
Dextromoramide is a powerful opioid analgesic approximately three times more potent than morphine but shorter acting. It is subject to drug prohibition regimes, both internationally through UN treaties and by the criminal law of individual nations, and is usually prescribed only in the Netherlands.

Levomethorphan (LVM) (INN, BAN) is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that has never been marketed. It is the L-stereoisomer of racemethorphan (methorphan). The effects of the two isomers of racemethorphan are quite different, with dextromethorphan (DXM) being an antitussive at low doses and a dissociative hallucinogen at much higher doses. Levomethorphan is about five times stronger than morphine.

Methorphan comes in two isomeric forms, each with differing pharmacology and effects:

Phenoperidine, is an opioid analgesic which is structurally related to pethidine and is used clinically as a general anesthetic.

Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the Netherlands. It comes in free form, is about 0.75x times as potent as morphine and is given parenterally for the treatment of severe pain. Nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression and constipation are believed to be less frequent with piritramide than with morphine, and it produces more rapid-onset analgesia when compared to morphine and pethidine. After intravenous administration the onset of analgesia is as little as 1–2 minutes, which may be related to its great lipophilicity. The analgesic and sedative effects of piritramide are believed to be potentiated with phenothiazines and its emetic (nausea/vomiting-inducing) effects are suppressed. The volume of distribution is 0.7-1 L/kg after a single dose, 4.7-6 L/kg after steady-state concentrations are achieved and up to 11.1 L/kg after prolonged dosing.

Nicodicodine is an opioid developed as a cough suppressant and analgesic. Synthesized in 1904, it is not commonly used, but has activity similar to other opioids. Nicodicodine is metabolised in the liver by demethylation to produce 6-nicotinoyldihydromorphine, and subsequently further metabolised to dihydromorphine. Since the final active metabolite is the slightly stronger opiate dihydromorphine rather than morphine, nicodicodine can be expected to be marginally more potent and longer acting than nicocodeine. Side effects are similar to those of other opioids and include itching, nausea and respiratory depression.

Acetyldihydrocodeine is an opiate derivative discovered in Germany in 1914 and was used as a cough suppressant and analgesic. It is not commonly used, but has activity similar to other opiates. Acetyldihydrocodeine is a very close relative derivative of thebacon, where only the 6-7 bond is unsaturated. Acetyldihydrocodeine can be described as the 6-acetyl derivative of dihydrocodeine and is metabolised in the liver by demethylation and deacetylation to produce dihydromorphine.

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

Nalorphine is a mixed opioid agonist–antagonist with opioid antagonist and analgesic properties. It was introduced in 1954 and was used as an antidote to reverse opioid overdose and in a challenge test to determine opioid dependence.

Phenomorphan is an opioid analgesic. It is not currently used in medicine, but has similar side-effects to other opiates, which include itching, nausea and respiratory depression.
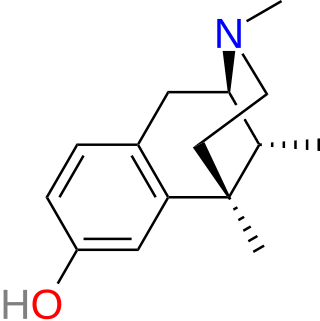
Metazocine is an opioid analgesic related to pentazocine. While metazocine has significant analgesic effects, mediated through a mixed agonist–antagonist action at the mu opioid receptor, its clinical use is limited by dysphoric and hallucinogenic effects which are most likely caused by activity at kappa opioid receptors and/or sigma receptors.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic and non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.
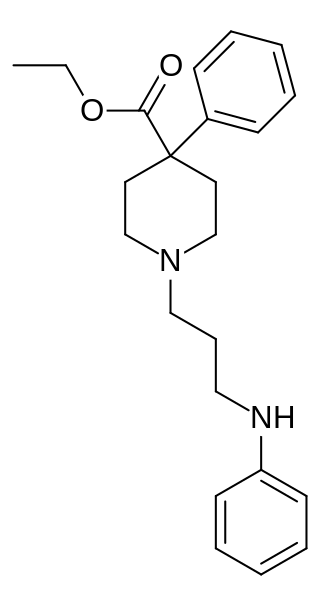
Piminodine (Alvodine) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of pethidine (meperidine). It was used in medicine briefly during the 1960s and 70s, but has largely fallen out of clinical use. It was used particularly for obstetric analgesia and in dental procedures and, like pethidine, could be combined with hydroxyzine to intensify the effects. The duration of action is 2–4 hours; 7.5–10 mg via the subcutaneous route is the most common starting dose, being equal to 80–100 mg of pethidine, 40–60 mg of alphaprodine and 10 mg of morphine. Oral formulations were also available.

Phenazocine is an opioid analgesic drug, which is related to pentazocine and has a similar profile of effects.
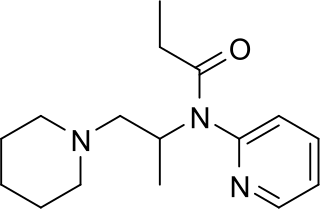
Propiram is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist and weak μ antagonist analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs related to other drugs such as phenampromide and diampromide. It was invented in 1963 in the United Kingdom by Bayer but was not widely marketed, although it saw some limited clinical use, especially in dentistry. Propiram reached Phase III clinical trials in the United States and Canada.

Phenampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and diampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid Co. Although never given a general release, it was research found that 60 mg of phenampromide is equivalent to about 50 mg of codeine. Tests on its two enantiomers showed that all of the analgesic effects were caused by the (S)-isomer. Introduction of a phenyl group to the 4-position of the piperidine-ring produces a drug 60-fold more potent than morphine. The most potent reported derivative is 4-hydroxy-4-phenyl phenapromide which displays analgesic activity some x150 greater than morphine.

Dimenoxadol (INN), or dimenoxadole (BAN), is an opioid analgesic which is a benzilic acid derivative, closely related to benactyzine. Further, the structure is similar to methadone and related compounds like dextropropoxyphene.

Drotebanol (Oxymethebanol) is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It was invented by Sankyo Company in Japan during the 1970s. It is synthesised from thebaine.

Methyldesorphine is an opioid analgesic. First synthesized in Germany in 1940 and patented in the US in 1952, it has a high potential for abuse as with any potent opioid agonist, and is sometimes found along with desomorphine as a component of the home-made opioid mixture known as "Krokodil" used in Russia and the neighboring former Soviet republics. It is approximately 15 times more potent than morphine as an analgesic but if the 6-7 bond is saturated, the β isomer is some 50 times more potent than morphine.

Isomethadone (INN, BAN; trade name Liden; also known as isoamidone) is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive related to methadone that was used formerly as a pharmaceutical drug but is now no longer marketed. Isomethadone was used as both an analgesic and antitussive. It binds to and activates both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with the (S)-isomer being the more potent of the two enantiomers. Isomethadone is a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States, with an ACSCN of 9226 and a 2014 aggregate manufacturing quota of 5 g. The salts in use are the hydrobromide (HBr, free base conversion ratio 0.793), hydrochloride (HCl, 0.894), and HCl monohydrate (0.850). Isomethadone is also regulated internationally as a Schedule I controlled substance under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961.



















