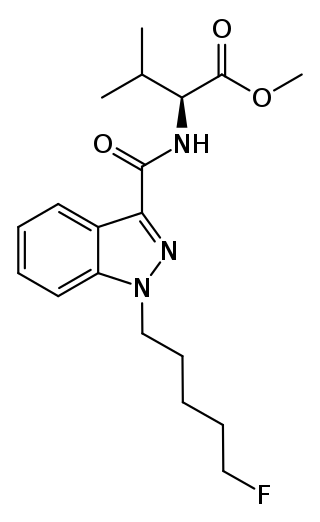
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|
| 7297 | 5-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)-2-[(1R,3S)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-phenol (CP-47,497) |
| 7298 | 5-(1,1-dimethyloctyl)-2-[(1R,3S)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-phenol (cannabicyclohexanol or CP-47,497 C8-homolog) |
| 7118 | 1-pentyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-018 and AM678) |
| 7173 | 1-butyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-073) |
| 7019 | 1-hexyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-019) |
| 7200 | 1-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl]-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-200) |
| 6250 | 1-pentyl-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole (JWH-250) |
| 7081 | 1-pentyl-3-[1-(4-methoxynaphthoyl)]indole (JWH-081) |
| 7122 | 1-pentyl-3-(4-methyl-1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-122) |
| 7398 | 1-pentyl-3-(4-chloro-1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-398) |
| 7201 | 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (AM2201) |
| 7694 | 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole (AM694) |
| 7104 | 1-pentyl-3-[(4-methoxy)-benzoyl]indole (SR-19 and RCS-4) |
| 7008 | 1-cyclohexylethyl-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole 7008 (SR-18 and RCS-8) |
| 7203 | 1-pentyl-3-(2-chlorophenylacetyl)indole (JWH-203) |
| 7144 | (1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)methanone, its optical, positional, and geometric isomers, salts and salts of isomers (UR-144, 1-pentyl-3-(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropoyl)indole) |
| 7011 | [1-(5-fluoro-pentyl)-1H-indol-3-yl](2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)methanone, its optical, positional, and geometric isomers, salts and salts of isomers (5-fluoro-UR-144, 5-F-UR-144, XLR-11, 1-(5-fluoro-pentyl)-3-(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropoyl)indole) |
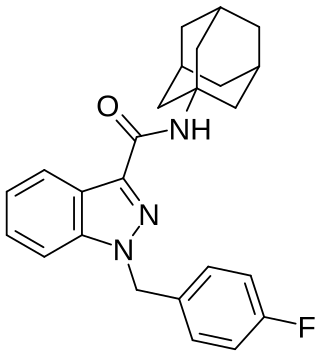
| 7048 | N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide, its optical, positional, and geometric isomers, salts and salts of isomers (APINACA, AKB-48) |
| 7222 | Quinolin-8-yl 1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxylate (QUPIC, PB-22) [21] |
| 7225 | Quinolin-8-yl 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate (5-fluoro-PB-22; 5F-PB-22) [21] |
| 7012 | N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-FUBINACA) [21] |
| 7035 | N-(1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (ADB-PINACA) [21] |
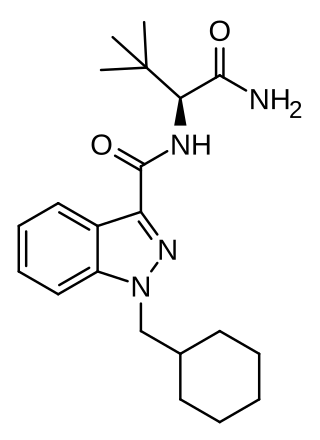
| 7031 | N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-CHMINACA) [22] |
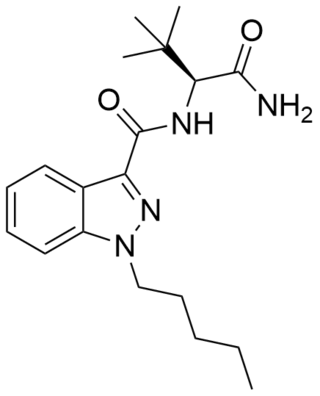
| 7023 | N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-PINACA) [22] |
| 7024 | [1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl](naphthalen-1-yl)methanone (THJ-2201) [22] |
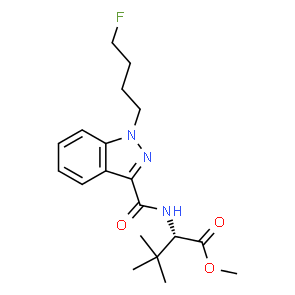
| 7034 | 2-(1-(5-Fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (5F-ADB, 5F-MDMB-PINACA) [23] |
| 7033 | Methyl 2-(1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3-methylbutanoate (5F-AMB) [23] |
| 7049 | N-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (5F-APINACA, 5F-AKB48) [23] |
| 7010 | N-(1-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (ADB-FUBINACA) [23] |
| 7042 | Methyl 2-(1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (MDMB-CHMICA, MMB-CHMINACA) [23] |
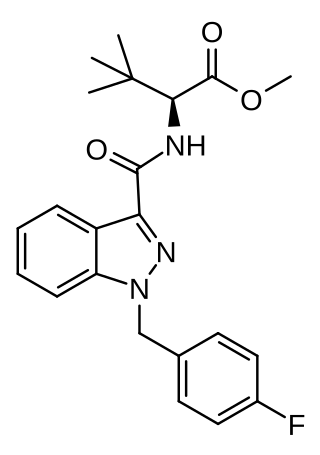
| 7020 | Methyl 2-(1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (MDMB-FUBINACA) [23] |
| 7032 | N-(1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (MAB-CHMINACA; ADB-CHMINACA) [24] |
| 7036 | ethyl 2-(1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (5F-EDMB-PINACA) [25] |
| 7041 | methyl 2-(1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (5F-MDMB-PICA) [25] |
| 7047 | N-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (FUB-AKB48; FUB-APINACA; AKB48 N-(4-FLUOROBENZYL)) [25] |
| 7083 | 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-N-(2-phenylpropan-2-yl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (5F-CUMYL-PINACA; SGT-25) [25] |
| 7014 | (1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl) methanone (FUB-144) [25] |
| 7021 | Methyl 2-(1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1Hindazole-3-carboxamido)-3-methylbutanoate (FUB–AMB, MMB– FUBINACA, AMB–FUBINACA) |
| 7025 | 5F-AB-PINACA (N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide) |
| 7044 | MMB-CHMICA (AMB-CHMICA, methyl 2-(1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamido)-3-methylbutanoate) |
| 7085 | 5F-CUMYL-P7AICA (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-N-(2-phenylpropan-2-yl)-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carboxamide) |
| 7089 | 4-CN-CUMYL-BUTINACA (1-(4-cyanobutyl)-N-(2-phenylpropan-2-yl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide, 4-cyano-CUMYL-BUTINACA, 4-CN-CUMYL BINACA, CUMYL-4CN-BINACA, SGT-78) |
| 7221 | NM-2201 (CBL2201, Naphthalen-1-yl 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate) |