Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.
An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis.
Thioesterases are enzymes which belong to the esterase family. Esterases, in turn, are one type of the several hydrolases known.
The enzyme acetylesterase (EC 3.1.1.6) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme acylcarnitine hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.28) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme carboxylesterase (or carboxylic-ester hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.1; systematic name carboxylic-ester hydrolase) catalyzes reactions of the following form:
The enzyme feruloyl esterase (EC 3.1.1.73) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5) catalyzes the reaction

The enzyme polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase (EC 3.1.1.78) catalyzes the following reaction:

The enzyme protein-glutamate methylesterase (EC 3.1.1.61) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme S-formylglutathione hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.12) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme sterol esterase (EC 3.1.1.13) catalyzes the reaction
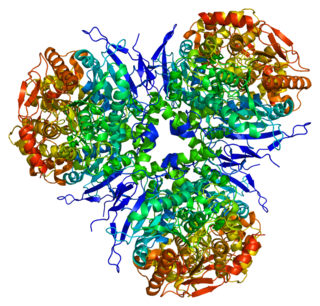
Liver carboxylesterase 1 also known as carboxylesterase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES1 gene. The protein is also historically known as serine esterase 1 (SES1), monocyte esterase and cholesterol ester hydrolase (CEH). Three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene. The various protein products from isoform a, b and c range in size from 568, 567 and 566 amino acids long, respectively.

Acyl-CoA thioesterase 2, also known as ACOT2, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ACOT2 gene.

Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACOT4 gene.

Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 11 also known as StAR-related lipid transfer protein 14 (STARD14) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACOT11 gene. This gene encodes a protein with acyl-CoA thioesterase activity towards medium (C12) and long-chain (C18) fatty acyl-CoA substrates which relies on its StAR-related lipid transfer domain. Expression of a similar murine protein in brown adipose tissue is induced by cold exposure and repressed by warmth. Expression of the mouse protein has been associated with obesity, with higher expression found in obesity-resistant mice compared with obesity-prone mice. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms.

The enzyme triacylglycerol lipase (also triglyceride lipase, EC 3.1.1.3;systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of ester linkages of triglycerides:
The enzyme Pimelyl-[acyl-carrier protein] methyl ester esterase (EC 3.1.1.85, BioH; systematic name pimelyl-[acyl-carrier protein] methyl ester hydrolase catalyses the reaction
The enzyme mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide esterase (EC 3.1.1.93, mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide deglucuronidase; AcMPAG deglucuronidase; systematic name mycophenolic acid O-acyl-glucuronide-ester hydrolase), is in humans encoded by the ABHD10 gene, and catalyses the reaction

Acyl-CoA thioesterase 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACOT1 gene.






