriculture, although today there is increased interest in their ability to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria, particularly vancomycin-resistant bacteria.

Absinthin is a naturally produced triterpene lactone from the plant Artemisia absinthium (Wormwood). It constitutes one of the most bitter chemical agents responsible for absinthe's distinct taste. The compound shows biological activity and has shown promise as an anti-inflammatory agent, and should not to be confused with thujone, a neurotoxin also found in Artemisia absinthium.

Aucubin is an iridoid glycoside. Iridoids are commonly found in plants and function as defensive compounds. Iridoids decrease the growth rates of many generalist herbivores.

Cobalamin biosynthesis is the process by which bacteria and archea make cobalamin, vitamin B12. Many steps are involved in converting aminolevulinic acid via uroporphyrinogen III and adenosylcobyric acid to the final forms in which it is used by enzymes in both the producing organisms and other species, including humans who acquire it through their diet.
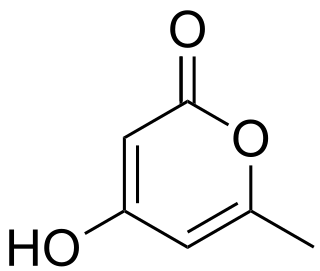
Triacetic acid lactone is an organic compound derived enzymatically from glucose. It is a light yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Lipase inhibitors belong to a drug class that is used as an antiobesity agent. Their mode of action is to inhibit gastric and pancreatic lipases, enzymes that play an important role in the digestion of dietary fat. Lipase inhibitors are classified in the ATC-classification system as A08AB . Numerous compounds have been either isolated from nature, semi-synthesized, or fully synthesized and then screened for their lipase inhibitory activity but the only lipase inhibitor on the market is orlistat . Lipase inhibitors have also shown anticancer activity, by inhibiting fatty acid synthase.











