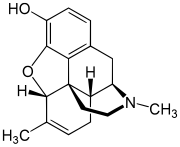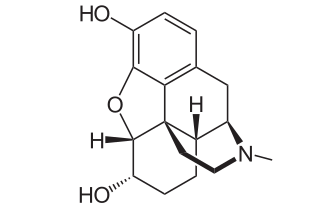
Dihydromorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid structurally related to and derived from morphine. The 7,8-double bond in morphine is reduced to a single bond to get dihydromorphine. Dihydromorphine is a moderately strong analgesic and is used clinically in the treatment of pain and also is an active metabolite of the analgesic opioid drug dihydrocodeine. Dihydromorphine occurs in trace quantities in assays of opium on occasion, as does dihydrocodeine, dihydrothebaine, tetrahydrothebaine, etc. The process for manufacturing dihydromorphine from morphine for pharmaceutical use was developed in Germany in the late 19th century, with the synthesis being published in 1900 and the drug introduced clinically as Paramorfan shortly thereafter. A high-yield synthesis from tetrahydrothebaine was later developed.

Dextromoramide is a powerful opioid analgesic approximately three times more potent than morphine but shorter acting. It is subject to drug prohibition regimes, both internationally through UN treaties and by the criminal law of individual nations, and is usually prescribed only in the Netherlands.

Levomethorphan (LVM) (INN, BAN) is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that has never been marketed. It is the L-stereoisomer of racemethorphan (methorphan). The effects of the two isomers of racemethorphan are quite different, with dextromethorphan (DXM) being an antitussive at low doses and a dissociative hallucinogen at much higher doses. Levomethorphan is about five times stronger than morphine.

Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the Netherlands. It comes in free form, is about 0.75x times as potent as morphine and is given parenterally for the treatment of severe pain. Nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression and constipation are believed to be less frequent with piritramide than with morphine, and it produces more rapid-onset analgesia when compared to morphine and pethidine. After intravenous administration the onset of analgesia is as little as 1–2 minutes, which may be related to its great lipophilicity. The analgesic and sedative effects of piritramide are believed to be potentiated with phenothiazines and its emetic (nausea/vomiting-inducing) effects are suppressed. The volume of distribution is 0.7-1 L/kg after a single dose, 4.7-6 L/kg after steady-state concentrations are achieved and up to 11.1 L/kg after prolonged dosing.

Thebacon, or dihydrocodeinone enol acetate, is a semisynthetic opioid that is similar to hydrocodone and is most commonly synthesised from thebaine. Thebacon was invented in Germany in 1924, four years after the first synthesis of hydrocodone. Thebacon is a derivative of acetyldihydrocodeine, where only the 6–7 double bond is saturated. Thebacon is marketed as its hydrochloride salt under the trade name Acedicon, and as its bitartrate under Diacodin and other trade names. The hydrochloride salt has a free base conversion ratio of 0.846. Other salts used in research and other settings include thebacon's phosphate, hydrobromide, citrate, hydroiodide, and sulfate.

Metopon is an opioid analogue that is a methylated derivative of hydromorphone which was invented in 1929 as an analgesic.

Benzylmorphine (Peronine) is a semi-synthetic opioid narcotic introduced to the international market in 1896 and that of the United States very shortly thereafter. It is much like codeine, containing a benzyl group attached to the morphine molecule just as the methyl group creates codeine and the ethyl group creates ethylmorphine or dionine. It is about 90% as strong as codeine by weight.

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

Nalorphine is a mixed opioid agonist–antagonist with opioid antagonist and analgesic properties. It was introduced in 1954 and was used as an antidote to reverse opioid overdose and in a challenge test to determine opioid dependence.

Phenomorphan is an opioid analgesic. It is not currently used in medicine, but has similar side-effects to other opiates, which include itching, nausea and respiratory depression.
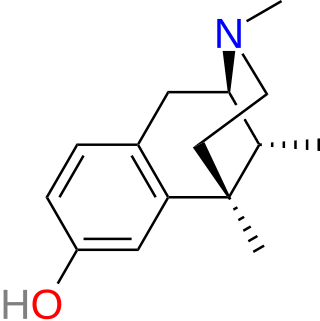
Metazocine is an opioid analgesic related to pentazocine. While metazocine has significant analgesic effects, mediated through a mixed agonist–antagonist action at the mu opioid receptor, its clinical use is limited by dysphoric and hallucinogenic effects which are most likely caused by activity at kappa opioid receptors and/or sigma receptors.

Prodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of pethidine (meperidine). It was developed in Germany in the late 1940s.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic and non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.

Phenazocine is an opioid analgesic drug, which is related to pentazocine and has a similar profile of effects.
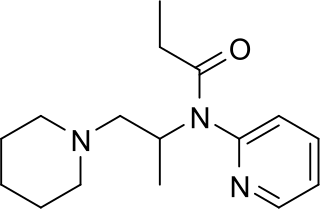
Propiram is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist and weak μ antagonist analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs related to other drugs such as phenampromide and diampromide. It was invented in 1963 in the United Kingdom by Bayer but was not widely marketed, although it saw some limited clinical use, especially in dentistry. Propiram reached Phase III clinical trials in the United States and Canada.

Phenampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and diampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid Co. Although never given a general release, it was research found that 60 mg of phenampromide is equivalent to about 50 mg of codeine. Tests on its two enantiomers showed that all of the analgesic effects were caused by the (S)-isomer. Introduction of a phenyl group to the 4-position of the piperidine-ring produces a drug 60-fold more potent than morphine. The most potent reported derivative is 4-hydroxy-4-phenyl phenapromide which displays analgesic activity some x150 greater than morphine.

Desomorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid commercialized by Roche, with powerful, fast-acting effects, such as sedation and analgesia. It was first discovered and patented in Germany by a German team working for Knoll in 1920 but was not generally recognized. It was later synthesized in 1932 by American chemist Lyndon Frederick Small. Small also successfully patented it in 1934 in the United States. Desomorphine was used in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland under the brand name Permonid and was described as having a fast onset and a short duration of action, with relatively little nausea compared to equivalent doses of morphine. Dose for dose it is roughly ten times more potent than morphine, with 1 mg desomorphine being equivalent 10 mg morphine, via the intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) routes.

Levophenacylmorphan is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It has potent analgesic effects and is around 10x more potent than morphine. Adverse effects associated with its use are those of the opioids as a whole, including pruritus, nausea, respiratory depression, euphoria and development of tolerance and dependence to its effects.
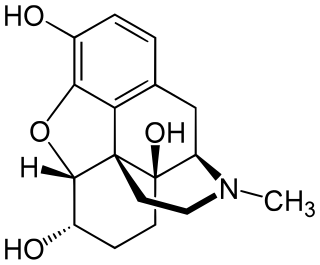
Hydromorphinol, is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation, analgesia and respiratory depression, but is twice as potent as morphine and has a steeper dose-response curve and longer half-life. It is used in medicine as the bitartrate salt and hydrochloride

Isomethadone (INN, BAN; trade name Liden; also known as isoamidone) is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive related to methadone that was used formerly as a pharmaceutical drug but is now no longer marketed. Isomethadone was used as both an analgesic and antitussive. It binds to and activates both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with the (S)-isomer being the more potent of the two enantiomers. Isomethadone is a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States, with an ACSCN of 9226 and a 2014 aggregate manufacturing quota of 5 g. The salts in use are the hydrobromide (HBr, free base conversion ratio 0.793), hydrochloride (HCl, 0.894), and HCl monohydrate (0.850). Isomethadone is also regulated internationally as a Schedule I controlled substance under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961.