
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a hitch fastens a rope to another object; a bend fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a loop knot is any knot creating a loop; and splice denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory.

The overhand knot is one of the most fundamental knots, and it forms the basis of many others, including the simple noose, overhand loop, angler's loop, reef knot, fisherman's knot, half hitch, and water knot. The overhand knot is a stopper, especially when used alone, and hence it is very secure, to the point of jamming badly. It should be used if the knot is intended to be permanent. It is often used to prevent the end of a rope from unraveling. An overhand knot becomes a trefoil knot, a true knot in the mathematical sense, by joining the ends. It can also be adjusted, faired, or mis-tied as a half hitch.

The constrictor knot is one of the most effective binding knots. Simple and secure, it is a harsh knot that can be difficult or impossible to untie once tightened. It is made similarly to a clove hitch but with one end passed under the other, forming an overhand knot under a riding turn. The double constrictor knot is an even more robust variation that features two riding turns.
A whipping knot or whipping is a binding of marline twine or whipcord around the end of a rope to prevent its natural tendency to fray.

Figure-eight loop is a type of knot created by a loop on the bight. It is used in climbing and caving.
The Flemish loop or figure-eight loop is perhaps stronger than the loop knot. Neither of these knots is used at sea, as they are hard to untie. In hooking a tackle to any of the loops, if the loop is long enough it is better to arrange the rope as a cat's paw.

The pile hitch is a kind of hitch, which is a knot used for attaching rope to a pole or other structure. The pile hitch is very easy to tie and can be tied in the bight, without access to either end of the rope, making it a valuable tool.

A grief knot is a knot which combines the features of a granny knot and a thief knot, producing a result which is not generally useful for working purposes. The word grief does not carry its usual meaning but is a portmanteau of granny and thief.

The klemheist knot or French Machard knot is a type of friction hitch that grips the rope when weight is applied, and is free to move when the weight is released. It is used similarly to a Prusik knot or the Bachmann knot to ascend or descend a climbing rope. One advantage is that webbing can be used as an alternative to cord. The Klemheist is easier to slide up than a Prusik. The klemheist is also a way to attach a snubber to the anchor rope of small boats, with the advantage that it is easy to undo.
The common whipping is the simplest type of whipping knot, a series of knots intended to stop a rope from unravelling. As it can slip off the rope easily, the common whipping should not be used for rope ends that will be handled. This whipping knot is also called 'wolf' whipping in some parts of the world. The 'Hangman's knot' is a variation of this whipping knot.

A stopper knot is a knot that creates a fixed thicker point on an otherwise-uniform thickness rope for the purpose of preventing the rope, at that point, from slipping through a narrow passage, such as a hole in a block. To pass a rope through a block, or hole, is to reeve it. To pull it out is to unreeve it. Stopper knots prevent the rope from unreeving on its own.

A Matthew Walker knot is a decorative knot that is used to keep the end of a rope from fraying. It is tied by unraveling the strands of a twisted rope, knotting the strands together, then laying up the strands together again. It may also be tied using several separate cords, in which case it keeps the cords together in a bundle. The traditional use of the knot is to form a knob or "stopper" to prevent the end of the rope from passing through a hole, for instance in rigging the lanyards which tension the shrouds on older sailing ships with standing rigging of fibre cordage.
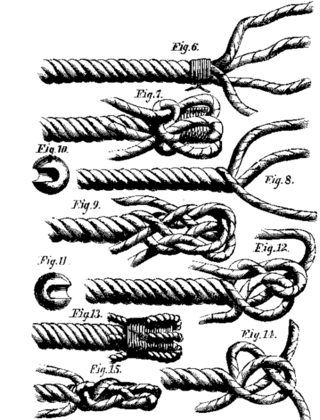
Rope splicing in ropework is the forming of a semi-permanent joint between two ropes or two parts of the same rope by partly untwisting and then interweaving their strands. Splices can be used to form a stopper at the end of a line, to form a loop or an eye in a rope, or for joining two ropes together. Splices are preferred to knotted rope, since while a knot typically reduces the strength by 20–40%, a splice is capable of attaining a rope's full strength. However, splicing usually results in a thickening of the line and, if subsequently removed, leaves a distortion of the rope. Most types of splices are used on 3-strand rope, but some can be done on 12-strand or greater single-braided rope, as well as most double braids.
While a spliced 3-strand rope's strands are interwoven to create the splice, a braided rope's splice is constructed by simply pulling the rope into its jacket.

A Prusik is a friction hitch or knot used to attach a loop of cord around a rope, applied in climbing, canyoneering, mountaineering, caving, rope rescue, ziplining, and by arborists. The term Prusik is a name for both the loops of cord used to tie the hitch and the hitch itself, and the verb is "to prusik". More casually, the term is used for any friction hitch or device that can grab a rope. Due to the pronunciation, the word is often misspelled Prussik, Prussick, or Prussic.

The West Country whipping is a quick practical whipping knot, a method of using twine to secure the end of a rope to prevent it fraying. It has several advantages: it can be tied without a needle; it is simple to understand and remember; if the whipping fails, the loose ends can usually be re-tied to temporarily prevent the rope's end from fraying.
West Country whipping was the name given by Biddlecombe in 1848 to this particular practice, but most subsequent seamanship books, including the British Admiralty Manual of Seamanship, have modified the name to West County whipping...I have not seen this whipping used but it has this advantage: if any part breaks it will be a very long while before the whole whipping lets go. The break will be evident and the whipping can be replaced in time.

The eye splice is a method of creating a permanent loop in the end of a rope by means of rope splicing.

The double overhand knot or barrel knot is simply an extension of the regular overhand knot, made with one additional pass. The result is slightly larger and more difficult to untie. It forms the first part of the surgeon's knot and both sides of a double fisherman's knot. According to The Ashley Book of Knots, "A double overhand knot tied in a cat-o'-nine-tails is termed a blood knot."

A coiling or coil is a curve, helix, or spiral used for storing rope or cable in compact and reliable yet easily attainable form. They are often discussed with knots.
Rope are often coiled and hung up in lofts for storage. They are also hung over stakes in farm wagons and on hooks in moving vans, fire apparatus and linesmen's repair trucks. For such active storage coils must be well made.
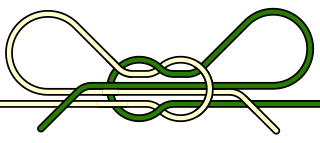
The shoelace knot, or bow knot, is commonly used for tying shoelaces and bow ties.

















