This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: the article is badly written and includes irrelevant content.(March 2014) |
| Nail knot | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Bend |
| Typical use | fly fishing |
The nail knot, also known as the tube knot or gryp knot, is mostly used in carp and fly-fishing. The nail knot was named because a nail was inserted as a guide when threading the line. Today, it is easier to use a small straw. The nail knot is an important fishing knot used to join two lines of different diameters and allows for line diameters to diminish down to the fly. I.E., it is useful for attaching your backing to the fly line, and your fly line to the leader, or tippet. The knot can be tied in multiple ways and is uniform.
Most common uses in fly-fishing are attaching the leader to the fly line and attaching the fly line to the backing. Fly-fishing is an angling method in which an artificial "fly" is used to catch fish. The fly is cast using a fly rod, reel, and specialized weighted line. Casting a nearly weightless fly or "lure" requires casting techniques significantly different from other forms of casting. Fly fishermen use hand-tied flies that resemble natural invertebrates or other food organisms, or "lures" to provoke the fish to strike. Carp anglers use the nail knot to attach monofilament-fishing line and/or braided fishing line to lead core leader material.
To tie the nail knot by hand is very difficult; therefore some anglers use a nail knot-tying tool. It is one of those deceptively simple, clever, useful, and easy to use tools that many seem to own. This tool also seems to fly "under the radar" in terms of public awareness. It allows fishermen to tie any size monofilament, fluorocarbon line or fishing braid to any size fishhook, fishing lure or lead core in just seconds. With it you can tie various knots, but it is best known for the nail/gryp knot. It can't come untied because the untied end is gripped by all the turns of the knot. This knot will not slip, even if you make a hair loop on a carp hair rig, as the tag end goes under all the wraps.
Method with a nail:
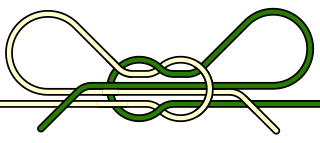
- Lay a nail or a large needle or small dowel or similar object along and parallel to the fly line (shown in purple in the illustration) near the tag end of the fly line , with the tag end of the fly line to the right and the working or standing end of the fly line to the left.
- Set the leader (shown in blue in the illustration) parallel to and against the fly line and nail, such that the tag ends are at opposite ends of the overlap of the two lines, with the tag end of the leader to the left. The leader is typically tapered and the large end of the leader is the tag end and the thin end of the leader is the working or standing end. Leave an extra 10–12″ of the leader's tag end to tie the knot. The tag end of the leader is assumed to be to the left and the tag end of the fly line to the right, in the next step described. Those who are left-handed may prefer to reverse left and right throughout (the illustration does this, and should perhaps be flipped).
- Form a loop of the leader such that a second section of the leader lies parallel to the fly line and nail, holding the fly line, nail and both passes of the leader in your left hand.
- Using your right hand, make 6–8 close-together wraps of the leader, using the section forming the right side of the loop, working right to left, back around the leader, fly line and nail and inside the loop of the leader.
- Pinch the coils between thumb and forefinger of your left hand.
- Pull the working end (thin end) of the leader to shorten and ultimately eliminate the loop in the leader, and snug up the coils.
- Remove the nail while continuing to pinch the coils between the thumb and forefinger of your left hand.
- Pull the tag end and the standing end of the leader to seat the knot firmly onto the fly line. Wetting the leader while alternately pulling the tag end and standing end of the leader will help dress the knot.
- Pull the standing ends of leader and of the fly line to further seat and test the knot.
- Trim the tag end of the leader close to the knot. If necessary trim the tag end of the fly line, but leave a couple of millimeters of it.
Method with a tube:
- Lay a hollow tube along and parallel to the fly line (shown in purple in the illustration) near the tag end of the fly line, with the tag end of the fly line to the right and the working or standing end of the fly line to the left.
- Set the leader (shown in blue in the illustration) parallel to and against the fly line and tube, such that the tag ends are at opposite ends of the overlap of the two lines, with the tag end of the leader to the left. The leader is typically tapered and the large end of the leader is the tag end and the thin end of the leader is the working or standing end. The tag end of the leader is assumed to be to the left and the tag end of the fly line to the right, in the next step described. Those who are left-handed may prefer to reverse left and right throughout (the illustration does this and should perhaps be flipped).
- Pinch the leader against the fly line and tube between the thumb and forefinger of your left hand, near the left end of the tube, leaving 10-12″ of the tag end of the leader free to tie the knot.
- Make 6–8 close together wraps, working left to right, away from the pinch, back around the fly line, leader, and tube.
- Pull the working or standing end of the leader lightly to tighten the coils and pass the tag end through the tube from right to left.
- Pinching the coils between thumb and forefinger of the right hand, remove the tube by pulling it to the left with the left hand.
- Pull the tag end of the leader to snug up the coils, then alternately pull the tag end and standing or working end of the leader to seat the knot firmly onto the fly line. Wetting the leader while alternately pulling the tag end and standing end of the leader will help dress the knot.
- Pull the standing ends of leader and of the fly line to further seat and test the knot.
- Trim the tag end of the leader close to the knot. If necessary trim the tag end of the fly line, but leave a couple of millimeters of it.
The tube method can also be used with a nail, passing the leader back through the coils against the nail rather than through a tube if the loop seems challenging.