
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens, and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid.
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances. The primary mineralocorticoid is aldosterone.
Steroid hormone receptors are found in the nucleus, cytosol, and also on the plasma membrane of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days. The best studied steroid hormone receptors are members of the nuclear receptor subfamily 3 (NR3) that include receptors for estrogen and 3-ketosteroids. In addition to nuclear receptors, several G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels act as cell surface receptors for certain steroid hormones.

The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone.

A selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM) is an agent that acts on the progesterone receptor (PR), the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. A characteristic that distinguishes such substances from full receptor agonists and full antagonists is that their action differs in different tissues, i.e. agonist in some tissues while antagonist in others. This mixed profile of action leads to stimulation or inhibition in tissue-specific manner, which further raises the possibility of dissociating undesirable adverse effects from the development of synthetic PR-modulator drug candidates.

Allopregnanolone, also known as brexanolone, is a medication and a naturally produced steroid that acts on the brain. As a medication it is sold under the brand name Zulresso and used to treat postpartum depression. It is used by injection into a vein over a 60-hour period under medical supervision.

The sigma-2 receptor (σ2R) is a sigma receptor subtype that has attracted attention due to its involvement in diseases such as cancer and neurological diseases. It is currently under investigation for its potential diagnostic and therapeutic uses.

Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 is a protein which co-purifies with progesterone binding proteins in the liver and ovary. In humans, the PGRMC1 protein is encoded by the PGRMC1 gene.
The progesterone receptor A (PR-A) is one of three known isoforms of the progesterone receptor (PR), the main biological target of the endogenous progestogen sex hormone progesterone. The other isoforms of the PR include the PR-B and PR-C.
The progesterone receptor B (PR-B) is one of three known isoforms of the progesterone receptor (PR), the main biological target of the endogenous progestogen sex hormone progesterone. The other isoforms of the PR include the PR-A and PR-C.
Membrane progesterone receptors (mPRs) are a group of cell surface receptors and membrane steroid receptors belonging to the progestin and adipoQ receptor (PAQR) family which bind the endogenous progestogen and neurosteroid progesterone, as well as the neurosteroid allopregnanolone. Unlike the progesterone receptor (PR), a nuclear receptor which mediates its effects via genomic mechanisms, mPRs are cell surface receptors which rapidly alter cell signaling via modulation of intracellular signaling cascades. The mPRs mediate important physiological functions in male and female reproductive tracts, liver, neuroendocrine tissues, and the immune system as well as in breast and ovarian cancer.
Membrane steroid receptors (mSRs), also called extranuclear steroid receptors, are a class of cell surface receptors activated by endogenous steroids that mediate rapid, non-genomic signaling via modulation of intracellular signaling cascades. mSRs are another means besides classical nuclear steroid hormone receptors (SHRs) for steroids to mediate their biological effects. SHRs can produce slow genomic responses or rapid, non-genomic responses in the case of mSRs.
Membrane sex steroid receptor may refer to:

Membrane progesterone receptor alpha (mPRα), or progestin and adipoQ receptor 7 (PAQR7), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAQR7 gene.

Membrane progesterone receptor epsilon (mPRɛ), or progestin and adipoQ receptor 9 (PAQR9), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAQR9 gene.
The progestin and adipoQ receptor (PAQR) family is a group of receptors related to but distinct from the G protein-coupled receptor family. It includes at least 11 receptors (PAQR1–PAQR11), including the adiponectin (adipoQ) receptors (AdipoRs), the membrane progesterone receptors (mPRs), and others.

Membrane progesterone receptor delta (mPRδ), or progestin and adipoQ receptor 6 (PAQR6), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAQR6 gene.
The progesterone receptor C (PR-C) is one of three known isoforms of the progesterone receptor (PR), the main biological target of the endogenous progestogen sex hormone progesterone. The other isoforms of the PR include the PR-A and PR-B.

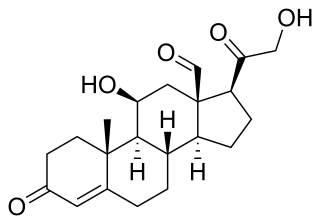
11-Ketoprogesterone, or 11-oxoprogesterone, also known as pregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione, is a pregnane steroid related to cortisone (11-keto-17α,21-dihydroxyprogesterone) that was formerly used in veterinary medicine in the treatment of bovine ketosis. It was synthesized in 1940. The steroid has profound effects on carbohydrate metabolism and possesses activities associated with adrenal cortex hormones like cortisone. However, it is non-toxic even in high dosages, suggesting that it lacks conventional glucocorticoid activity, and it does not possess mineralocorticoid activity, unlike other adrenocortical hormones. 11-Ketoprogesterone may act through membrane glucocorticoid receptors.

Progesterone receptor membrane component 2 is a protein which is encoded by the PGRMC2 gene. It has been detected in the placenta, liver, and spermatozoa, among other areas.











