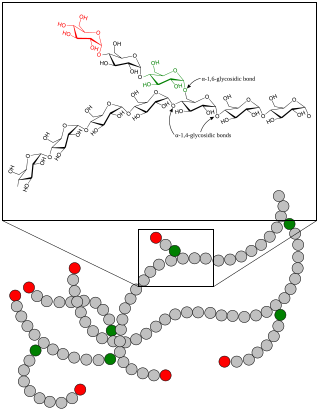
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycle, in the liver, and also activated by insulin in response to high glucose levels.

Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes. Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphorylase is also studied as a model protein regulated by both reversible phosphorylation and allosteric effects.
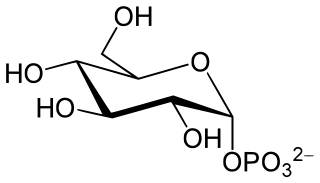
Glucose 1-phosphate is a glucose molecule with a phosphate group on the 1'-carbon. It can exist in either the α- or β-anomeric form.

The enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.9, G6Pase; systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate phosphohydrolase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate, resulting in the creation of a phosphate group and free glucose:

3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterases (EC 3.1.4.17) are a family of phosphodiesterases. Generally, these enzymes hydrolyze a nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate to a nucleoside 5′-phosphate:

6-Phosphogluconolactonase (EC 3.1.1.31, 6PGL, PGLS, systematic name 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone lactonohydrolase) is a cytosolic enzyme found in all organisms that catalyzes the hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconic acid in the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway:

Sucrose phosphorylase is an important enzyme in the metabolism of sucrose and regulation of other metabolic intermediates. Sucrose phosphorylase is in the class of hexosyltransferases. More specifically it has been placed in the retaining glycoside hydrolases family although it catalyzes a transglycosidation rather than hydrolysis. Sucrose phosphorylase catalyzes the conversion of sucrose to D-fructose and α-D-glucose-1-phosphate. It has been shown in multiple experiments that the enzyme catalyzes this conversion by a double displacement mechanism.
In enzymology, a phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.44) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme dolichylphosphate-glucose phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.48) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme glycerophosphoinositol inositolphosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.43) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme Inositol phosphate-phosphatase is of the phosphodiesterase family of enzymes. It is involved in the phosphophatidylinositol signaling pathway, which affects a wide array of cell functions, including but not limited to, cell growth, apoptosis, secretion, and information processing. Inhibition of inositol monophosphatase may be key in the action of lithium in treating bipolar disorder, specifically manic depression.
The enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester α-N-acetylglucosaminidase (EC 3.1.4.45) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme 6-phospho-β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.86) catalyzes the following reaction:
The enzyme α,α-phosphotrehalase (EC 3.2.1.93) catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
The enzyme maltose-6′-phosphate glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.122) catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a gluconokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-glucose—glycoprotein glucose phosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (coenzyme-F420) is an enzyme with systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate:F420 1-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










