Related Research Articles
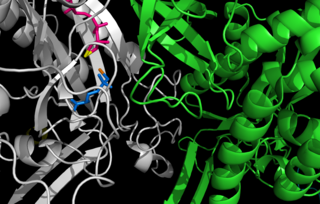
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen by catalyzing the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine:
sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate is the organic ion with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OPO32-. It is one of three stereoisomers of the ester of dibasic phosphoric acid (HOPO32-) and glycerol. It is a component of glycerophospholipids. From a historical reason, it is also known as L-glycerol 3-phosphate, D-glycerol 1-phosphate, L-α-glycerophosphoric acid.

Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible redox conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to sn-glycerol 3-phosphate.
In enzymology, a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD(P)+) (EC 1.2.1.59) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

o-Succinylbenzoate—CoA ligase, encoded from the menE gene in Escherichia coli, catalyzes the fifth reaction in the synthesis of menaquinone. This pathway is called 1, 4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate biosynthesis I. Vitamin K is a quinone that serves as an electron transporter during anaerobic respiration. This process of anaerobic respiration allows the bacteria to generate the energy required to survive.

ADP-ribose diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction in which water nucleophilically attacks ADP-ribose to produce AMP and D-ribose 5-phosphate. Enzyme hydrolysis occurs by the breakage of a phosphoanhydride bond and is dependent on Mg2+ ions that are held in complex by the enzyme.
The enzyme glycerol-1-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.21) catalyzes the reaction
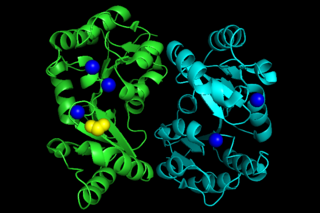
Phosphoglycolate phosphatase(EC 3.1.3.18; systematic name 2-phosphoglycolate phosphohydrolase), also commonly referred to as phosphoglycolate hydrolase, 2-phosphoglycolate phosphatase, P-glycolate phosphatase, and phosphoglycollate phosphatase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of 2-phosphoglycolate into glycolate and phosphate:
In enzymology, a 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diglucosyl diacylglycerol synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucosylglycerol-phosphate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 is a strain of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria. Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 is capable of both phototrophic growth by oxygenic photosynthesis during light periods and heterotrophic growth by glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation during dark periods. Gene expression is regulated by a circadian clock and the organism can effectively anticipate transitions between the light and dark phases.

The psaA RNA motif describes a class of RNAs with a common secondary structure. psaA RNAs are exclusively found in locations that presumably correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of operons formed of psaA and psaB genes. For this reason, it was hypothesized that psaA RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements of these genes. The psaAB genes encode proteins that form subunits in the photosystem I structure used for photosynthesis. psaA RNAs have been detected only in cyanobacteria, which is consistent with their association with photosynthesis.
Glycerol-3-phosphate 2-O-acyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acyl-CoA:sn-glycerol 3-phosphate 2-O-acyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucosyl-3-phosphoglycerate phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.85, GpgP protein) is an enzyme with systematic name α-D-glucosyl-3-phospho-D-glycerate phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Cyanophycinase (EC 3.4.15.6, cyanophycin degrading enzyme, beta-Asp-Arg hydrolysing enzyme, CGPase, CphB, CphE, cyanophycin granule polypeptidase, extracellular CGPase) is an enzyme. It catalyses the following chemical reaction

Cyanothece is a genus of unicellular, diazotrophic, oxygenic photosynthesizing cyanobacteria.
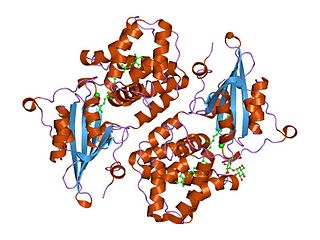
Orange carotenoid protein (OCP) is a water-soluble protein which plays a role in photoprotection in diverse cyanobacteria. It is the only photoactive protein known to use a carotenoid as the photoresponsive chromophore. The protein consists of two domains, with a single keto-carotenoid molecule non-covalently bound between the two domains. It is a very efficient quencher of excitation energy absorbed by the primary light-harvesting antenna complexes of cyanobacteria, the phycobilisomes. The quenching is induced by blue-green light. It is also capable of preventing oxidative damage by directly scavenging singlet oxygen (1O2).
Myxoxanthophyll is a carotenoid glycoside pigment present in the photosynthetic apparatus of cyanobacteria. It is named after the word "Myxophyceae", a former term for cyanobacteria. As a monocyclic xanthophyll, it has a yellowish color. It is required for normal cell wall structure and thylakoid organization in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. The pigment is unusual because it is glycosylated on the 2'-OH rather than the 1'-OH position of the molecule. Myxoxanthophyll was first isolated from Oscillatoria rubenscens in 1936.
References
- Hagemann M; Erdmann N (1994). "Activation and pathway of glucosylglycerol biosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803". Microbiology. 140 (6): 1427–1431. doi: 10.1099/00221287-140-6-1427 .
- Hagemann M, Richter S, Zuther E, Schoor A (1996). "Characterization of a glucosylglycerol-phosphate-accumulating, salt-sensitive mutant of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803". Arch. Microbiol. 166 (2): 83–91. doi:10.1007/s002030050360. PMID 8772170.
- Hagemann M, Schoor A, Jeanjean R, Zuther E, Joset F (1997). "The stpA gene form Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 encodes the glucosylglycerol-phosphate phosphatase involved in cyanobacterial osmotic response to salt shock". J. Bacteriol. 179 (5): 1727–33. PMC 178888 . PMID 9045835.