| Historical demographics | ||
|---|---|---|
 Altar of Domitius Ahenobarbus | ||
| Articles | ||
| Demographic history | ||
| Historical demography Classical · Medieval | ||
| World population estimates | ||
| List of Countries by Population | ||
| 1 | 1000 | 1500 |
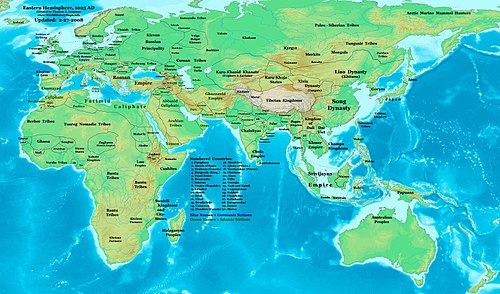
This is a list of countries by population in 1000. The bulk of these numbers are sourced from Alexander V. Avakov's Two Thousand Years of Economic Statistics, Volume 1, pages 12 to 14, which cover population figures from the year 1000 divided into modern borders. Avakov, in turn, cites a variety of sources, mostly Angus Maddison.
Contents
| Country/Territory | Population c. 1000 estimate | Percentage of World Population |
|---|---|---|
| World [1] | 390,000,000 [notes 1] | – |
| Song China [2] | 32,500,000–80,000,000 | 19.23% |
| subdivisions
| 4,000,000– 20,000,000 | 1.03%-5.13% |
| Pala Empire | Less than 16,000,000–17,000,000 [3] | 4.10%-4.36% |
| subdivisions
| 11,300,000–12,700,000 [6] | 3.26% |
| subdivisions
| 12,500,000 | 3.2051% |
| Eastern Roman Empire [9] [10] subdivisions
| 12,000,000 | 3.08% |
| Western Chalukya Empire | 9,000,000–10,000,000 | 2.44% |
| Buyid Persia | 6,500,000–8,500,000 | 2.18% |
| Khitan Liao [12] [13] [14] [15] | 5,250,000–7,750,000 | 1.99% |
| | 7,200,000 | 1.8% |
| | 7,000,000 | 1.79% |
| Al-Andalus | Less than 7,000,000 | 1.79% |
| Gurjara-Pratihara empire [4] subdivisions
| 6,000,000–7,000,000 | 1.79% |
| Kievan Rus' [17] | 5,400,000 | 1.38% |
| | 3,000,000–5,000,000 | 0.77%-1.28% |
| subdivisions
| 4,500,000 | 1.15% |
| subdivisions
| 4,000,000 | 1.0% |
| Wari Empire subdivisions
| 3,000,000 | 0.77% |
| subdivisions
| 2,087,000 | 0.54% |
| subdivisions
| 2,000,000 | 0.51% |
| Pagan Kingdom [21] | 1,500,000-2,000,000 | 0.38%-0.51% |
| | 1,300,000 | 0.33% |
| | 1,250,000 | 0.32% |
| Kingdom of England [24] [25] | 1,250,000 | 0.32% |
| Early Lê dynasty (Đại Việt) [26] | 1,200,000 | 0.31% |
| | 1,000,000 | 0.26% |
| subdivisions
| 1,000,000 | 0.26% |
| Zagwe Kingdom subdivisions
| 1,000,000 | 0.26% |
| | 900,000 | 0.23% |
| High Kingship of Ireland [24] | 630,000 | 0.15% |
| | 620,000 | 0.13% |
| Kingdom of Croatia [8] | 412,000 | 0.11% |
| Kingdom of Sweden [24] | 400,000 | 0.10% |
| Kingdom of Scotland [24] | 300,000 | 0.08% |
| Duchy of Bosnia [8] | 286,000 | 0.07% |
| Kingdom of Norway [24] | 200,000 | 0.05% |
| Republic of Venice [28] | 60,000 | 0.02% |