Dextromoramide is a powerful opioid analgesic approximately three times more potent than morphine but shorter acting. It is subject to drug prohibition regimes, both internationally through UN treaties and by the criminal law of individual nations, and is usually prescribed only in the Netherlands.

Levomethorphan (LVM) (INN, BAN) is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that has never been marketed. It is the L-stereoisomer of racemethorphan (methorphan). The effects of the two isomers of racemethorphan are quite different, with dextromethorphan (DXM) being an antitussive at low doses and a dissociative hallucinogen at much higher doses. Levomethorphan is about five times stronger than morphine.

Methorphan comes in two isomeric forms, each with differing pharmacology and effects:

Lefetamine (Santenol) is a drug which is a stimulant and also an analgesic with effects comparable to codeine.

Tilidine, sold under the brand name Valoron among others, is a synthetic opioid analgesic, used mainly in Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, Luxembourg, South Africa, and Switzerland for the treatment of moderate to severe pain, both acute and chronic. Its onset of pain relief after oral administration is about 10–15 minutes and peak relief from pain occurs about 25–50 minutes after administration.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic and non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.
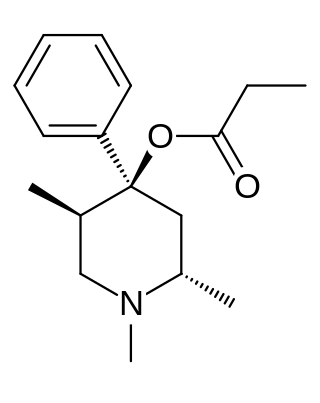
Trimeperidine (Promedol) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of prodine. It was developed in the early 1950s in the USSR during research into the related drug pethidine.

Meprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of pethidine (meperidine). It is closely related to the drug prodine, the only difference being that meprodine has an ethyl group rather than a methyl at the 3-position of the piperidine ring.

Proheptazine is an opioid analgesic related to pethidine. It was invented in the 1960s.

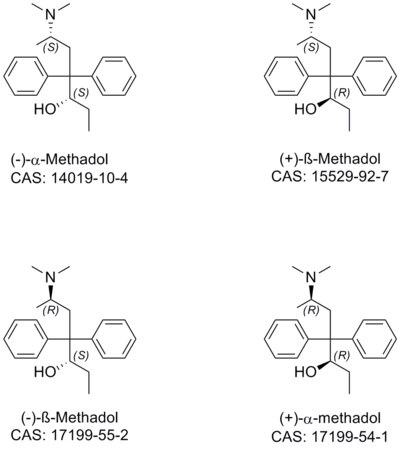
Acetylmethadol, also known as methadyl acetate, is a synthetic opioid analgesic. It is a racemic mixture of alphacetylmethadol (α-acetylmethadol) and betacetylmethadol (β-acetylmethadol), which are in turn racemic mixtures of levacetylmethadol and D-α-acetylmethadol and L-β-acetylmethadol and D-β-acetylmethadol, respectively. Hence, acetylmethadol has four possible optical isomers. All of these isomers have been shown to partially or fully substitute for the discriminative stimulus effects of heroin in rats, and thus it can be inferred that, in addition to LAAM which is used clinically as such, they are all likely to be active opioid analgesics in humans.

Alphamethadol (INN), or α-methadol, also known as alfametadol, is a synthetic opioid analgesic. It is an isomer of dimepheptanol (methadol), the other being betamethadol (β-methadol). Alphamethadol is composed of two isomers itself, L-α-methadol, and D-α-methadol. Both of alphamethadol's isomers bind to and activate the μ-opioid receptor and are active as opioid analgesics, similarly to those of alphacetylmethadol (α-acetylmethadol).

Betamethadol (INN), or β-methadol, also known as betametadol, is a synthetic opioid analgesic. It is an isomer of dimepheptanol (methadol), the other being alphamethadol (α-methadol). Betamethadol is composed of two isomers itself, L-β-methadol, and D-β-methadol. Based on structure-activity relationships it can be inferred that both isomers are likely to be active as opioid analgesics, similarly to those of betacetylmethadol (β-acetylmethadol).
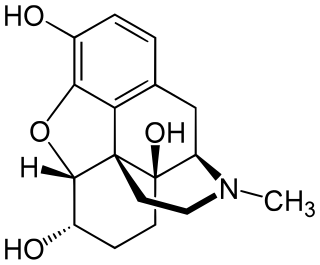
Hydromorphinol, is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation, analgesia and respiratory depression, but is twice as potent as morphine and has a steeper dose-response curve and longer half-life. It is used in medicine as the bitartrate salt and hydrochloride

Levomoramide is the inactive isomer of the opioid analgesic dextromoramide, invented by the chemist Paul Janssen in 1956. Unlike dextromoramide, which is a potent analgesic with high abuse potential, levomoramide is virtually without activity.

Methyldesorphine is an opioid analgesic. First synthesized in Germany in 1940 and patented in the US in 1952, it has a high potential for abuse as with any potent opioid agonist, and is sometimes found along with desomorphine as a component of the home-made opioid mixture known as "Krokodil" used in Russia and the neighboring former Soviet republics. It is approximately 15 times more potent than morphine as an analgesic but if the 6-7 bond is saturated, the β isomer is some 50 times more potent than morphine.

Racemoramide, or simply moramide, is an opioid analgesic and a racemic mixture of the substances dextromoramide and levomoramide, two enantiomers of a chiral molecule.

Racemorphan, or morphanol, is the racemic mixture of the two stereoisomers of 17-methylmorphinan-3-ol, each with differing pharmacology and effects:

Isomethadone (INN, BAN; trade name Liden; also known as isoamidone) is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive related to methadone that was used formerly as a pharmaceutical drug but is now no longer marketed. Isomethadone was used as both an analgesic and antitussive. It binds to and activates both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with the (S)-isomer being the more potent of the two enantiomers. Isomethadone is a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States, with an ACSCN of 9226 and a 2014 aggregate manufacturing quota of 5 g. The salts in use are the hydrobromide (HBr, free base conversion ratio 0.793), hydrochloride (HCl, 0.894), and HCl monohydrate (0.850). Isomethadone is also regulated internationally as a Schedule I controlled substance under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961.

Alphacetylmethadol (INN), or α-acetylmethadol (AAM), is a synthetic opioid analgesic. Its levorotary enantiomer, levacetylmethadol, is an FDA-approved treatment for opioid addiction; however as of 2003 it is no longer used in the United States for this purpose. Alphacetylmethadol is very similar in structure to methadone, a widely prescribed treatment for opioid addiction. In the United States, it is a Schedule I controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act, with an ACSCN of 9603 and a 2013 annual manufacturing quota of 2 grammes.

Noracymethadol (INN) is a synthetic opioid analgesic related to methadone that was never marketed. In a clinical trial of postpartum patients it was reported to produce analgesia comparable to that of morphine but with less nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness. Other side effects included salivation, ataxia, and respiratory depression that was reversible by naloxone. Similarly to many of its analogues, noracymethadol is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States with an ACSCN of 9633 and 2013 annual manufacturing quota of 12 grammes. and is also controlled internationally under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961. The salts known are the gluconate and hydrochloride (0.903).