Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.

β-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as 3-hydroxybutyric acid or BHB, is an organic compound and a beta hydroxy acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CO2H; its conjugate base is β-hydroxybutyrate, also known as 3-hydroxybutyrate. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is a chiral compound with two enantiomers: D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and L-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Its oxidized and polymeric derivatives occur widely in nature. In humans, D-β-hydroxybutyric acid is one of two primary endogenous agonists of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).

Glycoside hydrolases catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cellulase), hemicellulose, and starch (amylase), in anti-bacterial defense strategies, in pathogenesis mechanisms and in normal cellular function. Together with glycosyltransferases, glycosidases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of glycosidic bonds.
Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens KI72, popularly known as nylon-eating bacteria, is a strain of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens that can digest certain by-products of nylon 6 manufacture. It uses a set of enzymes to digest nylon, popularly known as nylonase.
Paucimonas lemoignei, formerly [Pseudomonas lemoignei], is a Gram-negative soil bacterium. It is aerobic, motile, and rod-shaped.

In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.61) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.83) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a beta-diketone hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme acetolactate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.5) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.55) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme acetoacetyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.11) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme phorbol-diester hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.51) catalyzes the reaction
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase (EC 3.1.1.75, PHB depolymerase, systematic name poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutanoate] hydrolase) is an enzyme used in the degradation processes of a natural polyester poly(3-hydroxyburate). This enzyme has growing commercialization interests due to it implications in biodegradable plastic decomposition.
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.2.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
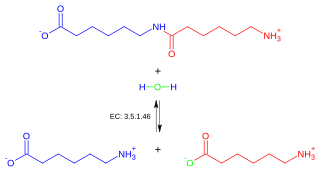
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.46) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate + H2O 2 6-aminohexanoate. Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate and H2O, whereas its product is two molecules of 6-aminohexanoate.
In enzymology, a gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.94) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a formylmethanofuran-tetrahydromethanopterin N-formyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BDH1 gene.








