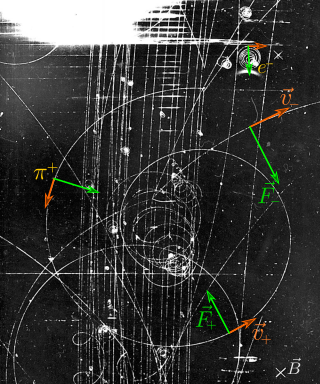
In physics, the Lorentz force is the combination of electric and magnetic force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. A particle of charge q moving with a velocity v in an electric field E and a magnetic field B experiences a force of

The Navier–Stokes equations are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances, named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and Irish physicist and mathematician George Gabriel Stokes. They were developed over several decades of progressively building the theories, from 1822 (Navier) to 1842-1850 (Stokes).
In statistical mechanics and information theory, the Fokker–Planck equation is a partial differential equation that describes the time evolution of the probability density function of the velocity of a particle under the influence of drag forces and random forces, as in Brownian motion. The equation can be generalized to other observables as well. The Fokker-Planck equation has multiple applications in information theory, graph theory, data science, finance, economics etc.

In mathematics, the Laplace operator or Laplacian is a differential operator given by the divergence of the gradient of a scalar function on Euclidean space. It is usually denoted by the symbols , (where is the nabla operator), or . In a Cartesian coordinate system, the Laplacian is given by the sum of second partial derivatives of the function with respect to each independent variable. In other coordinate systems, such as cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the Laplacian also has a useful form. Informally, the Laplacian Δf (p) of a function f at a point p measures by how much the average value of f over small spheres or balls centered at p deviates from f (p).
In mathematics, Itô's lemma or Itô's formula is an identity used in Itô calculus to find the differential of a time-dependent function of a stochastic process. It serves as the stochastic calculus counterpart of the chain rule. It can be heuristically derived by forming the Taylor series expansion of the function up to its second derivatives and retaining terms up to first order in the time increment and second order in the Wiener process increment. The lemma is widely employed in mathematical finance, and its best known application is in the derivation of the Black–Scholes equation for option values.
Linear elasticity is a mathematical model of how solid objects deform and become internally stressed due to prescribed loading conditions. It is a simplification of the more general nonlinear theory of elasticity and a branch of continuum mechanics.
The Feynman–Kac formula, named after Richard Feynman and Mark Kac, establishes a link between parabolic partial differential equations (PDEs) and stochastic processes. In 1947, when Kac and Feynman were both Cornell faculty, Kac attended a presentation of Feynman's and remarked that the two of them were working on the same thing from different directions. The Feynman–Kac formula resulted, which proves rigorously the real case of Feynman's path integrals. The complex case, which occurs when a particle's spin is included, is still an open question.

In physics, the Hamilton–Jacobi equation, named after William Rowan Hamilton and Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi, is an alternative formulation of classical mechanics, equivalent to other formulations such as Newton's laws of motion, Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics.
In stochastic processes, the Stratonovich integral or Fisk–Stratonovich integral is a stochastic integral, the most common alternative to the Itô integral. Although the Itô integral is the usual choice in applied mathematics, the Stratonovich integral is frequently used in physics.

Toroidal coordinates are a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system that results from rotating the two-dimensional bipolar coordinate system about the axis that separates its two foci. Thus, the two foci and in bipolar coordinates become a ring of radius in the plane of the toroidal coordinate system; the -axis is the axis of rotation. The focal ring is also known as the reference circle.

In mathematics, parabolic cylindrical coordinates are a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system that results from projecting the two-dimensional parabolic coordinate system in the perpendicular -direction. Hence, the coordinate surfaces are confocal parabolic cylinders. Parabolic cylindrical coordinates have found many applications, e.g., the potential theory of edges.

The shallow-water equations (SWE) are a set of hyperbolic partial differential equations that describe the flow below a pressure surface in a fluid. The shallow-water equations in unidirectional form are also called Saint-Venant equations, after Adhémar Jean Claude Barré de Saint-Venant.

There are various mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field that are used in the study of electromagnetism, one of the four fundamental interactions of nature. In this article, several approaches are discussed, although the equations are in terms of electric and magnetic fields, potentials, and charges with currents, generally speaking.
The intent of this article is to highlight the important points of the derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations as well as its application and formulation for different families of fluids.
In mathematics — specifically, in stochastic analysis — Dynkin's formula is a theorem giving the expected value of any suitably smooth statistic of an Itō diffusion at a stopping time. It may be seen as a stochastic generalization of the (second) fundamental theorem of calculus. It is named after the Russian mathematician Eugene Dynkin.
In mathematics — specifically, in stochastic analysis — the Green measure is a measure associated to an Itō diffusion. There is an associated Green formula representing suitably smooth functions in terms of the Green measure and first exit times of the diffusion. The concepts are named after the British mathematician George Green and are generalizations of the classical Green's function and Green formula to the stochastic case using Dynkin's formula.
In the theory of stochastic processes, filtering describes the problem of determining the state of a system from an incomplete and potentially noisy set of observations. While originally motivated by problems in engineering, filtering found applications in many fields from signal processing to finance.
The Cauchy momentum equation is a vector partial differential equation put forth by Cauchy that describes the non-relativistic momentum transport in any continuum.
Lagrangian field theory is a formalism in classical field theory. It is the field-theoretic analogue of Lagrangian mechanics. Lagrangian mechanics is used to analyze the motion of a system of discrete particles each with a finite number of degrees of freedom. Lagrangian field theory applies to continua and fields, which have an infinite number of degrees of freedom.
Quantum stochastic calculus is a generalization of stochastic calculus to noncommuting variables. The tools provided by quantum stochastic calculus are of great use for modeling the random evolution of systems undergoing measurement, as in quantum trajectories. Just as the Lindblad master equation provides a quantum generalization to the Fokker–Planck equation, quantum stochastic calculus allows for the derivation of quantum stochastic differential equations (QSDE) that are analogous to classical Langevin equations.

































































